Powder metallurgical brake shoe for railway locomotive
A technology of powder metallurgy and railway locomotives, applied in mechanical equipment, friction linings, etc., can solve problems such as low strength of connection structure, easy riveting structure, safety accidents, etc., and achieve simple structure, low manufacturing cost and stable friction coefficient Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
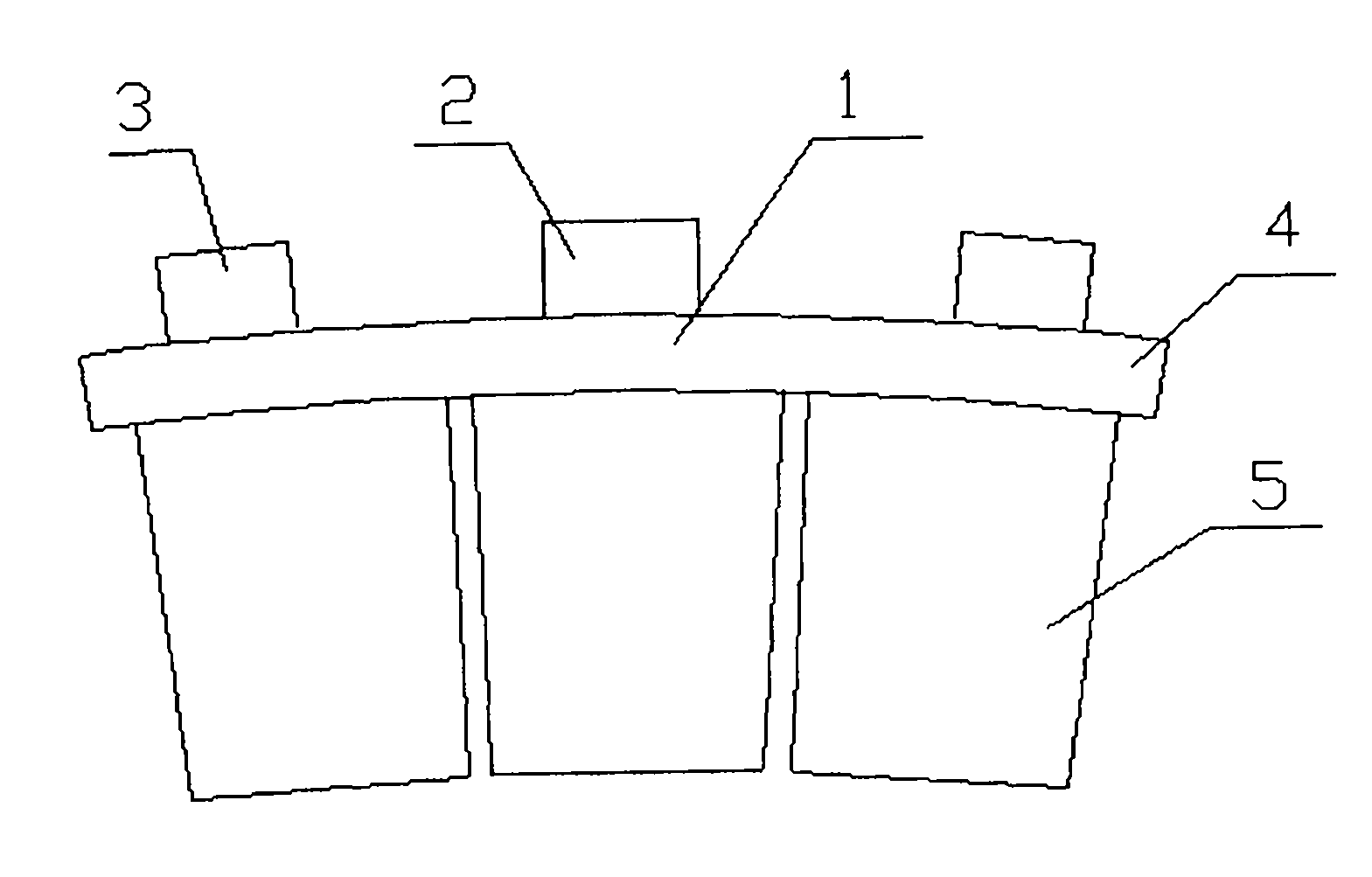
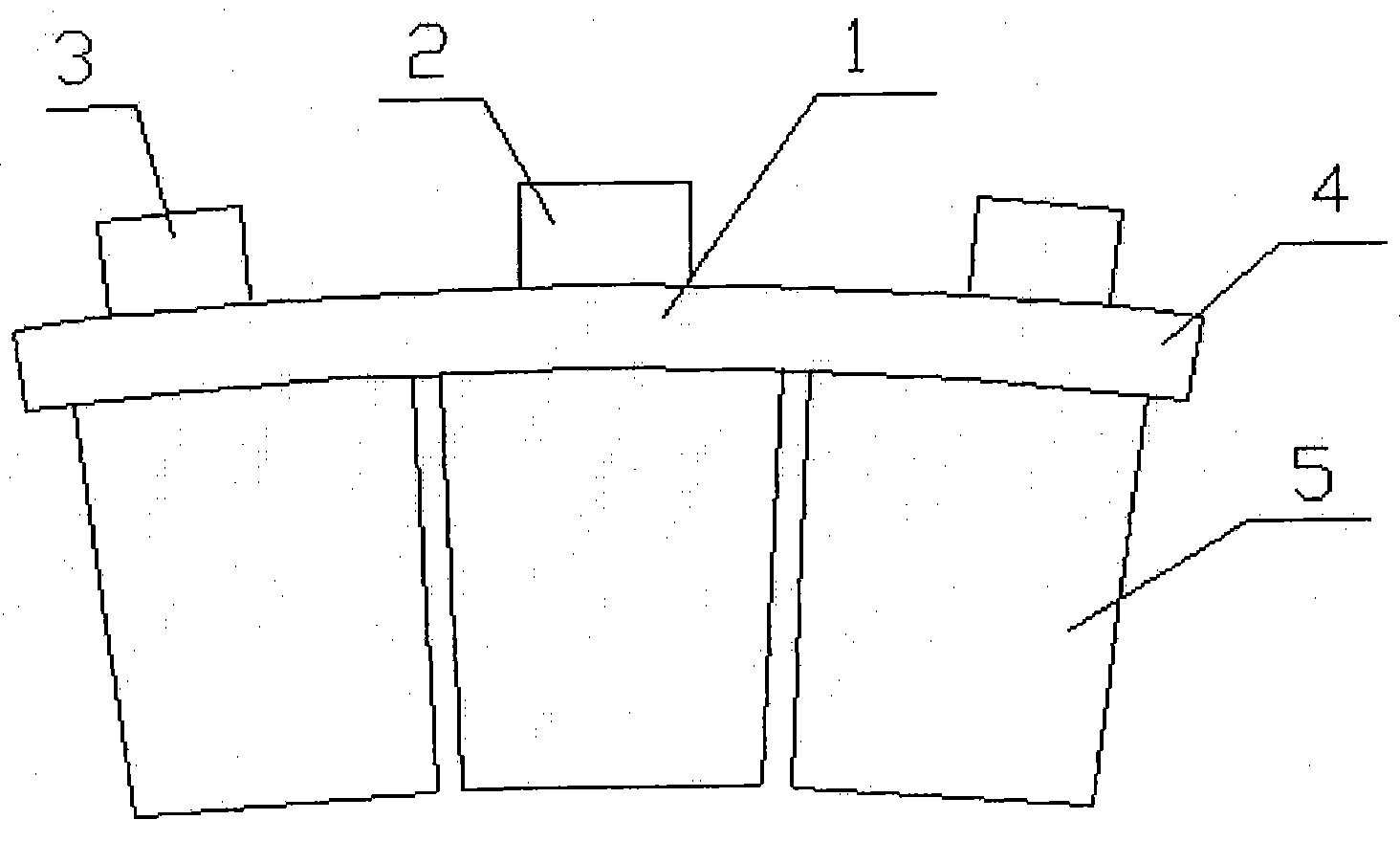
[0018] The tile nose 2, the positioning groove 3 and the steel back 4 are stamped and formed separately by using a low carbon steel plate, and then welded together to form the tile back 1.
[0019] The friction material block 5 is made by powder metallurgy process, wherein the weight percentage of the friction material block is composed of: graphite 12%, copper 5%, manganese 3%, chromium 3%, nickel 3%, aluminum 2%, molybdenum disulfide 5% , 2% mullite, 4% molybdenum trioxide, and the rest is iron. During the manufacturing process, firstly, the various raw materials are uniformly mixed according to the above-mentioned ratio, and then press-formed, and then the press-formed block and the above-mentioned tile back 1 are put into a sintering mold and assembled together. Then put it into a pressure sintering furnace to complete the sintering process, and the sintering temperature is 1030°C. During the sintering process, the friction material block 5 and the tile back 1 are sintere...
Embodiment 2
[0021] The tile nose 2, the positioning groove 3 and the steel back 4 are stamped and formed separately by using a low carbon steel plate, and then welded together to form the tile back 1.
