Method for synthesizing low-viscosity epoxy resin curing agent
A technology of epoxy resin curing and synthesis method, which is applied in the synthesis field of low-viscosity epoxy resin curing agent, can solve the problem of poor compatibility of epoxy resin, inconvenient operation and construction of low-viscosity epoxy system, lack of low-viscosity curing agent, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of fast curing at room temperature, good product quality, and a large dosage range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Weigh 22g of adipic acid and 46mL of triethylenetetramine (the molar ratio of adipic acid: triethylenetetramine = 1:3), add all the triethylenetetramine into the stirring reactor and add 3g of adipic acid to mix well and start Stir and heat, and the temperature rises to 160°C. After the solution in the stirred reactor becomes light yellow and clear, add 3g of adipic acid every 10 minutes, maintain 160°C for 1.5h, stop heating, and obtain an amber polyamide product after cooling.
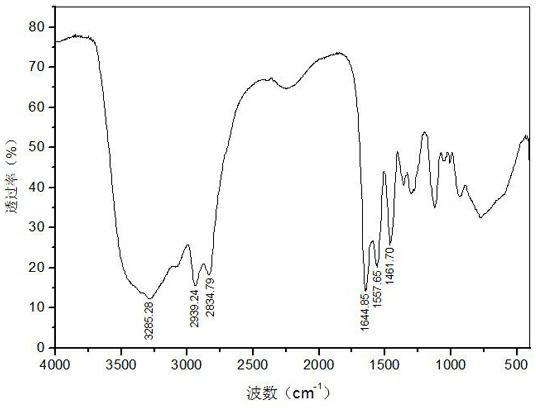
[0024] The infrared spectroscopic analysis (FTIR) of the obtained polyamide sample was carried out with a Nicolet-6700 infrared spectrometer, the amine value was measured by "perchloric acid non-aqueous titration method", and the viscosity was measured with an NDJ-8S digital viscometer.
[0025] attached figure 1 It is a polyamide sample at 500~4000cm -1 FTIR spectra in the wavelength range, located at 3285cm -1 The wider band at the place is the absorption vibration peak of hydroxyl group o...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Weigh 20g of adipic acid and 41mL of triethylenetetramine (the molar ratio of adipic acid: triethylenetetramine = 1:2), add all the triethylenetetramine into the stirring reactor and add 5g of adipic acid to mix well and start Stir and heat, and the temperature rises to 160°C. After the solution in the stirred reactor becomes light yellow and clear, add 5 g of adipic acid every 15 minutes, keep the reaction at 160°C for 1 hour, stop heating, and obtain an amber polyamide product after cooling. The amine value of the polyamide sample is 640 mgKOH / g, and the viscosity is 7800 mPa·s.
[0030]
Embodiment 4
[0035] Weigh 22g of adipic acid and 59mL of tetraethylenepentamine (adipic acid: tetraethylenepentamine = 1:3 in molar ratio), add all tetraethylenepentamine into the stirring reactor and add 3g of adipic acid to mix well and start Stir and heat, and the temperature rises to 170°C. After the solution in the stirring reactor becomes yellowish-brown and clear, add 3g of adipic acid every 7 minutes, maintain 170°C for 1 hour, stop heating, and obtain a reddish-brown polyamide product after cooling. The amine value of the polyamide sample is 730 mgKOH / g, and the viscosity is 8140 mPa·s.
[0036]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com