Circuit used for programming resistance memory
A resistance memory and circuit technology, applied in the field of information storage, can solve the problems of increased circuit complexity, shrinkage, and low writing and erasing speed of floating gate memory, and achieve the effect of improving distribution uniformity and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
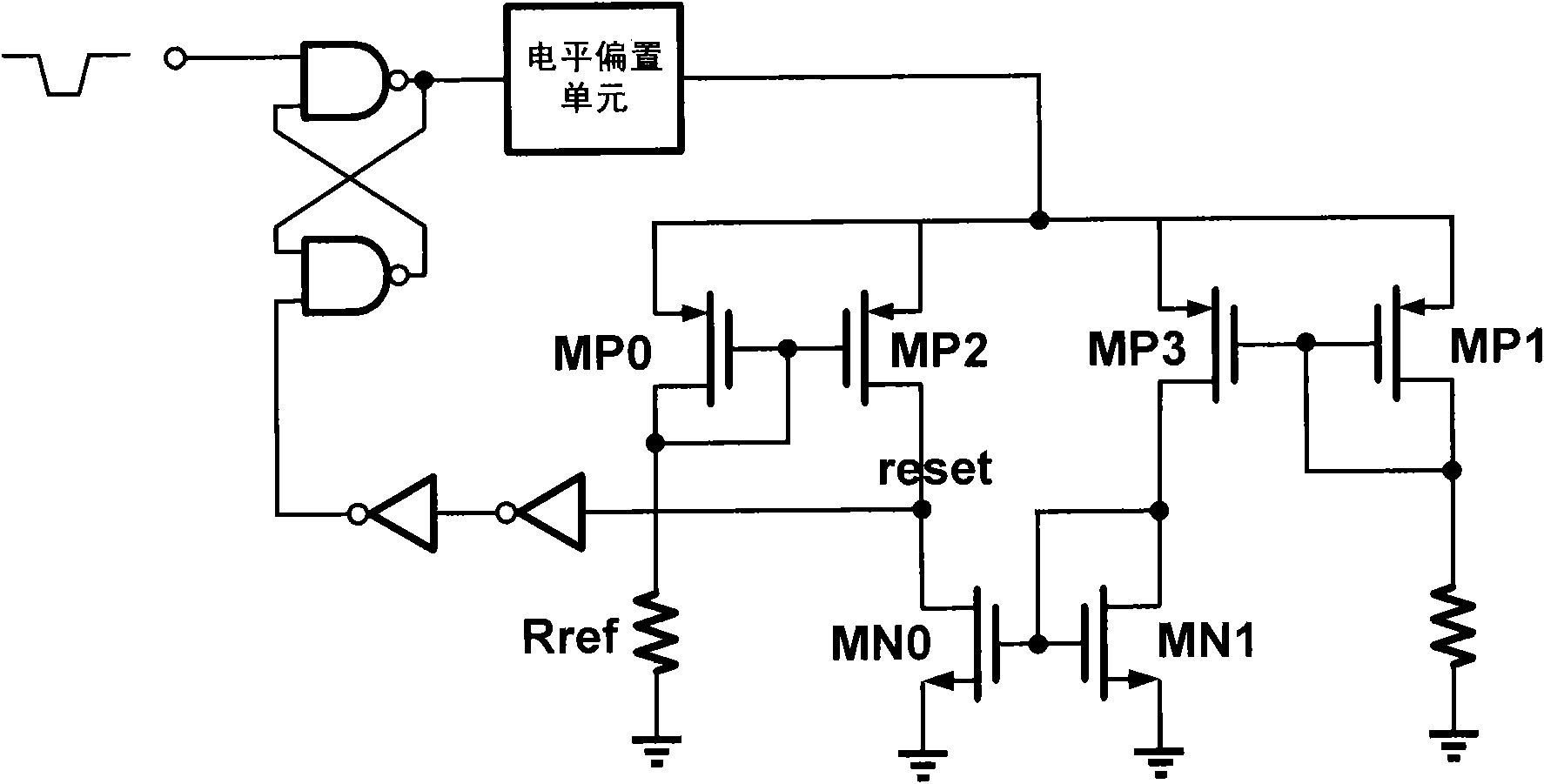