[0022] The friction material block 5 is made by powder metallurgy process, wherein the weight percentage of the friction material block is composed of: graphite 14%, copper 3%, manganese 1%, chromium 1%, nickel 1%, aluminum 1%, molybdenum disulfide 2% , 5% mullite, 2% molybdenum trioxide, and the rest is iron. During the manufacturing process, firstly, the various raw materials are uniformly mixed according to the above-mentioned ratio, and then press-formed, and then the press-formed block and the above-mentioned tile back 1 are put into a sintering mold and assembled together. Then put it into a pressure sintering furnace to complete the sintering process, and the sintering temperature is 1030°C. During the sintering process, the friction material block 5 and the tile back 1 are sintere...
Embodiment 3
[0024] The tile nose 2, the positioning groove 3 and the steel back 4 are stamped and formed separately by using a low carbon steel plate, and then welded together to form the tile back 1.
[0025] The friction material block 5 is made by powder metallurgy process, wherein the weight percentage of the friction material block is composed of: graphite 13%, copper 4%, manganese 2%, chromium 2%, nickel 2%, aluminum 1%, molybdenum disulfide 4% , 4% mullite, 3% molybdenum trioxide, and the rest is iron. During the manufacturing process, firstly, the various raw materials are uniformly mixed according to the above-mentioned ratio, and then press-formed, and then the press-formed block and the above-mentioned tile back 1 are put into a sintering mold and assembled together. Then put it into a pressure sintering furnace to complete the sintering process, and the sintering temperature is 1030°C. During the sintering process, the friction material block 5 and the tile back 1 are sintere...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com