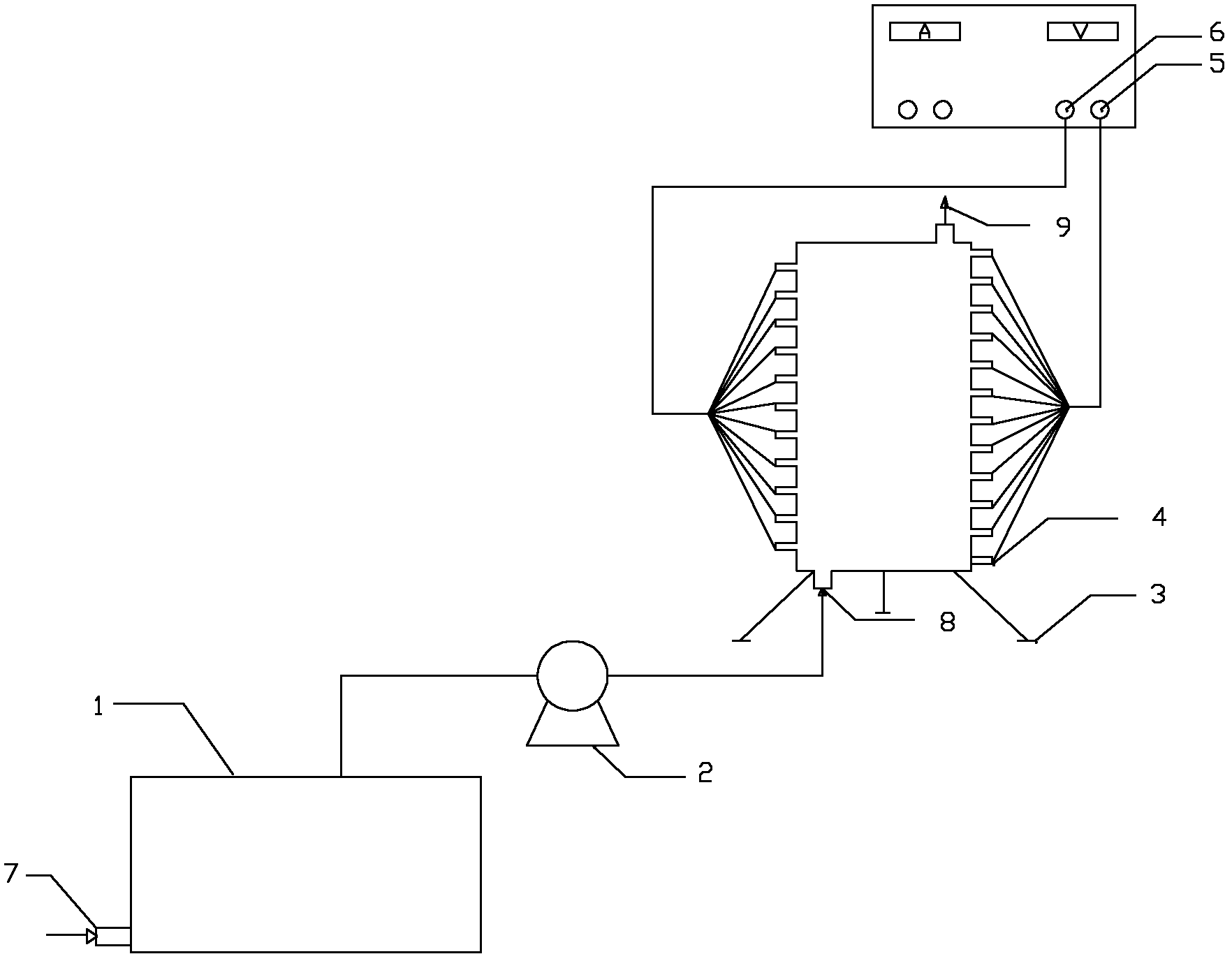
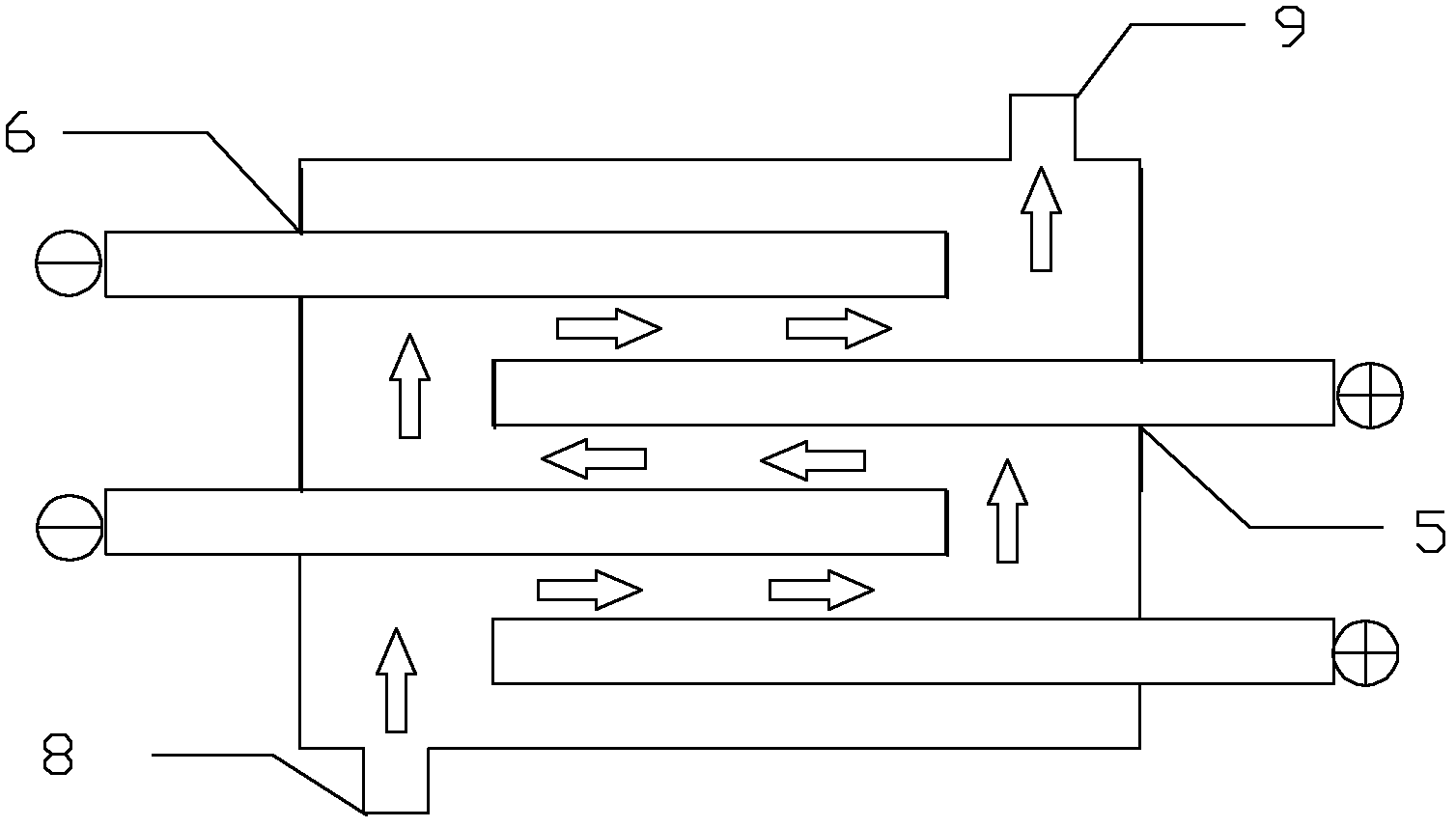
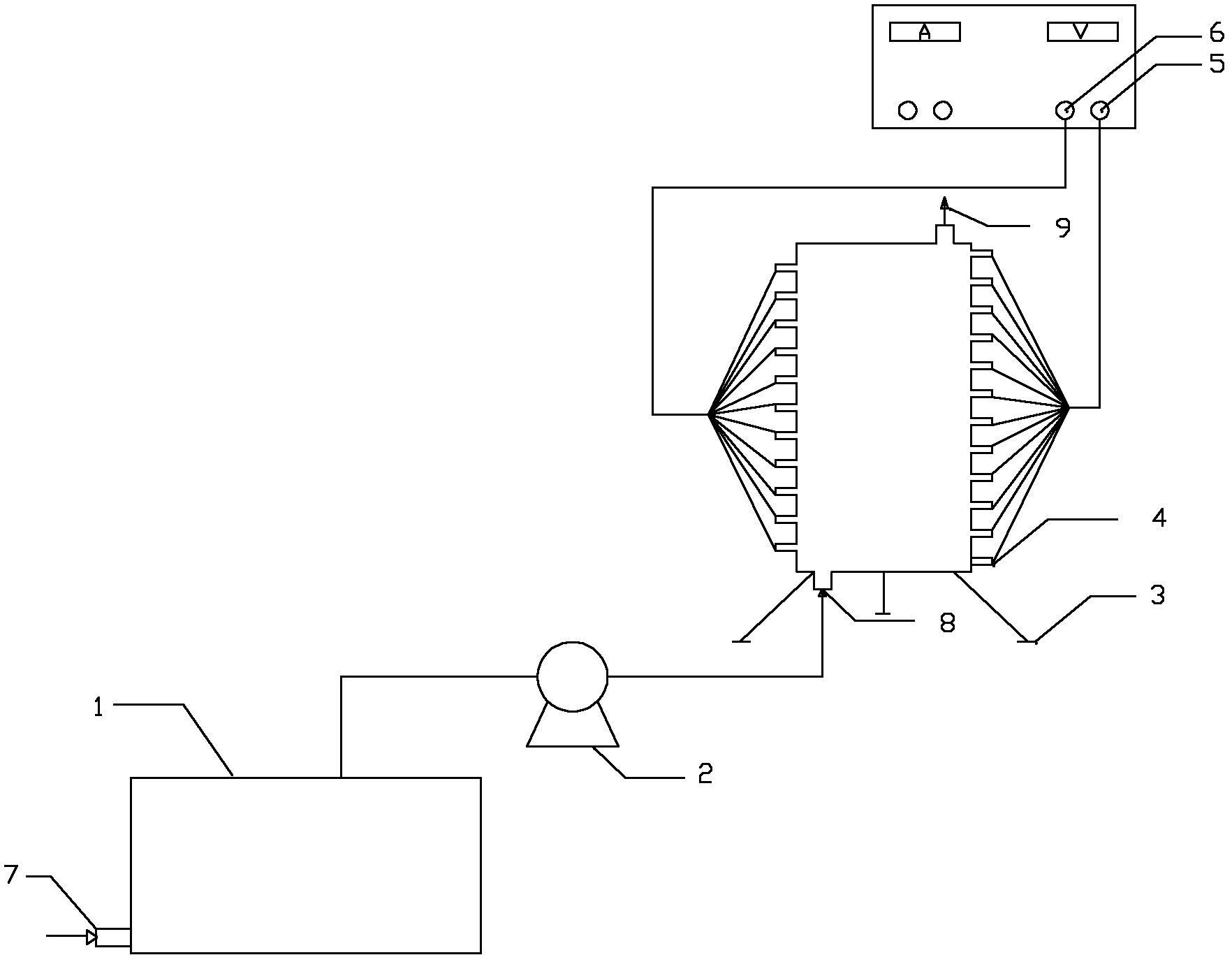
Device and method for treating zinc smelting waste water by using parallelly-connected aluminum electrodes with electro-coagulation method
An electro-flocculation and parallel technology, which is applied in the fields of metallurgical wastewater treatment, water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of spending a lot of time in microbial domestication and difficulty in screening strains, achieving low cost, simple equipment, The effect of short operating cycles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] The anode in the electroflocculation unit is an aluminum plate, the cathode is a stainless steel plate, the distance between the plates is 1cm, the power supply is a constant current and constant voltage power supply, the current is controlled at 7.6A, and the voltage is stable at 3.7v. 2+ and Cd 2+ Concentrations are 434.80mg / L and 17.39mg / L respectively, add lime to adjust the pH value of the influent to 8.0, electrolyze for 100 seconds at a temperature of 25°C, and let stand for 10 minutes.
[0015] After determination, using the present invention to treat Zn in zinc smelting wastewater 2+ and Cd 2+ , where Zn 2+ and Cd 2+ The removal rates were 99.4% and 96.3%, respectively.
Embodiment 2
[0017] The anode in the electroflocculation unit is an aluminum plate, the cathode is a stainless steel plate, the distance between the plates is 1cm, the power supply is a constant current and constant voltage power supply, the current is controlled at 7.6A, and the voltage is stable at 3.7v. 2+ and Cd 2+ Concentrations are 522.69mg / L and 31.10mg / L respectively, add lime to adjust the pH value of the influent water to 9.0, electrolyze for 100 seconds at a temperature of 25°C, and then let stand for 10 minutes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com