Method for improving reading redundancy of static random access memory
A technology of static randomness and redundancy, applied in the field of microelectronics, can solve the problems such as the negative effect of the electron mobility of NMOS devices, and achieve the effects of improving readout redundancy, reducing potential, and increasing equivalent resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described below in combination with principle diagrams and specific operation examples.
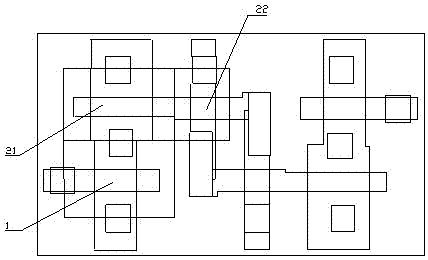
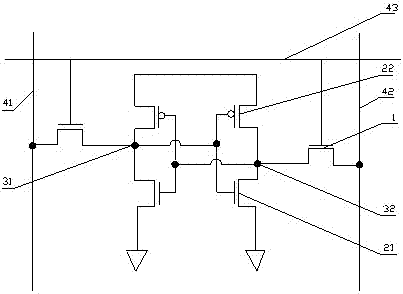
[0025] see image 3 Shown, a kind of method of improving SRAM read redundancy of the present invention, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0026] Step S1: performing shallow trench isolation (STI) on the silicon substrate to form shallow trench isolation;
[0027] Step S2: Implanting well ions on the silicon substrate to form a well bottom;
[0028] In this step, according to the different types of semiconductor devices to be formed, the formed wells are also different. For example, to manufacture a PMOS type device, it is necessary to implant boron ions into the silicon substrate to form a P well. For NMOS type devices, phosphorus ions need to be implanted into the silicon substrate to form an N well.
[0029] Step S3: performing polysilicon gate fabrication and sidewall formation on the silicon substrate respectively.
[0030] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com