Preparation method of micro-fluidic chip interface for two-dimensional protein electrophoretic separation
A microfluidic chip and two-dimensional electrophoresis technology, which is applied in the direction of material analysis, material analysis, and measurement devices through electromagnetic means, can solve the problems of time-consuming, laborious, small resistance, and poor repeatability, and achieve simple and fast production Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
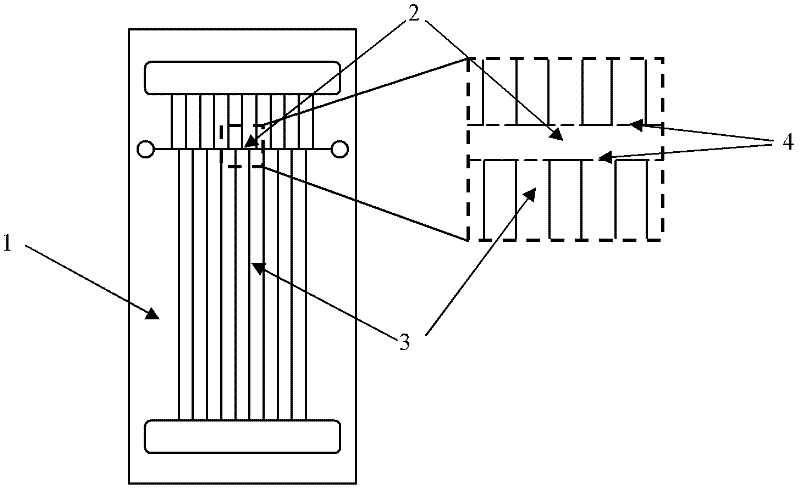
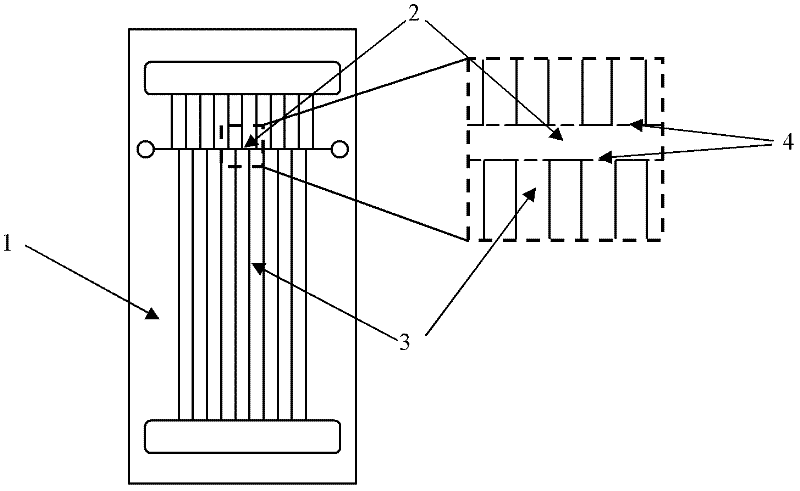
[0018] 1. Microfluidic chip design and interface processing
[0019] designed as figure 1 In the microfluidic chip 1 shown in , the horizontal channels are used as the first dimension for isoelectric focusing, and the vertical parallel channels (100-500) are used as the second dimension for gel electrophoresis. The channel width is 50 μm, the spacing is also 50 μm, and the depth is 25 μm. The parallel vertical channels are to ensure that the proteins that have been separated according to the isoelectric point remain separated during gel electrophoresis. The combination of the number of vertical channels and the high resolution of isoelectric focusing together ensures the peak capacity of two-dimensional separation.
[0020] Add acrylamide prepolymer and initiator in the microchannel (including isoelectric focusing channel 2 and gel electrophoresis channel 3), and use photopolymerization to process polyacrylamide gel, wherein isoelectric focusing channel 2 is used in the expos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com