Hepatitis B virus antigen formulation for cell stimulation followed by therapeutic immunization
A technology of hepatitis B virus and antigen, applied in the field of medicine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
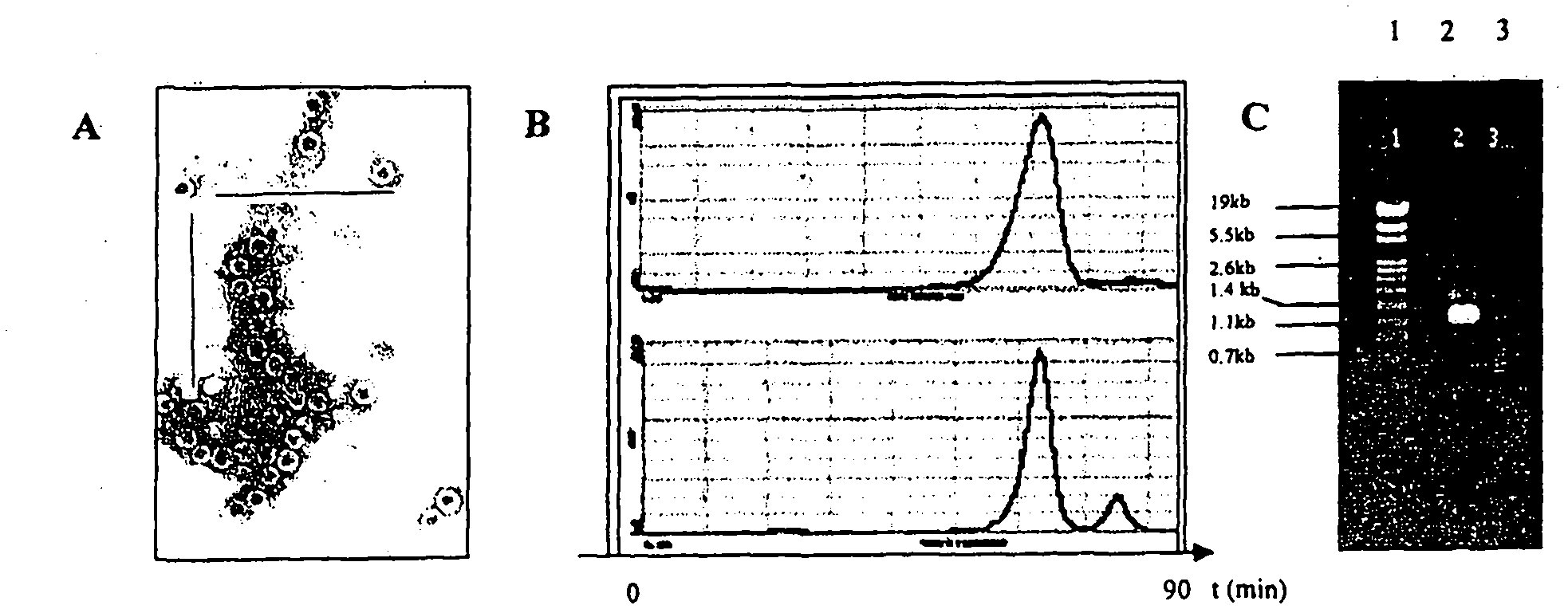
[0029] Example 1. Generation of Acid Precipitate of HBV Surface Antigen and Nucleocapsid Antigen in Suspension
[0030] HBcAg (CIGB, Cuba) was expressed as a recombinant protein of 183 amino acids, purified from Escherichia coli. Recombinant HBsAg, subtype adw2 was produced in Pichia pastoris (CIGB, Cuba). The fermentation and purification process of HBcAg protein was performed as previously described (Aguilar JC. Immunol Cell Biology 2004; 82:539-546). This antigen purification process yields highly purified nucleocapsid antigens (>95%), as figure 1 Visible in A. The molecular size of this antigen is similar to that of HBsAg, which means that virus-like particles are also formed ( figure 1 B), and additionally contains trace amounts of nucleic acid bound to its chemical structure, which functions as a TLR stimulator, such as figure 1 Visible in C. These trace amounts of bound TLR ligands can be characterized primarily as RNA and residual amounts of DNA, both of bacterial...
