Method for preparing structured graphene based on reaction of Cl2 and Ni film annealing
A graphene and structured technology, applied in the field of microelectronics, can solve the problems of strong interaction between graphene sheets and substrates, loss of single-layer graphene properties, poor continuity of graphene, etc., and achieve low cost, The effect of easy thickness control and fast reaction rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
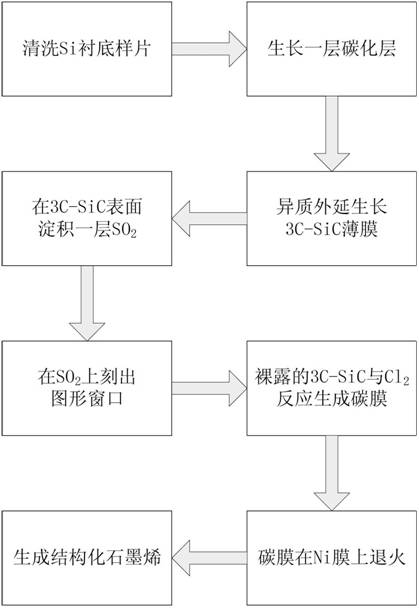
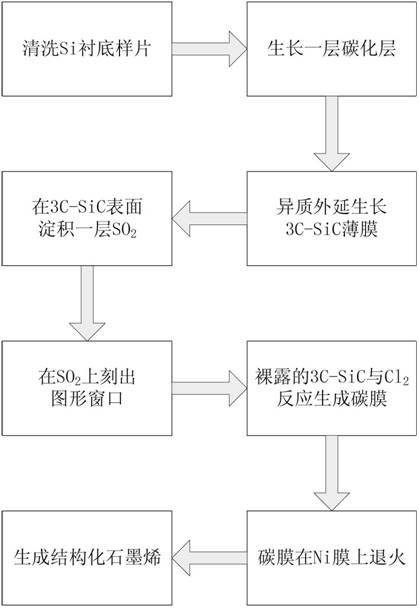
[0030] Step 1: Remove sample surface contamination.
[0031] Clean the surface of the 4-inch Si substrate substrate, that is, use NH 4 OH+H 2 o 2 Soak the sample in the reagent for 10 minutes, take it out and dry it to remove the organic residue on the surface of the sample; then use HCl+H 2 o 2 The reagent soaked the sample for 10 minutes, took it out and dried it to remove ionic contamination.
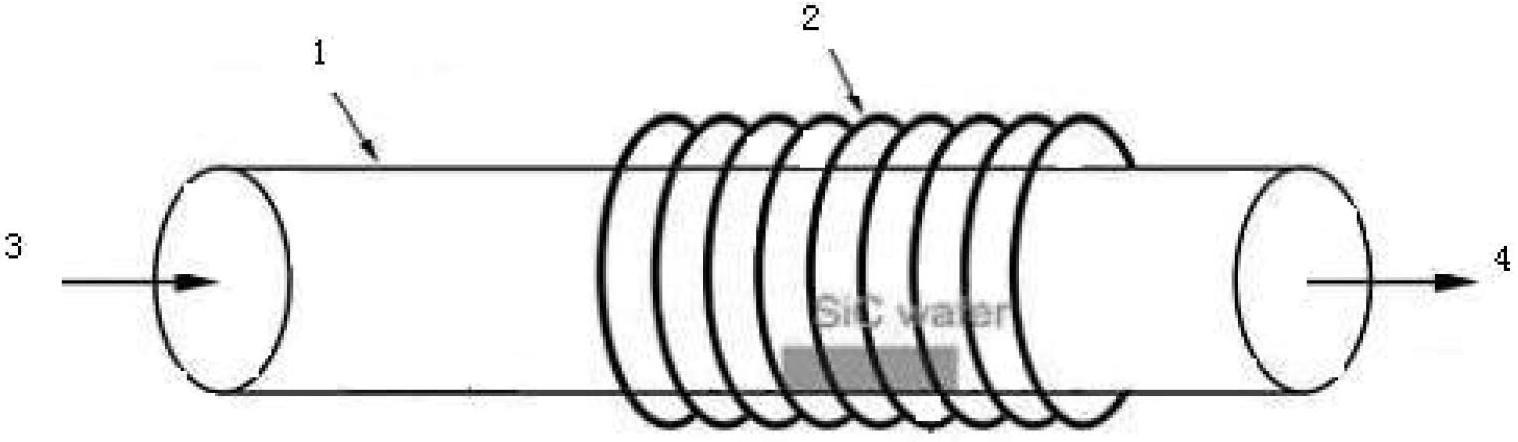
[0032] Step 2: Put the Si substrate substrate into the reaction chamber of the CVD system, and evacuate the reaction chamber to 10 -7 mbar level.
[0033] Step 3: growing the carbonized layer.
[0034] in H 2 In the case of protection, the temperature of the reaction chamber is raised to the carbonization temperature of 900 ° C, and then the flow rate of 30 sccm is introduced into the reaction chamber. 3 h 8 , grow a layer of carbonized layer on the Si substrate, the growth time is 10min.
[0035] Step 4: growing a 3C-SiC film on the carbide layer.
[0036] The temperature...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Step 1: Remove sample surface pollutants.
[0061] Clean the surface of the 8-inch Si substrate substrate, that is, use NH 4 OH+H 2 o 2 Soak the sample in the reagent for 10 minutes, take it out and dry it to remove the organic residue on the surface of the sample; then use HCl+H 2 o 2 The reagent soaked the sample for 10 minutes, took it out and dried it to remove ionic contamination.
[0062] Step 2: Same as Step 2 of Example 1.
[0063] Step 3: growing a carbonized layer.
[0064] in H 2 In the case of protection, the temperature of the reaction chamber is raised to the carbonization temperature of 1050 ° C, and then the flow rate of 30 sccm is introduced into the reaction chamber. 3 h 8 , grow a layer of carbonized layer on the Si substrate, the growth time is 7min.
[0065] Step 4: growing a 3C-SiC thin film on the carbide layer.
[0066] Rapidly raise the temperature of the reaction chamber to the growth temperature of 1200°C, and feed in SiH with flow r...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Step A: Clean the surface of the 12-inch Si substrate, that is, use NH 4 OH+H 2 o 2 Soak the sample in the reagent for 10 minutes, take it out and dry it to remove the organic residue on the surface of the sample; then use HCl+H 2 o 2 The reagent soaked the sample for 10 minutes, took it out and dried it to remove ionic contamination.
[0081] Step B: Same as Step 2 of Example 1.
[0082] Step C: In H 2 In the case of protection, the temperature of the reaction chamber is raised to the carbonization temperature of 1200 ° C, and then the flow rate of 30 sccm is introduced into the reaction chamber. 3 h 8 , for 5 min to grow a carbonized layer on the Si substrate.
[0083] Step D: Rapidly increase the temperature of the reaction chamber to the growth temperature of 1300° C., and feed SiH with flow rates of 30 sccm and 60 sccm respectively 4 and C 3 h 8 , carry out 3C-SiC film heteroepitaxial growth for 30min, and then in H 2 Gradually cool down to room temperat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com