Method for amplifying GGC repetitive sequence of NOTCH2NLC gene
A repetitive sequence and gene technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency, inability to meet large-scale sample amplification, long amplification time, etc., to achieve convenient use and economical Reagent cost, high reproducibility of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1 NOTCH2NLC gene GGC repeat sequence amplification method
[0039] (1) Obtain human genomic DNA;
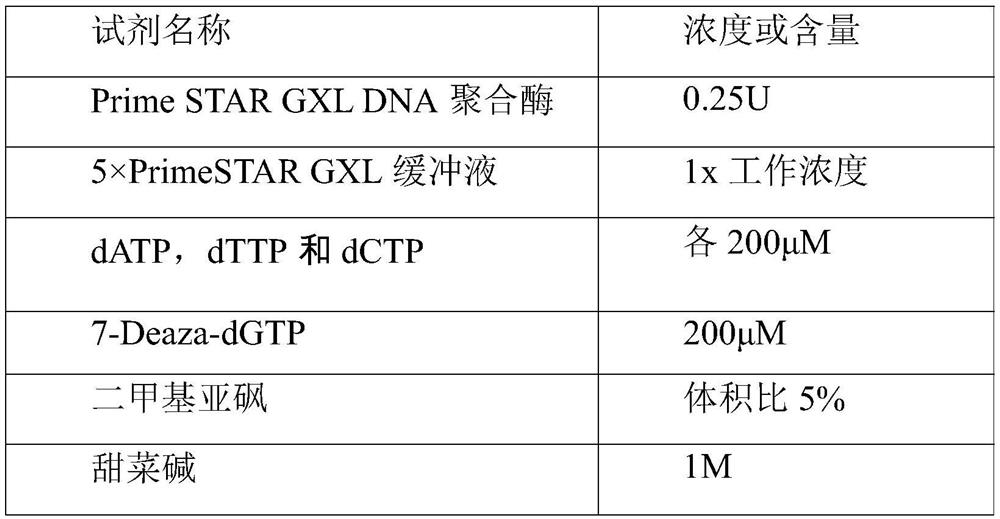
[0040] (2) Take 100ng of the above-mentioned genomic DNA and add it to the PCR amplification reaction system of the GGC repeat sequence of the NOTCH2NLC gene, as shown in Table 1 below;
[0041] Table 1: PCR amplification reaction system
[0042]
[0043]
[0044] (3) Put the PCR reaction solution in step (2) into a PCR instrument for PCR (BioRad MyCycler ThermalCycler) reaction. The temperature change rate of all cycle steps is 1°C / s. The PCR reaction procedure is as follows:
[0045]
[0046] (4) The PCR amplification product obtained in step (3) is subjected to capillary fluorescence electrophoresis detection.
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2 NOTCH2NLC Gene GGC Repeat Sequence Amplification Kit
[0048] The kit described in this embodiment includes a PCR amplification reaction system for the GGC repeat sequence of the NOTCH2NLC gene, as shown in Table 2 below.
[0049] Table 2: PCR amplification reaction system
[0050]
[0051]
[0052] Further, the nucleotide sequence of the primer NOTCH2NLC-F is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, the nucleotide sequence of the primer M13-LINKER-R is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the primer M13- The nucleotide sequence of (GGC)4(GGA)2-R is shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The 5' end of the above primer NOTCH2NLC-F has a fluorescent group FAM, that is, NOTCH2NLC-F is: 5'-FAM-GGCATTTGCGCCTGTGCTTCGGACCGT-3'.
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3 Detection of the repeat sequence GGC in the NOTCH2NLC gene
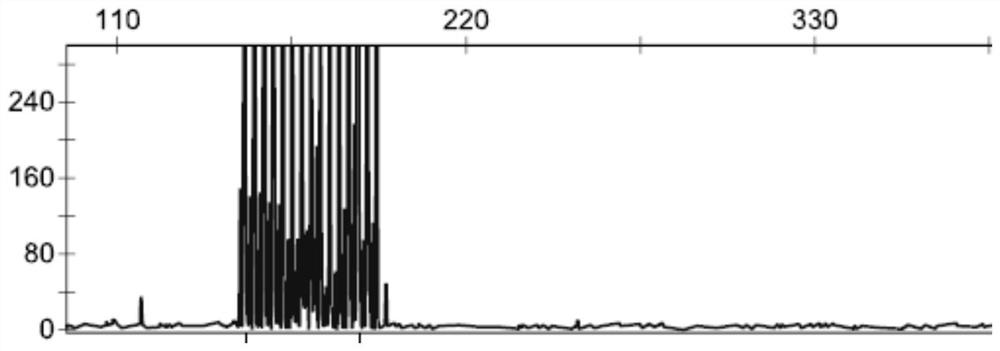
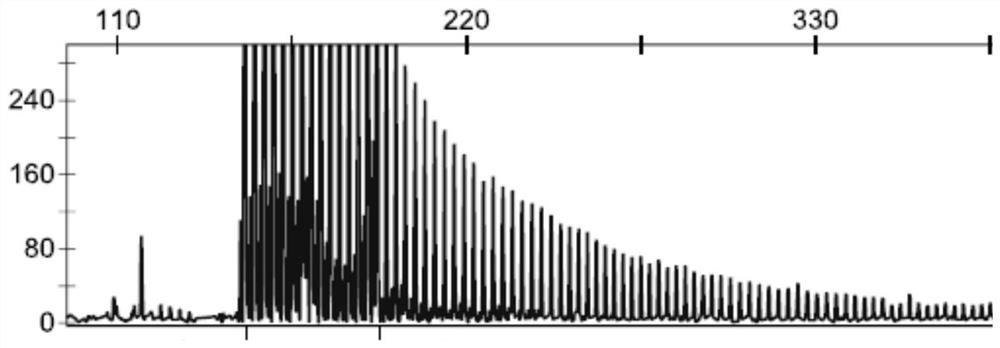
[0054] The genomic DNA of the NIID patient and the genomic DNA of the normal person were respectively taken to amplify the GGC repeat sequence of the NOTCH2 NLC gene according to the method in Example 1. The obtained PCR reaction product was detected by capillary electrophoresis fluorescence detection method (Denget al., Journal of medical genetics. 2019) to identify whether the GGC repeat number of NOTCH2NLC gene reached the pathogenic abnormal repeat number.
[0055] Identification results such as Figure 1-2 As shown, on the one hand, the above results show that the NOTCH2NLC gene GGC repeat sequence amplification method of the present embodiment can specifically amplify the NOTCH2NLC gene GGC repeat sequence, which greatly shortens the amplification time and effectively reduces the cost. On the other hand, it shows that The NOTCH2NLC gene of NIID patients has an abnormal GGC repeat sequence, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com