Patents
Literature
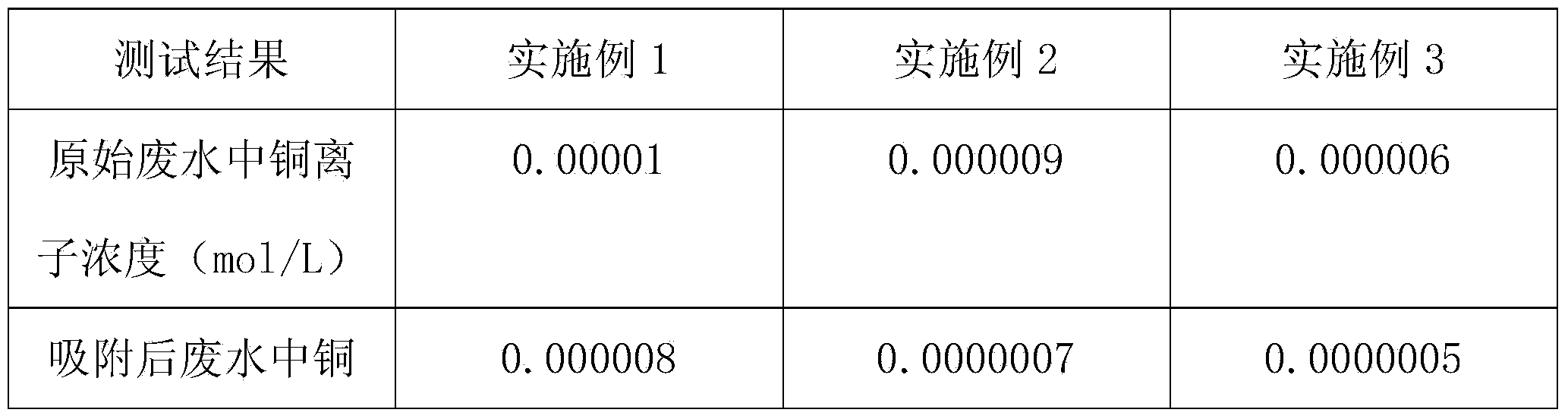
54 results about "Ionic contamination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
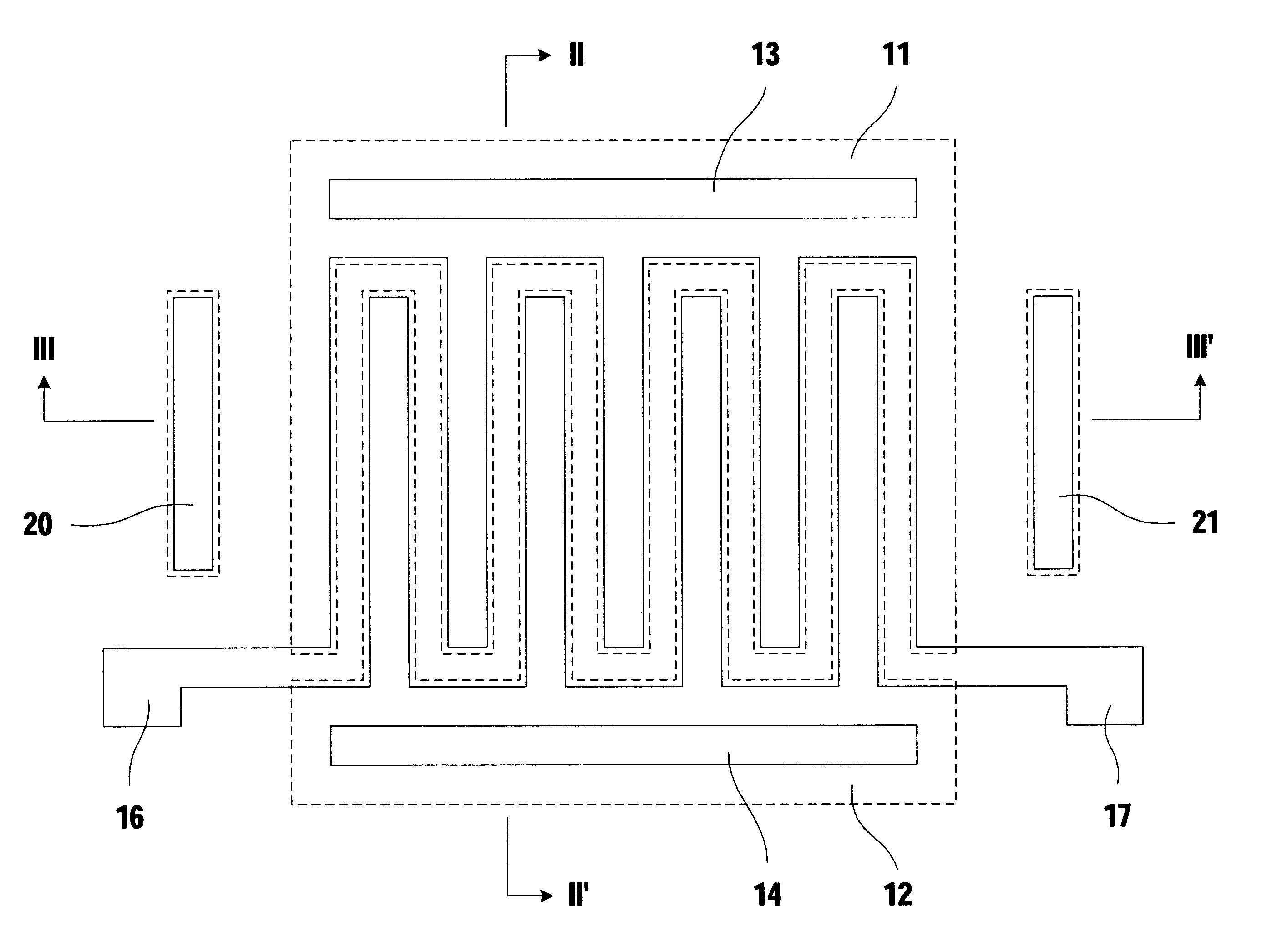
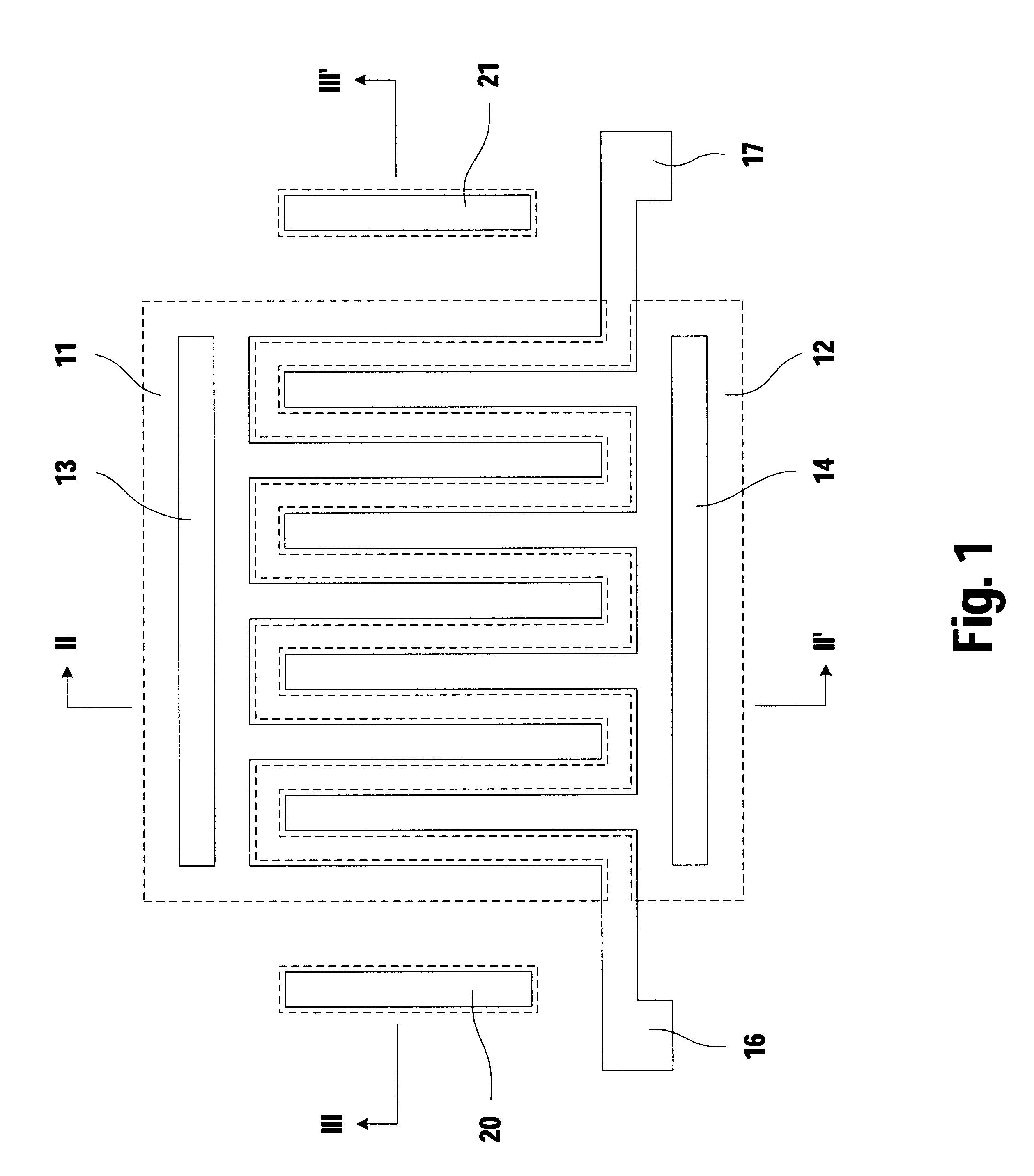
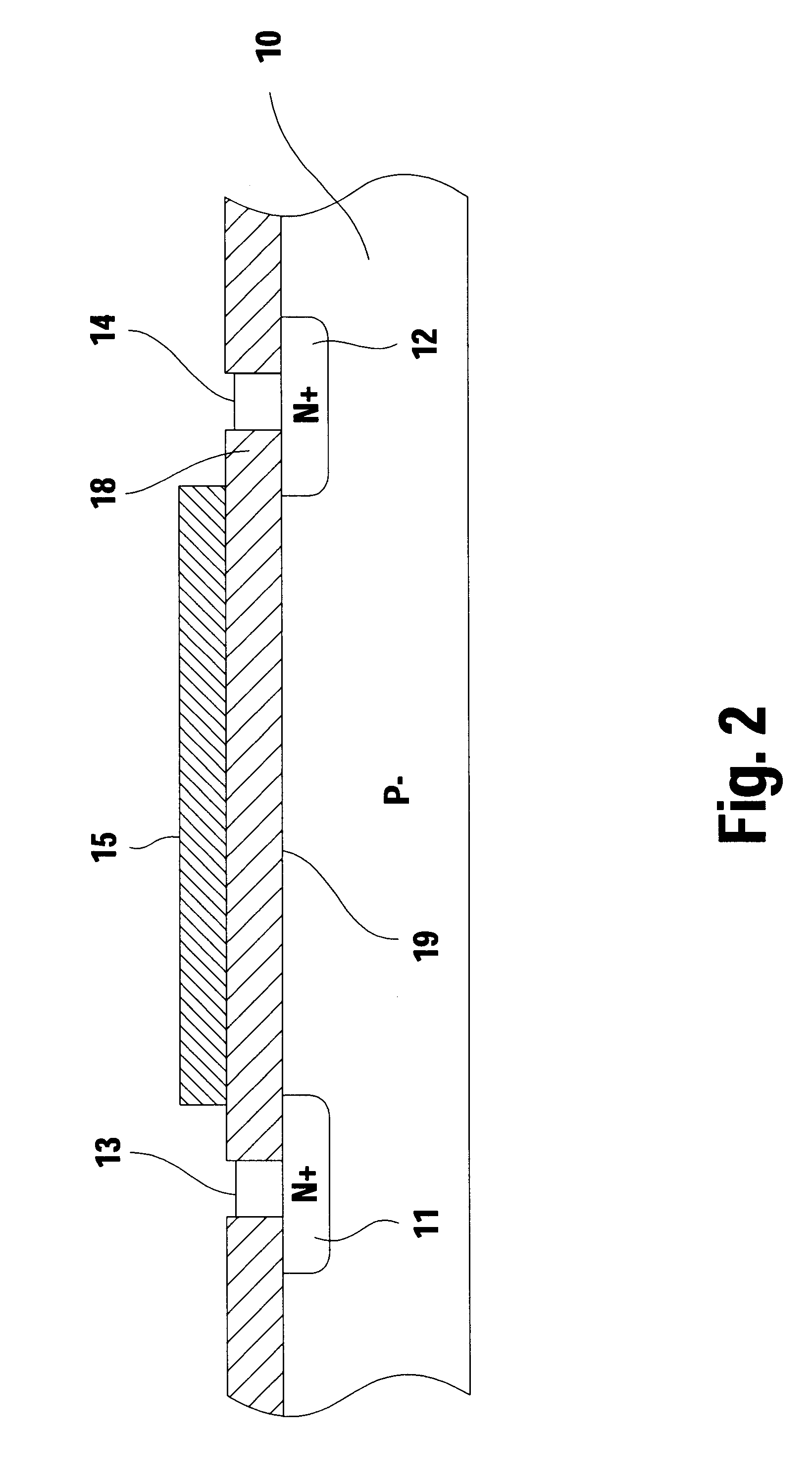
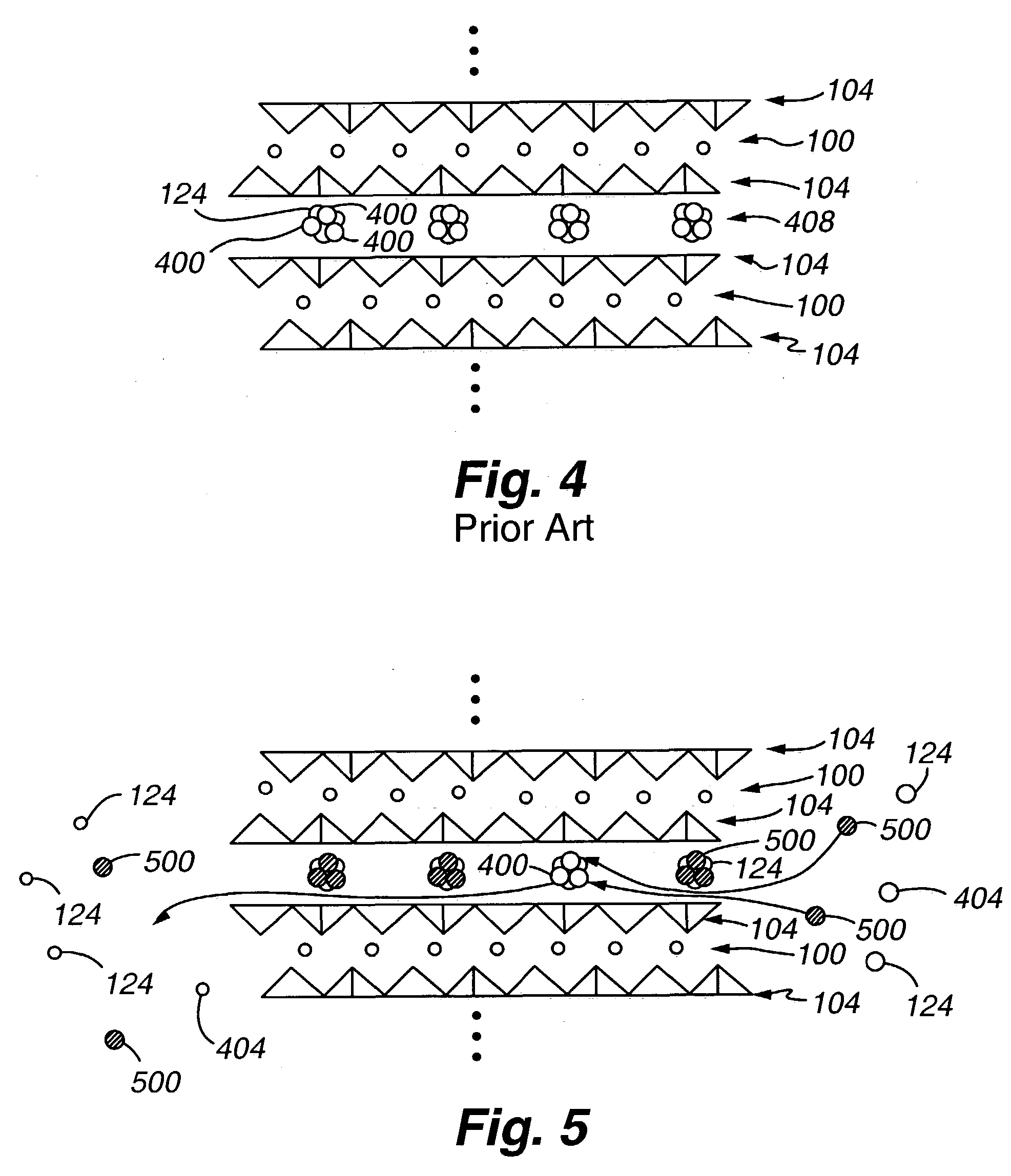
Mobile ionic contamination detection in manufacture of semiconductor devices
InactiveUS6348808B1Efficient detectionElectronic circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingEngineeringSemiconductor device fabrication
A test transistor structure formed in a semiconductor device has a thick-oxide transistor with an elongated serpentine-shaped metal gate. The gate is used to first measure the threshold voltage of the thick-oxide test structure. Then, a current is passed through the elongated metal line which forms the serpentine gate to heat the area of the test structure. While being heated, a stress voltage is applied between the substrate and one end of the gate electrode, this stress voltage being much larger than the logic voltage used in operating