Embodiment 2
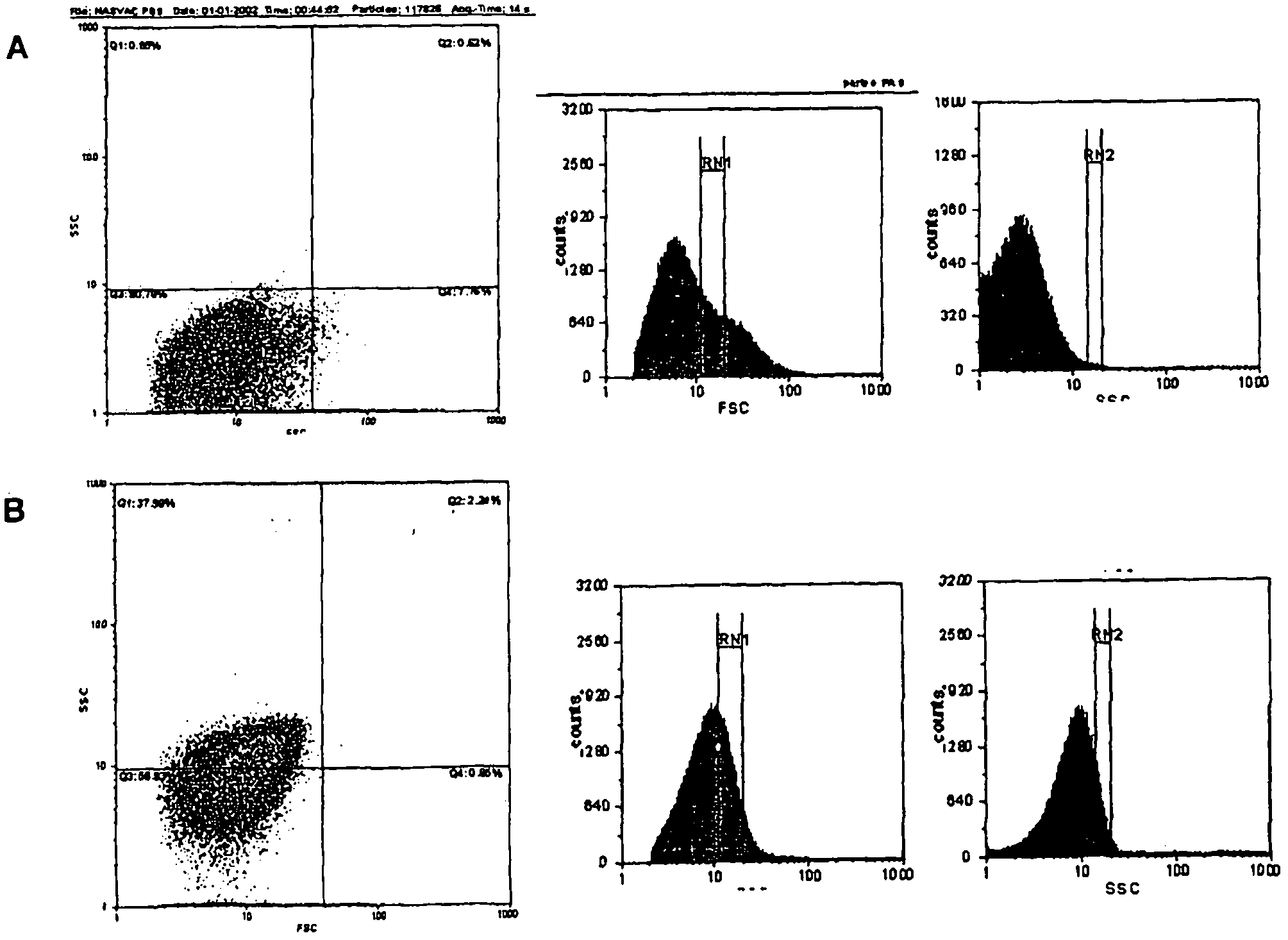
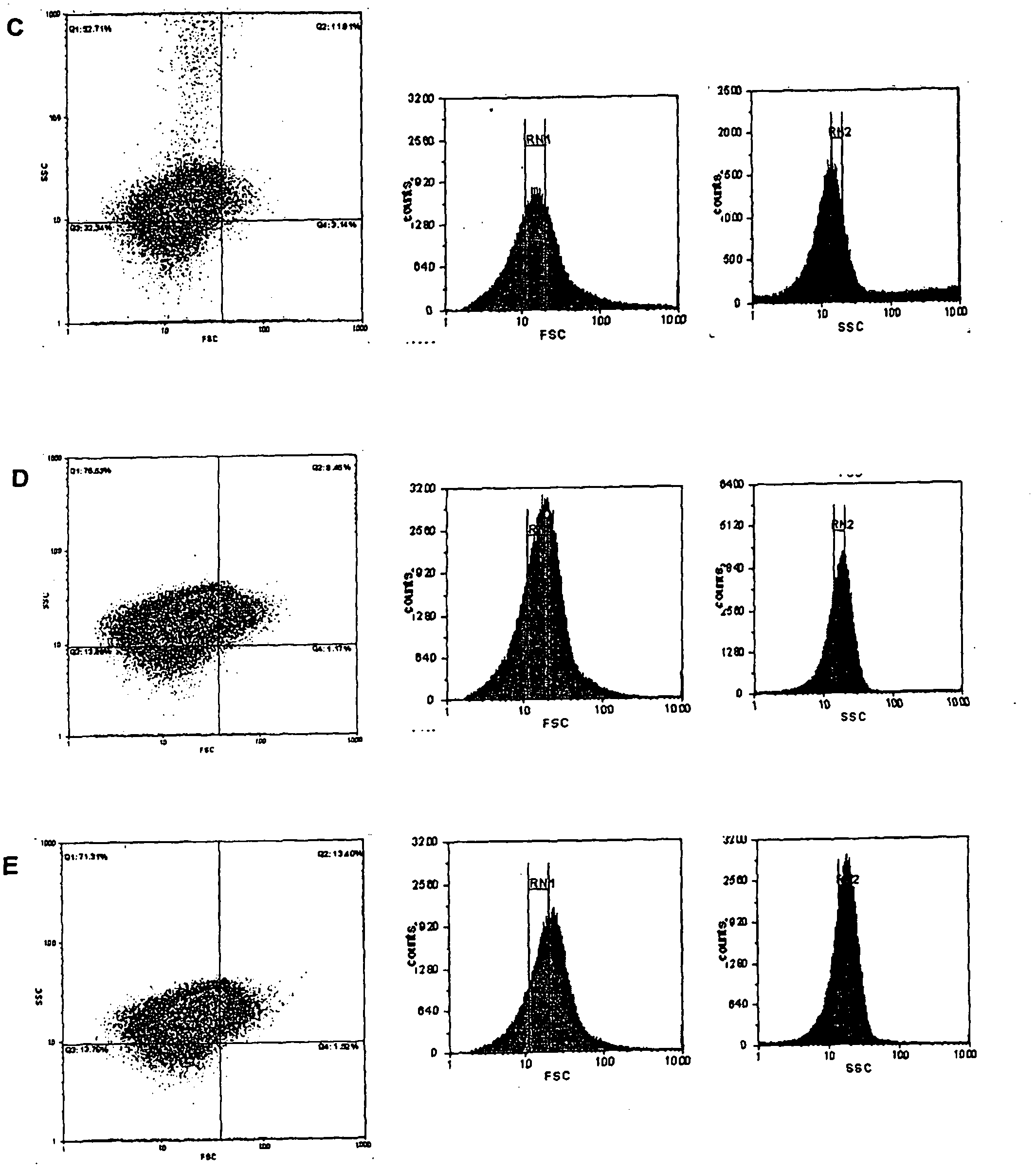
[0035] Example 2. Characterization of the Molecular Size of HBsAg and HBcAg Antigen Suspensions and Method of Selection of Optimal Size for Assimilation and Antigen Stimulation
[0036] In order to select the optimal size pellet for stimulating professional antigen presenting cells, 4 pellet variants were selected. Precipitate variants were produced by the method described in Example 1, dialysis and diafiltration, pH adjusted to 4.0, and incubation times predetermined.
[0037] Size selection was performed by flow cytometry, and for calibration, size-spec beads of 2.5 μm were used as an upper limit. 50 nm to 2.5 μm were used in the experiments, which demonstrated that, in general, assimilation and cell stimulation differed in dependence of pellet size and cell type. Macrophages appear to be the more readily assimilable cells, with pellet sizes greater than 500nm. In this way, the precipitate mixture was selected to increase the stimulating capacity of the antigenic mixture. ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3. Study of Passive Immunization Using Adoptive Transfer of Cells from Balb / c Mice Previously Immunized with a Preparation Containing HBsAg and HBcAg Antigens to Transgenic Balb / c Mice Expressing HBsAg
[0041] Immunotherapy based on the development of vaccine candidates constitutes one of the strategies for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. The effectiveness of candidates depends on the generation of robust humoral and cellular immune responses capable of overcoming the state of tolerance to viral antigens that characterizes the disease.
[0042] In the present invention, anti-HBsAg and anti-HBcAg immune responses in the donor are boosted by active immunization with a formulation comprising HBsAg and HBcAg. Additionally, the cells to be transferred are activated in vitro prior to transfer so that the response to these antigens is optimal when the cells are inoculated into the recipient organism. In this artificial way, a response type that does not exist i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com