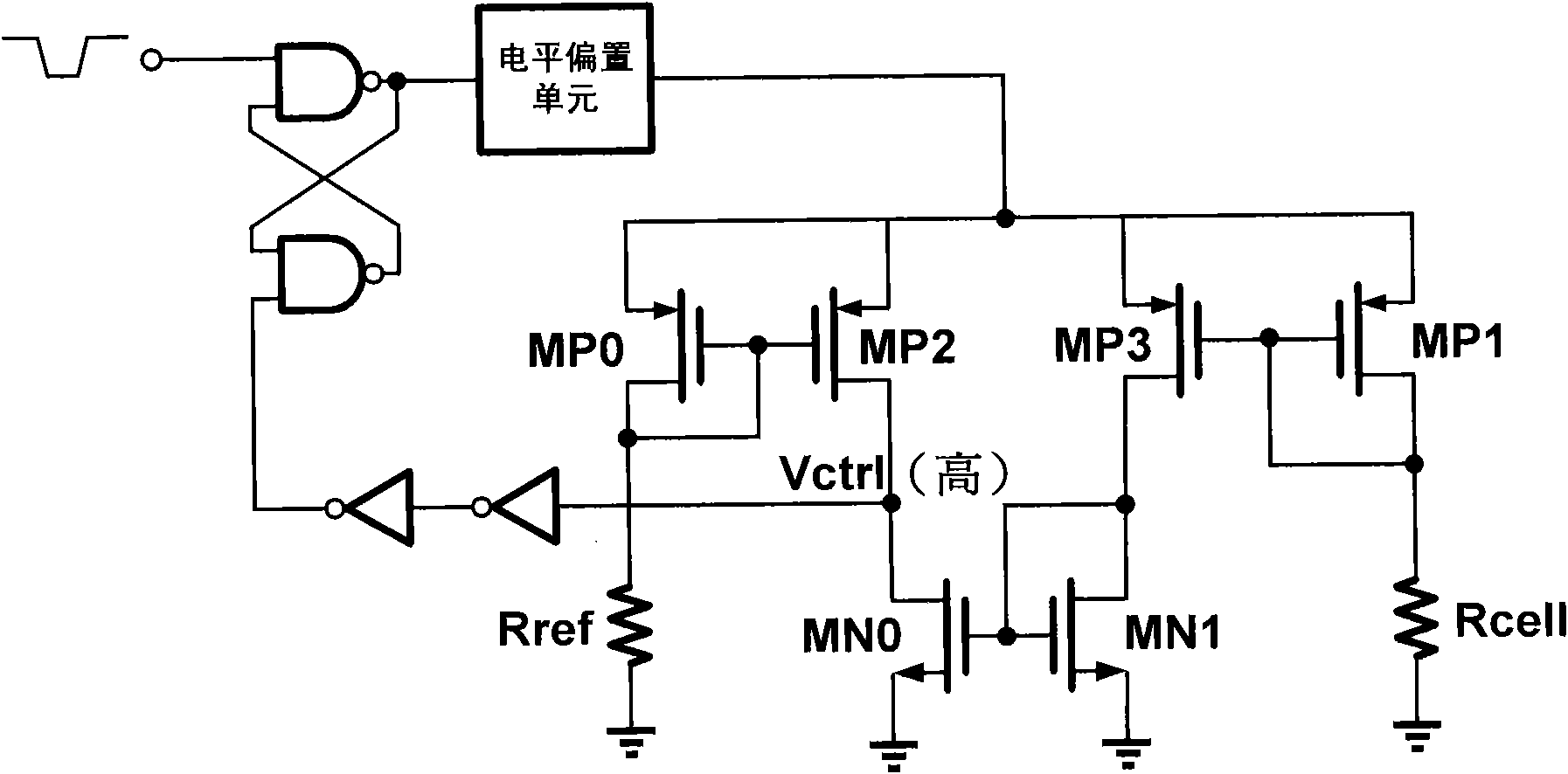
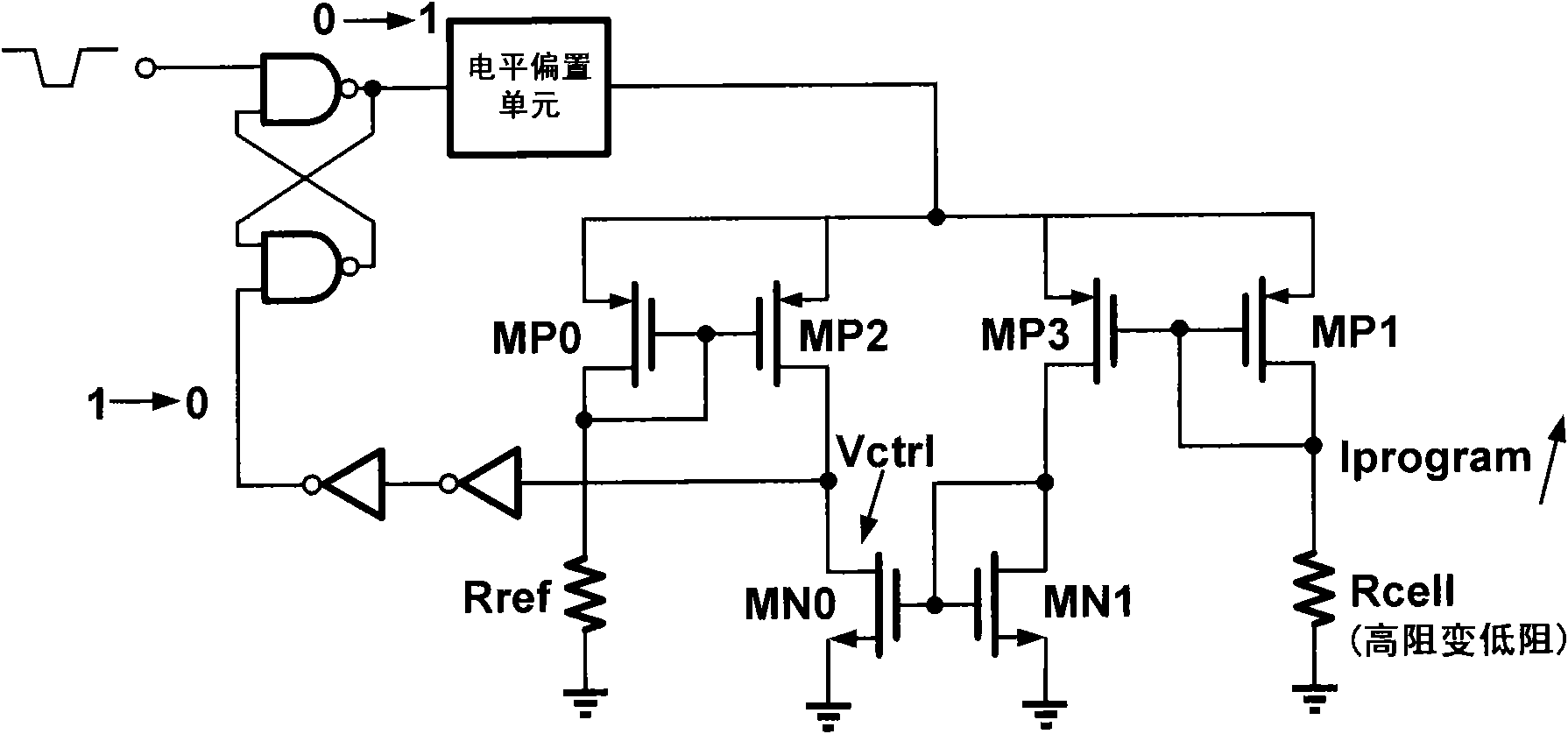
[0028] Taking the programming circuit that drives the resistance transition memory from high resistance to low resistance as an example, figure 1 is its schematic diagram. The circuit is composed of an RS flip-flop, a level bias unit, a current mirror, a current comparison circuit and an inverter. The output of the RS flip-flop controls the level bias unit; the level output by the level bias unit is used to program or erase the resistance memory; the signal returned by the feedback unit resets the RS flip-flop.
[0029] Among them, the RS flip-flop is composed of two double-input NAND gates, the input valid enabling level is low level, and the output valid level is high level. The output of the RS flip-flop controls a l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com