thin-oxide transistors on the chip. After a selected time, the current is removed, the stress voltage is removed, and the threshold voltage of the thick-oxide transistor is again measured and compared to the original value. Any reduction in threshold voltage can be attributed to the migration of positive charge to the silicon-to-oxide interface beneath the gate, and is proportional to the area between the source and drain regions of the test transistor.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Soldering flux for lead-free solder and preparation method of soldering flux
ActiveCN103286477AActiveAdjustable pHWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaEnvironmental resistanceMetallurgy
The invention relates to soldering flux for lead-free solder and a preparation method of the soldering flux. The soldering flux comprises, by mass, 2.0-4.0% of activating agent, 0.05-0.5% of surfactant, 0.4-1.0% of film-forming agent, 18-30% of cosolvent, 0.1-0.4% of corrosion inhibitor and the balance deionized water. The soldering flux is free of rosin and less than 3% in solid content, so that solid residual quantity is less during soldering, ionic contamination degree is low, and cleaning is avoided after soldering. By using the deionized water as solvent, the water-soluble no-clean soldering flux is colorless, transparent, free of pungent smell, easy in raw material getting approach and low in cost. Activating components in the soldering flux are halogen-free, so that insulativity of a soldered circuit board is improved; by the aid of the film-forming agent, a dense protecting film is formed on the surface of the circuit board after the film-forming agent is subjected to a soldering procedure, and accordingly, electromigration of soldered residues is lowered, and insulation stability of the circuit board is improved effectively; and harm caused when organic soldering flux is used for soldering can be reduced, and the soldering flux meets the environment-friendly requirements.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
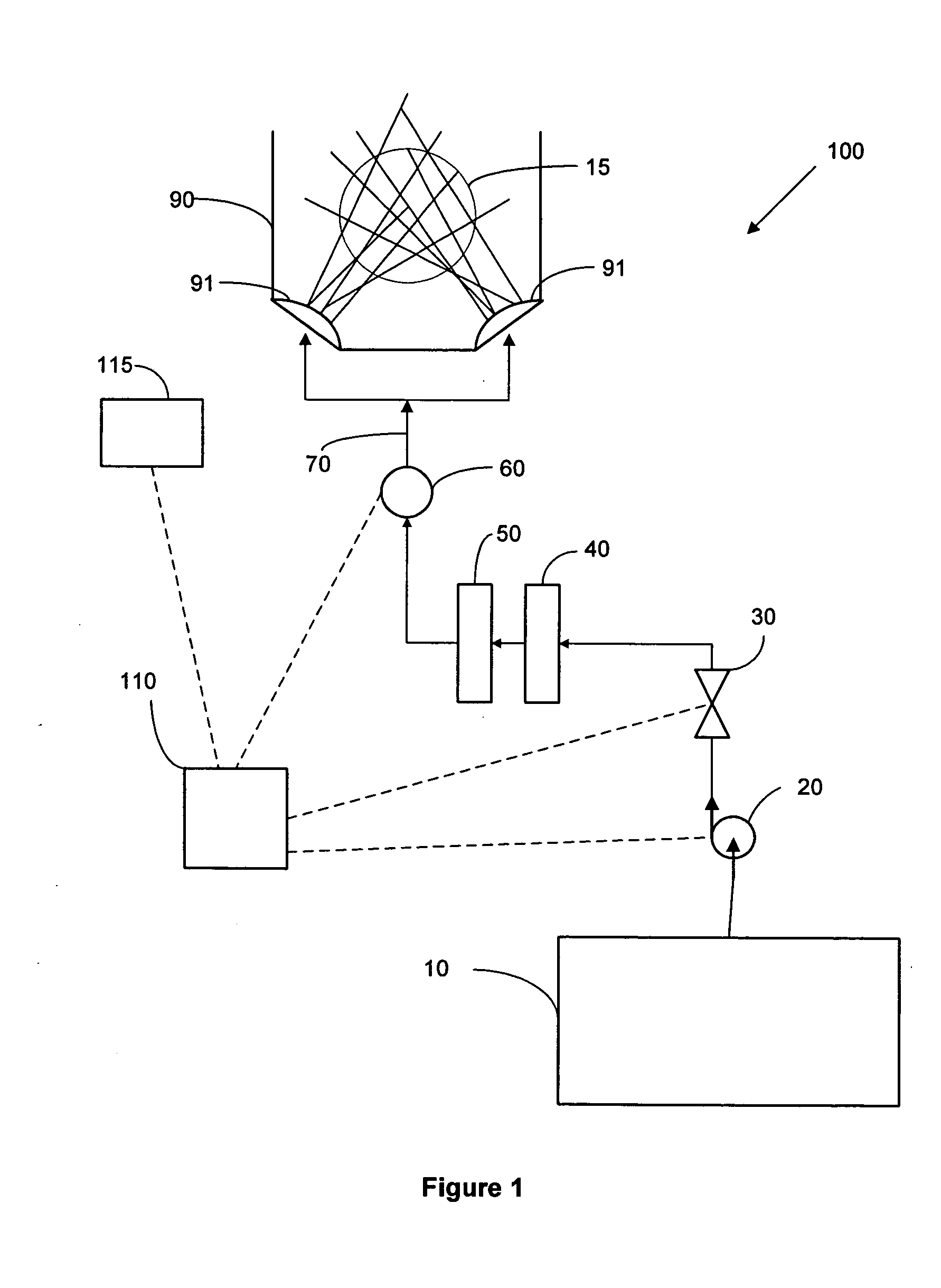
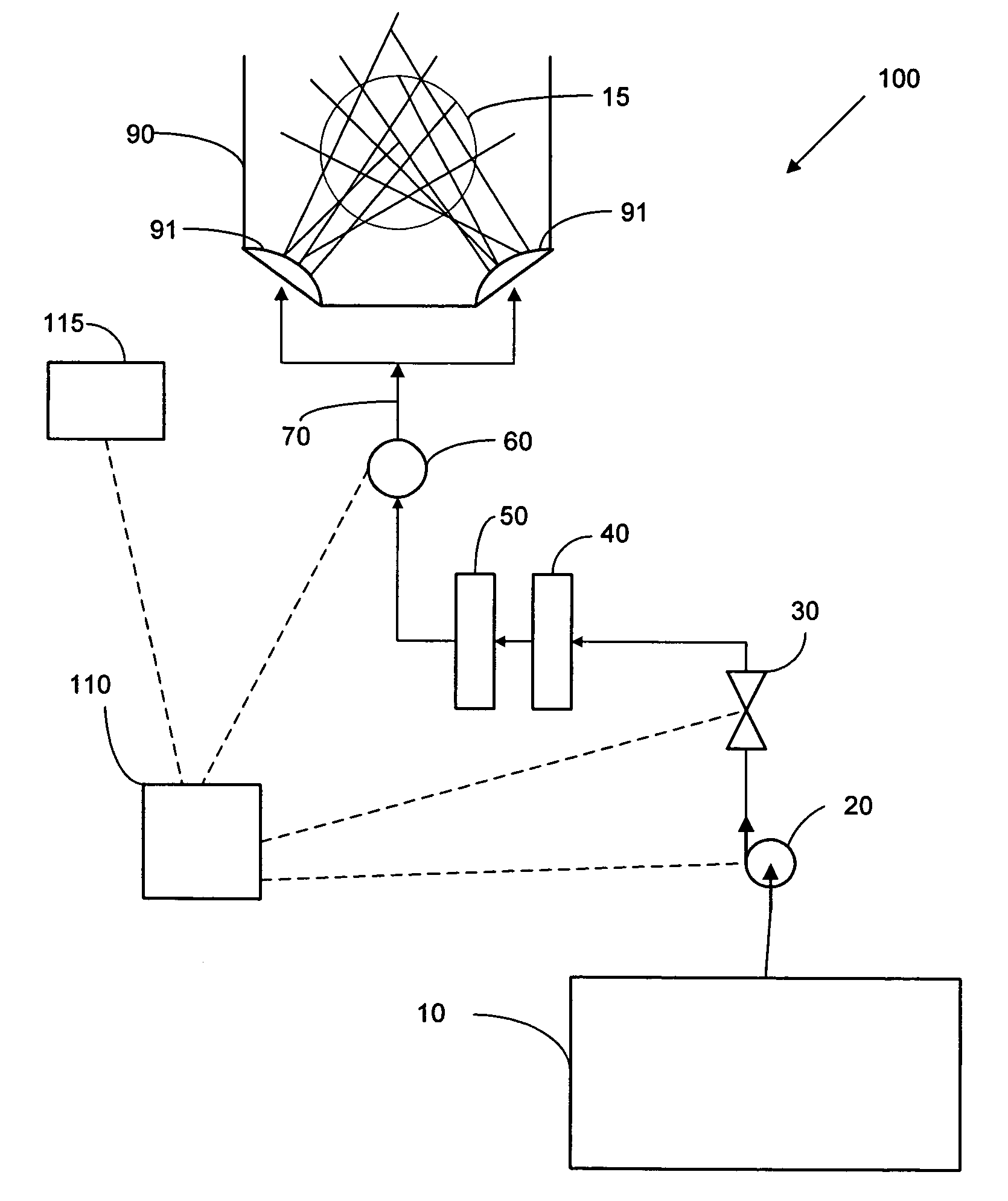
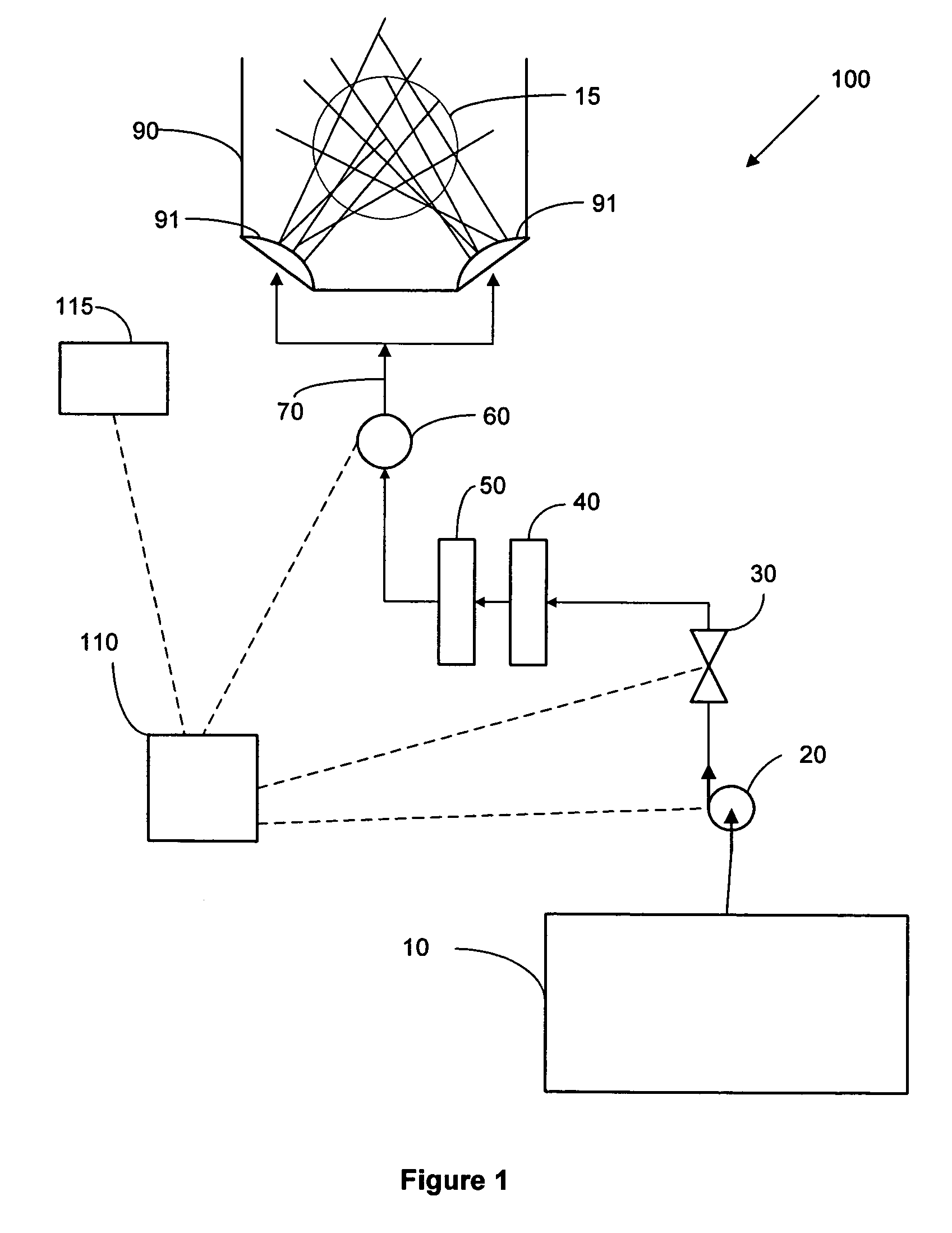
