Microprobe scratching machining method with force feedback control function for manufacturing microstructure
A processing method and micro-probe technology, applied in the directions of micro-structure technology, micro-structure device, manufacturing micro-structure device, etc., can solve the problems of inability to meet, low processing efficiency, small processing range, etc., and achieve shape precision elimination and installation. The effect of precision error elimination and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0020] Embodiment 1: A microprobe marking processing method with force feedback control for microstructure manufacturing, the processing method is realized by the following steps:
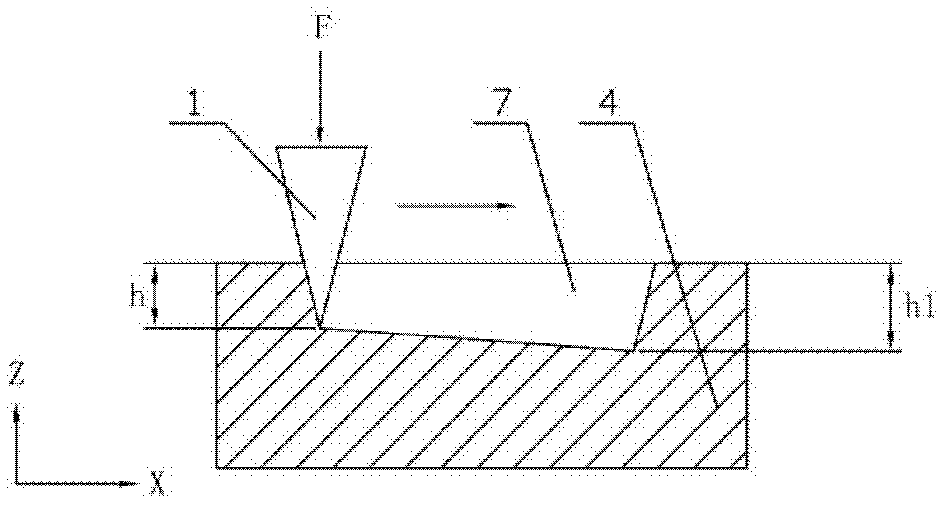
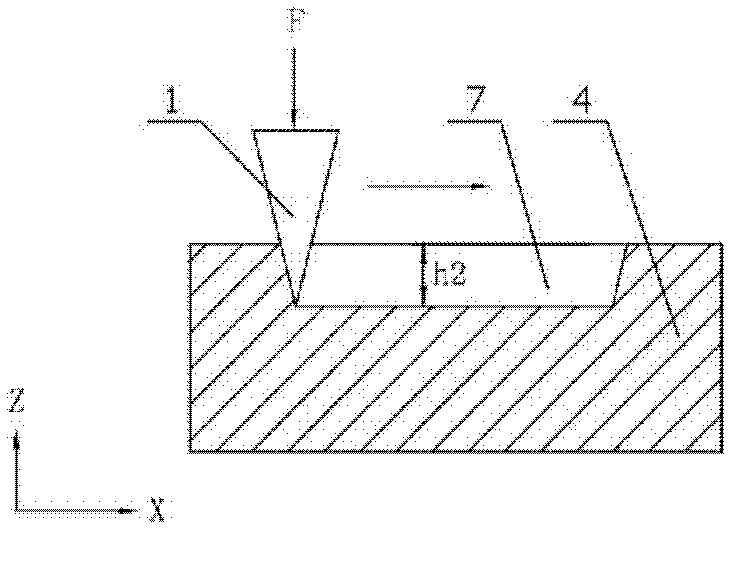
[0021] Step 1: The microprobe tool automatically approaches the surface of the workpiece (this process is realized by detecting the force value received by the microprobe tool 1 in the Z direction, and controlling the stepping motor to realize the rough feed of the Z direction coarse motion table 2 and control the piezoelectric ceramics to drive the precision feed of the micro-motion table 3 in the Z direction to achieve the set initial force value, thereby realizing the initial contact between the microprobe tool 1 and the surface of the workpiece 4);
[0022] First place the workpiece 4 on the precision table 5 in the X-Y direction, and make the microprobe tool 1 automatically approach the surface of the workpiece 4 and maintain a constant force F according to the set initial force value, referred...
specific Embodiment approach 2
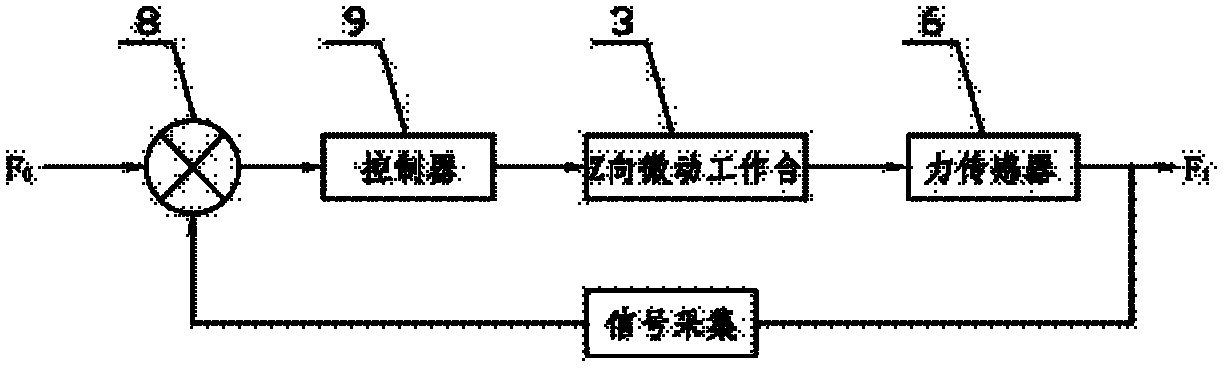
[0029] Specific embodiment two: what this embodiment provides is a kind of microprobe marking processing device with force feedback control, see Figure 5 , the device mainly includes a Z-direction support plate 11, a support platform 12, a computer 13,
[0030] Z-direction coarse motion table 2, Z-direction micro-motion table 3, force sensor 6, microprobe tool 1, X-Y direction precision table 5 and UMAC control unit 10; where:
[0031] The X-Y direction precision workbench 5 is set on the support platform 12, the workpiece 4 is set on the X-Y direction precision workbench 5, and the lower end of the Z-direction support plate 11 is fixed on the support platform 12; the UMAC control unit 10 sends two analog signals, Control the movement of the Z-direction coarse motion table 2 and the Z-direction micro-motion table 3 respectively. The communication between the computer 13 and the UMAC control unit 10 is realized by network cable transmission, and the computer control software sen...
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Set the initial value of the constant force to 17mN, process on the surface of the polymer polycarbonate (PC) material workpiece, the scoring length is 2000μm, the scoring speed is 0.02mm / s, and the marking is measured every 250μm stroke depth, Kp=18000, Ki=36500, from Figure 4 It is not difficult to see from the relationship curve between processing depth and scoring length under the medium-force open-loop state that the processing depth of the micro-groove 7 decreases gradually with the increase of the scoring length; Figure 4 It is not difficult to see the relationship curve between processing depth and scoring length under the medium-force closed-loop state. Although the relationship curve is not completely a straight line (within the experimental error range), there is no tendency to increase with the scoring length. The experimental results verify the feasibility of this method.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com