Amidoxime-based chelate polyacrylonitrile fiber and its preparation method and application
A polyacrylonitrile fiber and amidoxime-based technology, which is applied in the field of amidoxime-based chelated polyacrylonitrile fiber and its preparation, can solve problems such as fracture, broken, and poor mechanical properties, and achieve extended service life and stable performance , the effect of good mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] (1) Raw material: 2dtex polyacrylonitrile fiber, breaking strength is 7.2cN / dtex.
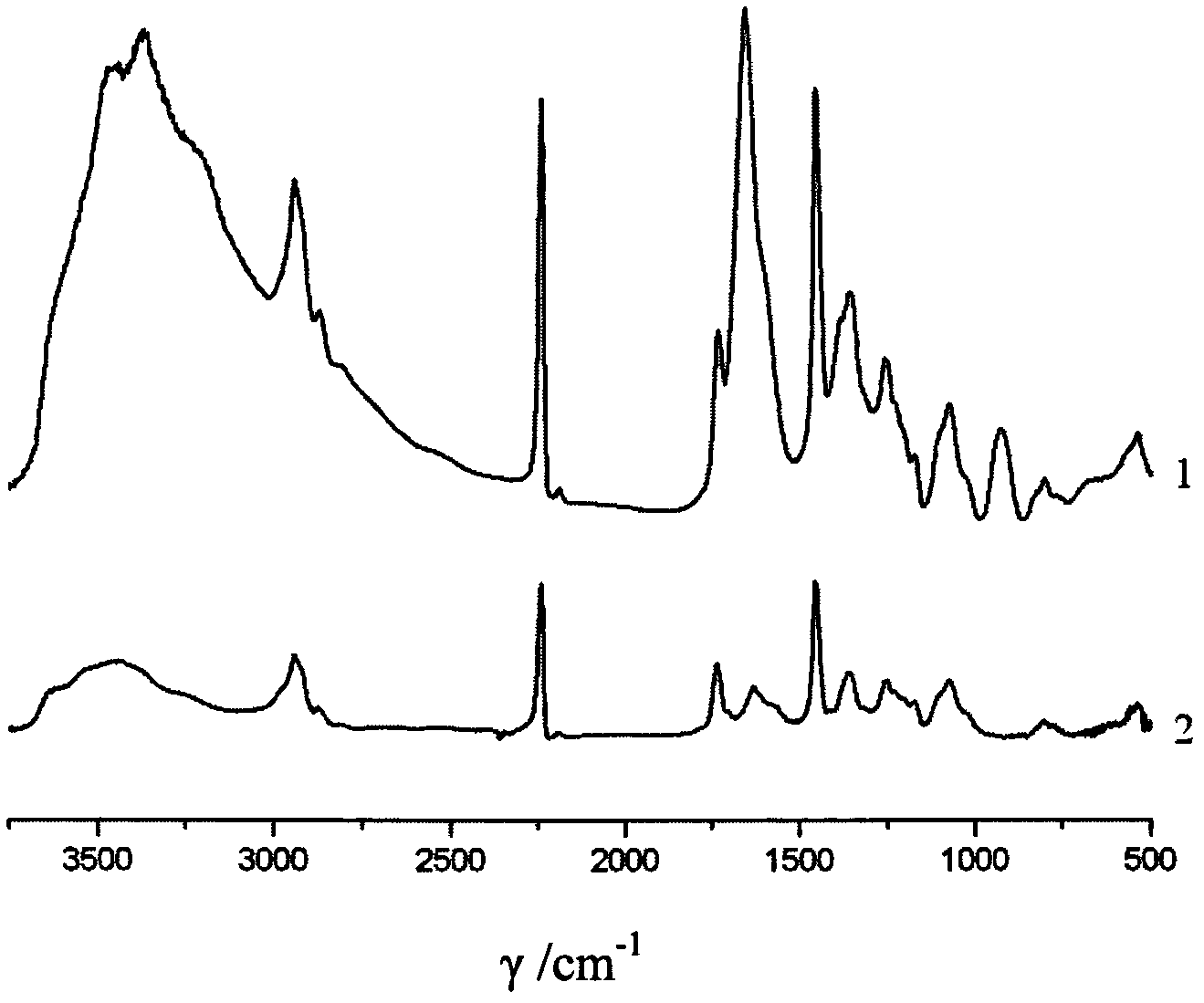
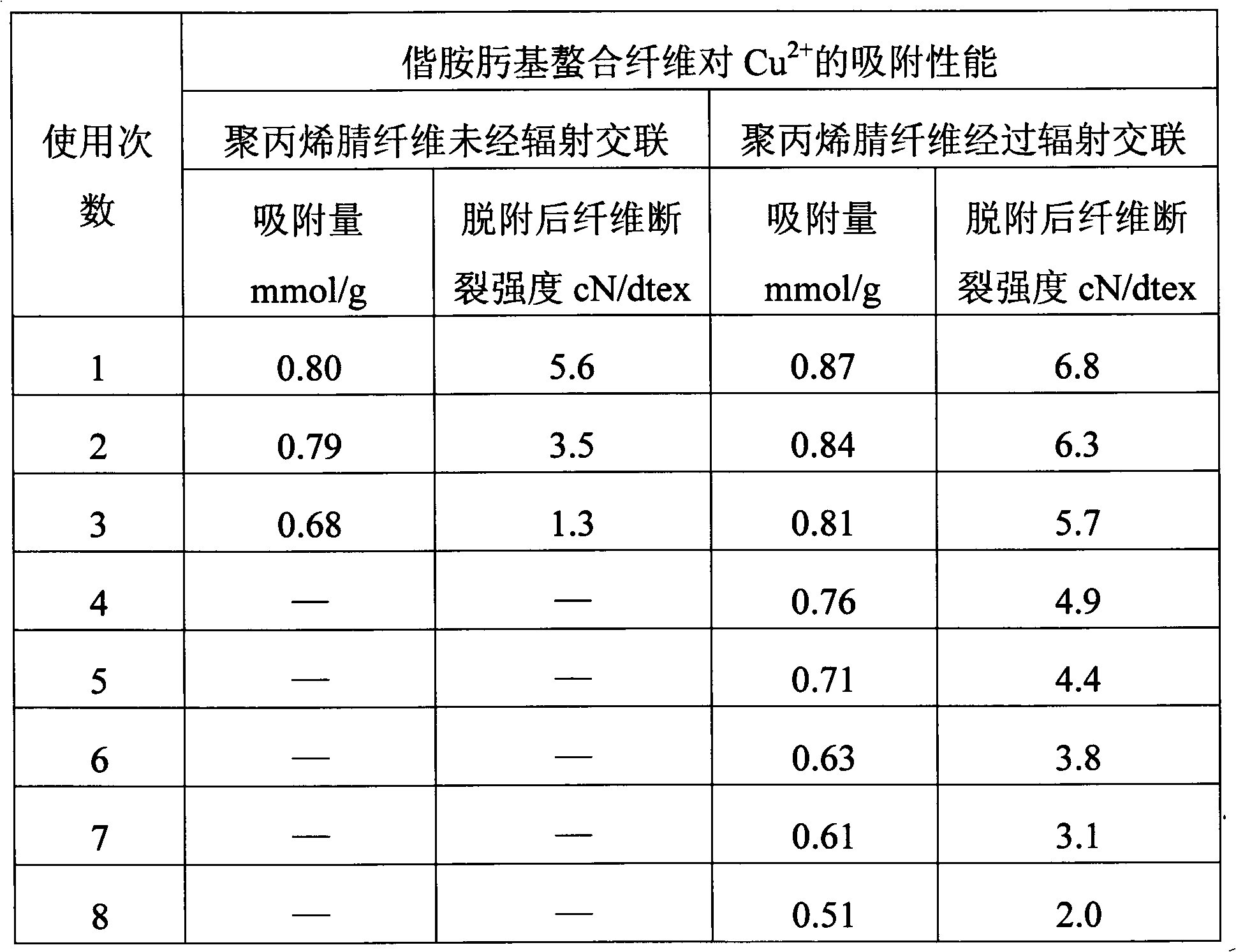
[0055] (2) Preparation method: 0.53g is irradiated and cross-linked with a cobalt source under the protection of nitrogen, and the irradiation dose is 500kGy. After irradiation, the fiber breaking strength of polyacrylonitrile is 7.0cN / dtex, which is compared with that before irradiation. Has not changed much. The preparation is carried out according to the molar ratio of nitrile group, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and anhydrous sodium carbonate in the polyacrylonitrile fiber being 1:1:0.5. Accurately weigh 0.69g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride and 0.53g of anhydrous sodium carbonate into 24.8ml of deionized water to prepare a solution with a pH of 7, and heat the solution to 70°C. Put 0.53g of irradiated polyacrylonitrile fibers into the prepared solution. After reacting for 3 hours, the fibers were taken out, washed with water, and dried to obtain 0.63 g of amidoxime-based chelated pol...
Embodiment 2
[0079] (1) Raw material: 2dtex polyacrylonitrile fiber, breaking strength is 7.2cN / dtex.
[0080] (2) Preparation method: the polyacrylonitrile fiber is irradiated and cross-linked with a cobalt source under the protection of nitrogen, and the irradiation dose is 500kGy. The breaking strength of the irradiated polyacrylonitrile fiber is 7.0cN / dtex, which is the same as Little changed from before. The preparation is carried out according to the molar ratio of nitrile group, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and anhydrous sodium carbonate in the polyacrylonitrile fiber being 1:1:0.5. Accurately weigh 0.69g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride and 0.53g of anhydrous sodium carbonate into 24.8ml of deionized water to prepare a solution with a pH of 7, and heat the solution to 70°C. Put 0.53g of irradiated polyacrylonitrile fibers into the prepared solution, take out the fibers after reacting for 3 hours, wash with water, and dry to obtain 0.63g of amidoxime-based chelated polyacrylonitrile f...