System and method for point-of-use filtration and purification of fluids used in substrate processing
ActiveUS20050016929A1Reduce and eliminate particleReduce and eliminate and ionicIon-exchanger regenerationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityFiltration
A method and system for supplying an ultra-pure fluid to a substrate process chamber using point-of-use filtration and purification. The method and system provide ability to automatically monitor and control contamination levels in fluids in real time and to stop substrate processing when contamination levels exceed predetermined thresholds. In one aspect, the invention is a system comprising: a fluid supply line adapted to supply a fluid to the process chamber; filtration means operably coupled to the fluid supply line for removing positively and negatively charged particles from the fluid prior to the fluid passing into the process chamber; a purifier operably coupled to the fluid supply line in series with the filtration means for removing ionic contaminants from the fluid prior to the fluid passing into the process chamber; sensor means for repetitively measuring particle and ionic impurity levels in the fluid that has passed through the filtration means and the purifier, the sensor means producing signals indicative of the measured particle and ionic impurity levels; a controller electrically coupled to the sensor means for receiving the signals created by the sensor means, the controller adapted to respectively compare the measured particle level and the measured ionic impurity level indicated by the signals to a predetermined particle threshold and a predetermined ionic impurity threshold, wherein upon the controller determining that either the measured particle level is above the predetermined particle threshold and / or that the measured ionic impurity level is above the predetermined ionic impurity threshold, the controller further adapted to (1) activate means to alert a user, (2) cease processing of substrates in the process chamber, and / or (3) prohibit processing of substrates in the process chamber.
Owner:AKRION TECH
