In-vivo degradable polymer tubular material for subcutaneous implantation of capsules and preparation method thereof
A polymer and polymer solution technology, applied in medical science, surgery, etc., can solve the problems of patients' pain and increase the cost of surgery, and achieve the effects of avoiding pain, excellent processability, and avoiding inflammatory reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
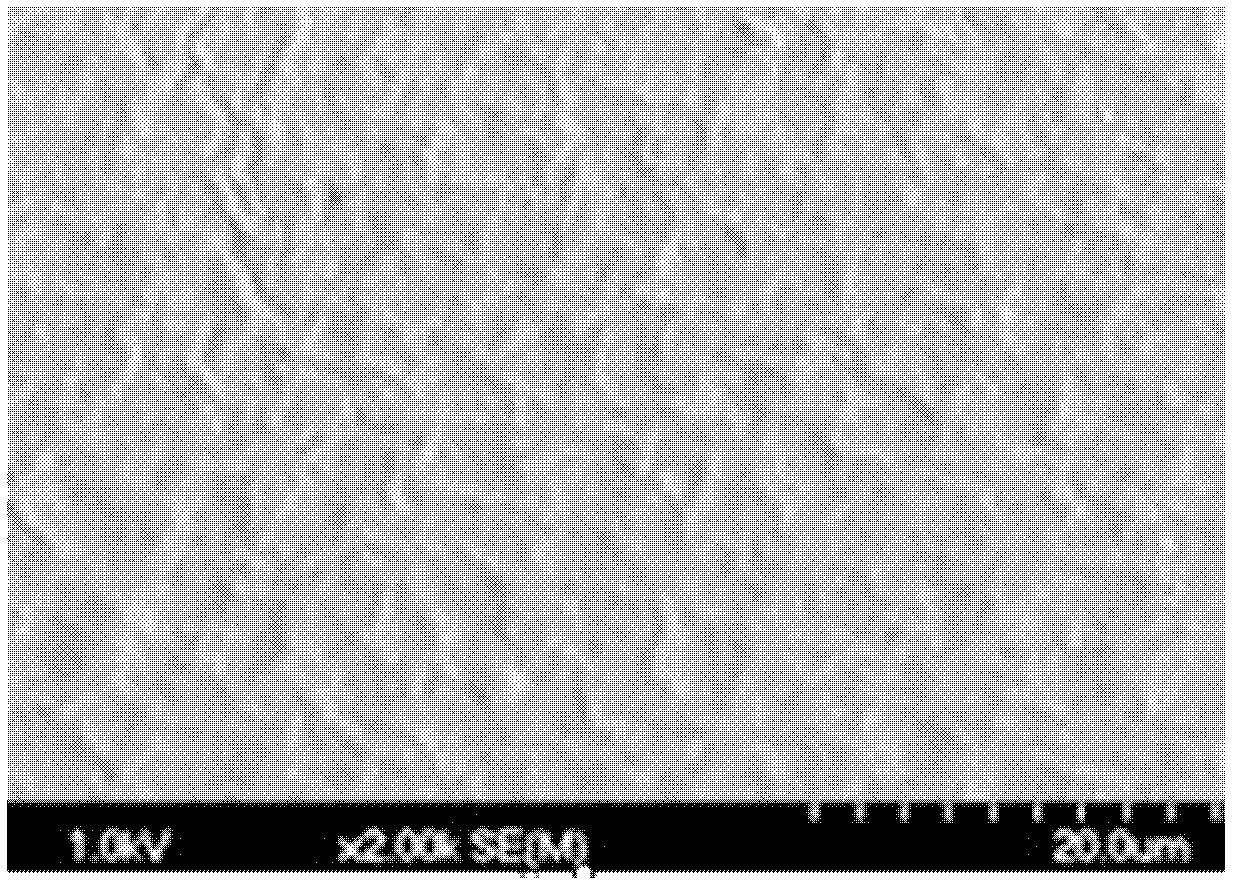
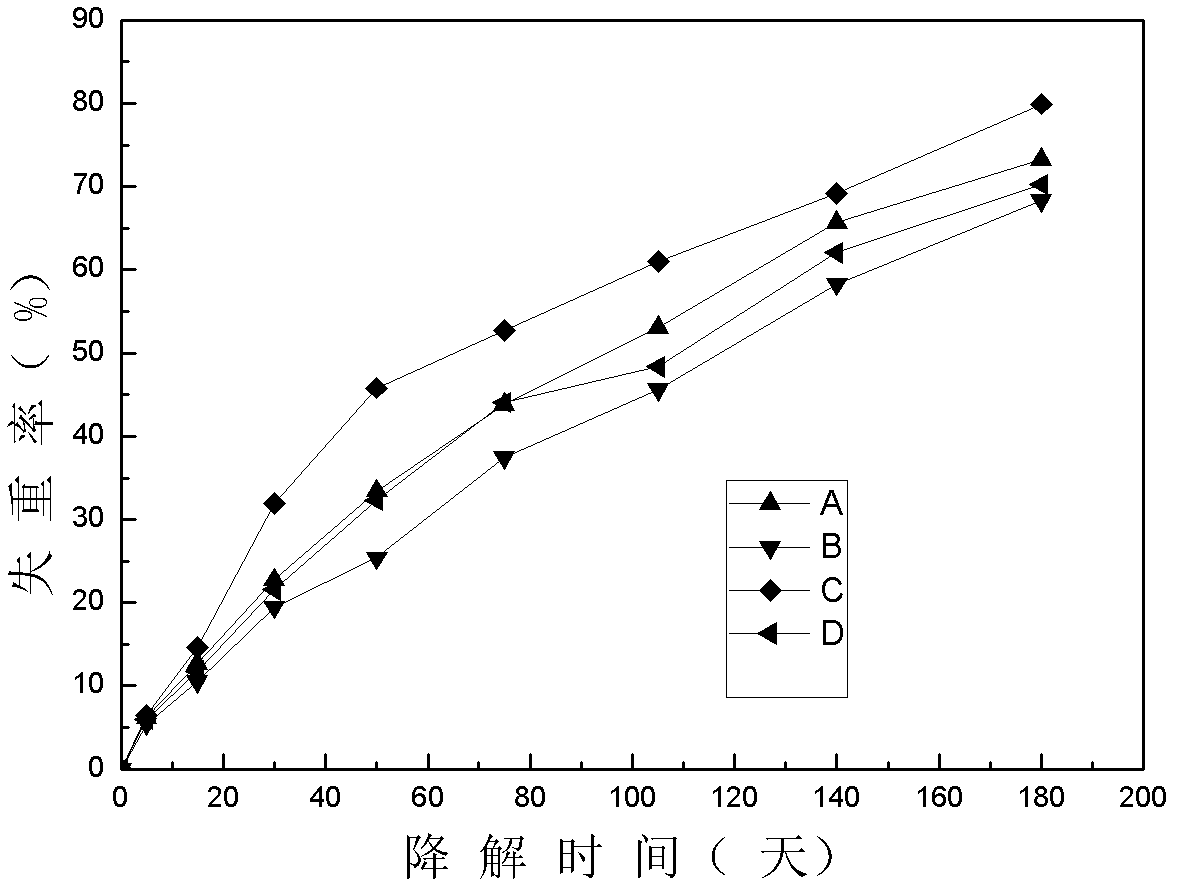
[0029] Embodiment 1: Dissolve 0.90g PLGA (PL: GA 85 / 15 Mw: 65000) and 0.10g PEG (Mw: 6000) into 10ml of dichloromethane, stir to form a uniform polymer solution, and let it stand for defoaming , set aside; in the obtained homogeneous solution, adopt the pulling method to form a polymer tube film on the surface of the columnar mold, dry at room temperature for 1 hour, pull and shape again, repeat 5 times, and reach the desired thickness, and finally vacuum dry at 40°C for 24 hours to remove Organic solvent; the obtained product is soaked in deionized water for 24 hours, and demolded to obtain a polymer tubular product with an inner diameter of 3mm and a wall thickness of about 0.02mm. The surface appearance of the obtained tubular material is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the in vitro degradation mass change curve is shown as figure 2 -A shown.