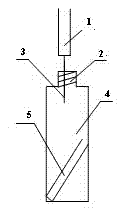
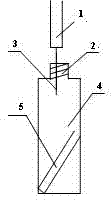
Solid phase micro-extraction device and method for measuring volatile organic acid in tobacco leaf
A volatile organic acid, extraction device technology, applied in measurement devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of low analysis sensitivity, complex processing methods, long analysis time, etc., to achieve short analysis time, avoid complexity, The effect of high analytical sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Determination of volatile organic acids content in first-cured tobacco leaves:
[0027] The first flue-cured tobacco leaves were dried and pretreated at 40°C for 1 h, crushed and passed through a 40-mesh sieve to obtain tobacco powder, which was dried in a vacuum dryer for 12 h for later use. Weigh 20 mg of the above smoke powder into a headspace vial (23×75 mm), add 2 μL of trans-2-hexenoic acid internal standard, and weigh 0.5 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate at the same time, mix well, pour into the glass Add 15 μL of derivatization reagent N, O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide to the inner cannula (6×31 mm), place it in the headspace sample vial, and when it is down 60-80° angle, the top of the glass insert is 40-50 mm from the upper cap of the headspace vial, and seal it with the headspace cap. Use the above-mentioned device to perform simultaneous derivation-headspace solid-phase microextraction with a fully automatic solid-phase microextraction device. The con...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Repeatability and recovery determination:
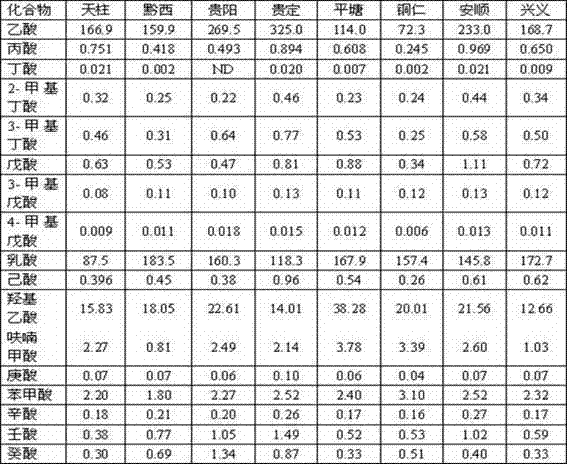
[0035] The same sample analysis method was used to carry out 5 parallel determinations on the same sample by using the device, and the recovery rate was determined by the linear equation obtained by the standard addition method, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0036] Table 2 Recovery and repeatability of the method
[0037]
[0038] Note: Relative standard deviation (RSD) measurements are five
[0039]The results show that the recovery rates of the 17 kinds of volatile organic acids in the measured tobacco leaves are in the range of 80%-100%, and the average relative standard deviation of the five measurements is 4.1-11.5%, which shows that the determination results of this method High accuracy.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com