Embodiment 3
[0091] (1) The polyacrylonitrile fiber whose raw material is 2dtex has a breaking strength of 7.2cN / dtex.
[0092] (2) Preparation method:
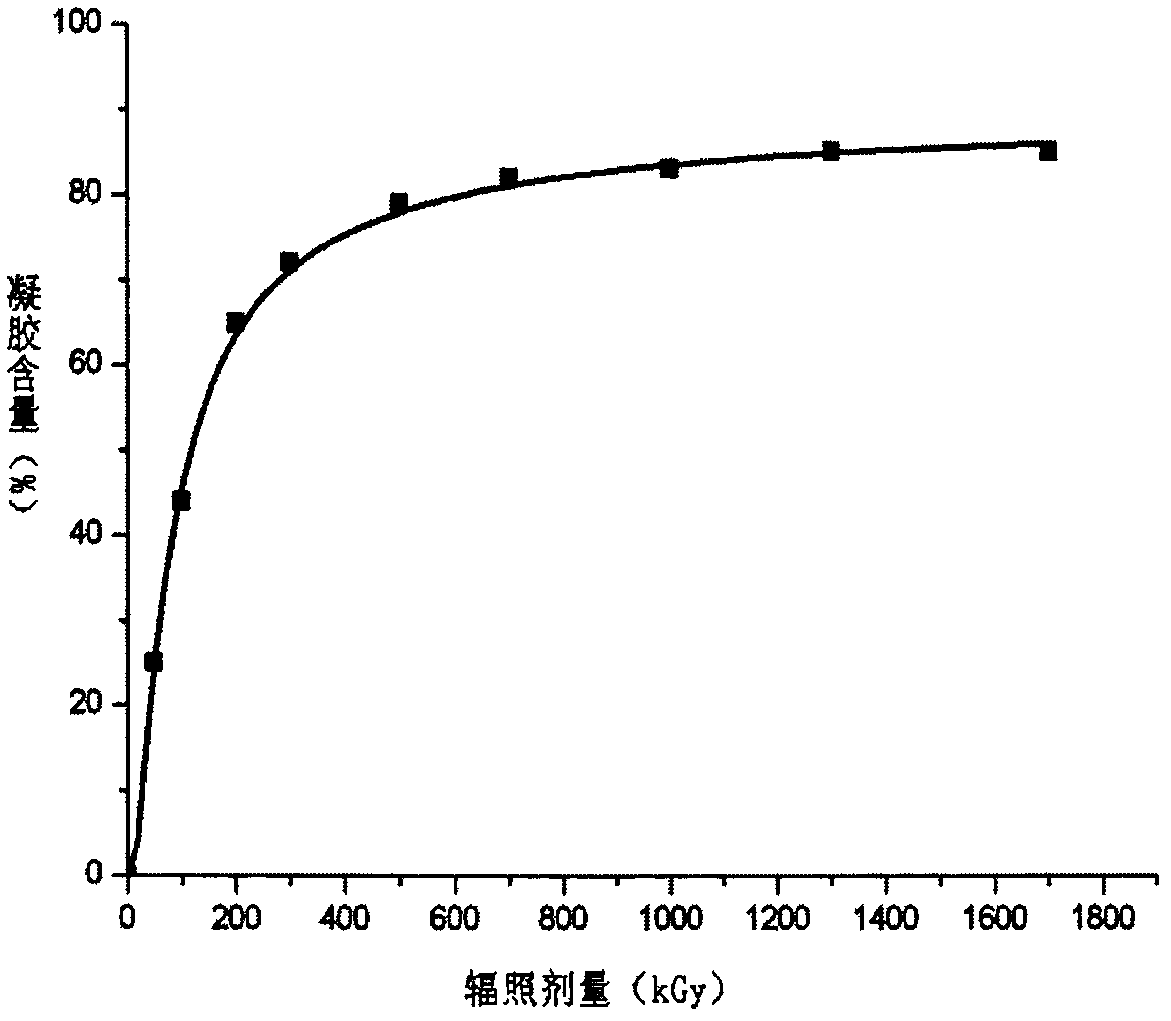
[0093] Accurately weigh 27 parts of 0.53g polyacrylonitrile fiber, and use cobalt source to irradiate and crosslink the polyacrylonitrile fiber under nitrogen environment, divide it into 9 groups, each group has three fibers, and the irradiation dose of each group is 100kGy , 300kGy, 500kGy, 700kGy, 900kGy, 1100kGy, 1300kGy, 1500kGy and 1700kGy. The breaking strength of each group of fibers is 7.1cN / dtex, 7.1cN / dtex, 7.0cN / dtex, 6.9cN / dtex, 6.8cN / dtex, 6.7cN / dtex, 6.6cN / dtex, 6.5cN / dtex, 6.3cN / dtex, has little change in strength compared with polyacrylonitrile fibers.
[0094] The preparation is carried out according to the molar ratio of nitrile group, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and anhydrous sodium carbonate in the polyacrylonitrile fiber being 1:1:0.5. Accurately weigh 15 parts each of 0.69g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride and 0.53...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com