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0030] Specific embodiment two: Dissolve 0.95g PLGA (PL: GA 85 / 15 Mw: 65000) and 0.05g PEG (Mw: 6000) in 10ml of dichloromethane, stir to form a homogeneous polymer solution, and stand for defoaming , set aside; in the obtained homogeneous solution, adopt the pulling method to form a polymer tube film on the surface of the columnar mold, dry at room temperature for 1 hour, pull and shape again, repeat 5 times, and reach the desired thickness, and finally vacuum dry at 40°C for 24 hours to remove Organic solvent; the obtained product is soaked in deionized water for 24 hours, and demolded to obtain a polymer tubular product with an inner diameter of 3 mm and a wall thickness of about 0.02 mm. The in vitro degradation quality change curve of the obtained tubular material is as follows: figure 2 -B is shown.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0031] Specific embodiment three: Dissolve 0.90g PLGA (PL: GA 75 / 25 Mw: 100000) and 0.10g PEG (Mw: 6000) in 10ml of dichloromethane, stir to form a uniform polymer solution, and let it stand for defoaming , set aside; in the obtained homogeneous solution, use the pulling method to form a polymer tube film on the surface of the columnar mold, dry at room temperature for 1 hour, pull and shape again, repeat 5 times, to reach the expected thickness, and finally vacuum dry at 40°C for 24 hours to remove Organic solvent; the obtained product is soaked in deionized water for 24 hours, and demolded to obtain a polymer tubular product with an inner diameter of 3 mm and a wall thickness of about 0.02 mm. The in vitro degradation quality change curve of the obtained tubular material is as follows: figure 2 -C curve shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com