Chlorella microbiological fuel cell reactor
A technology of fuel cells and chlorella, applied in biochemical fuel cells, biological water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of poor treatment effect of inorganic substances such as nitrogen and phosphorus, high treatment cost, and incomplete treatment of organic substances To achieve the effect of improving the ability of photosynthesis and oxygen release and cell biomass, and reducing the overall operating cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] This example illustrates the specific structure and structure of the chlorella microbial fuel cell reactor of the present invention, as well as its working principle.
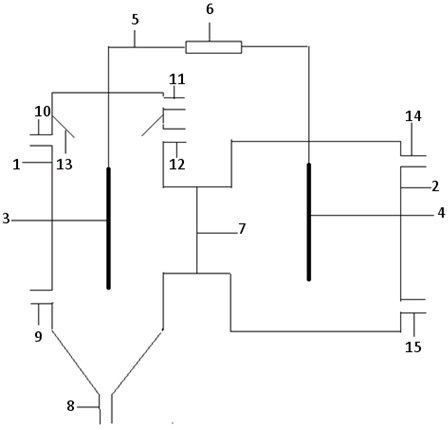
[0034] Chlorella microbial fuel cell reactor of the present invention such as figure 1 As described above, it is mainly composed of an anode chamber 1, a cathode chamber 2, an anode electrode 3, a cathode electrode 4, a wire 5, a load 6, a proton exchange membrane 7, and a three-phase separator 13; the anode chamber 1 communicates with the cathode chamber 2 And separated by proton exchange membrane 7; anode electrode 3 is arranged in the chamber of anode chamber 1, cathode electrode 4 is arranged in the chamber of cathode chamber 2, anode electrode 3 and cathode electrode 4 are arranged on the anode through wire 5 The external circuits outside the chamber 1 and the cathode chamber 2 are respectively connected to both ends of the load 6; the bottom side opening of the cathode chamber 2 is provided with a ...
Embodiment 2
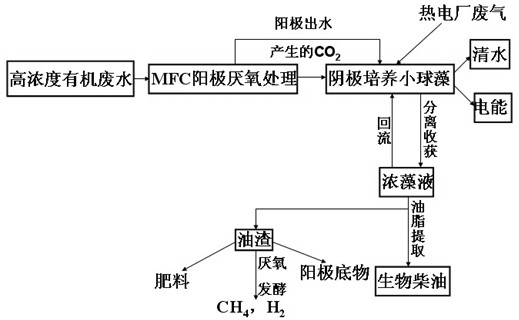
[0044] This embodiment combines figure 2 A low-cost method for treating high-concentration organic wastewater using the chlorella cathode microbial fuel cell described in Example 1 is described.
[0045] 1) Start the reactor:
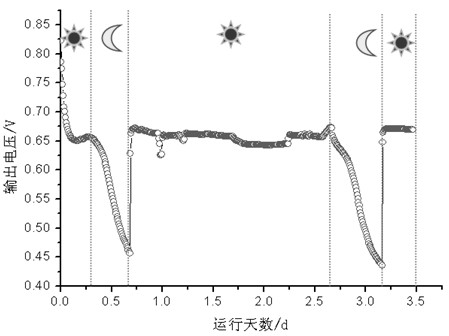
[0046] At room temperature, the domestic sewage or the anode effluent of the microbial fuel cell (as a bacterial source) and the anolyte are respectively injected into the anode chamber 1 through the water inlet 8 of the anode chamber 1; for OD 680 =0.5), and inject phosphate buffered saline (NaH 2 PO 4 2.452 g / L, Na 2 HPO 4 4.576 g / L, KCl 0.13 g / L, pH=7.0) and BG11 medium formula solution; the load 6 is connected between the anode electrode 3 and the cathode electrode 4 as a fixed-value resistor of 1000Ω to monitor the change of the resistance voltage. Domestic sewage with different initial COD concentrations or anode effluent from microbial fuel cells domesticate the anode flora step by step. / L, finally when the initial COD concentration is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com