High capacity regenerable sorbent for removal or arsenic and other toxic ions from drinking water
InactiveUS20060030476A1Improved and cost-effective controlLower unit costMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesSorbentAluminosilicate
The present invention is directed to a sorbent comprising a disordered polyvalent metal oxide on the surface of an inert substrate. The substrate can be a layered silicate, such as vermiculite, an aluminosilicate such as montmorillonite, or a nonlayered silicate such as a zeolite. The sorbent removes ionic contaminants, such as arsenic, from process streams.
Owner:ADA TECH
Halogen-free scaling powder
InactiveCN101412166ANo pollution in the processNo pollutionWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSurface-active agentsSolvent
The invention relates to a soldering flux for welding in the electronic industry, in particular to a no-clean and halogen-free soldering flux. The soldering flux consists of organic solvent, abietic resin and derivate of the abietic resin, synthetic resin surface active agent, organic acid activated agent, anticorrosive agent, latent solvent and film forming agent. The soldering flux has the advantages of transparency, no environmental pollution, no penetrating odor, little smoke fume, shining welding spot, strong wetting power, excellent weldability, few residues left on the plate surface after welding, clean plate surface, low ionic contamination, unnecessary cleaning after welding and high surface insulation resistance, and conforms the environmental protection requirements, meets the no-clean requirement of a printing component plate and has stronger market competitiveness.
Owner:廖龙根
Flux
InactiveCN102513733AHigh insulation resistanceModerate weldabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSolventMaterials science
The invention belongs to the field of welding materials, and particularly relates to a halogen-free, low-residue, high-impedance and cleaning-free flux, which comprises the following components: 2-15wt% of activator, 0.05-2wt% of dispersing agent, 0.5-4wt% of film-forming agent, 0.1-4wt% of additive and 75-97.35wt% of solvent. Compared with the prior art, the flux has the advantages that the expansion ratio of the flux is higher than 80% of the standard, the flux is moderate in weldability and halogen-free, ionic contamination is at the highest I grade, the flux is applicable to high-reliability electronic products, the surface insulation resistance of the flux is at a 1010 grade after a copper mirror corrosion test, and the flux has the advantages that the flux is high in insulation impedance, high in insulation resistance, low in electric leakage risk, low in solid content, environment-friendly, clean and cleaning-free, residue is less, a post-weld board is tack-free and the like.
Owner:广东中实金属有限公司
Method for preparing micro intercommunicated hole structure transmission electron microscope sample
InactiveCN104075918ALow costSimple processPreparing sample for investigationForeign matterInsulation layer
The invention discloses a method for preparing a micro intercommunicated hole structure transmission electron microscope sample. The method includes the steps that a hollow through hole is filled with adhesive diluted with acetone, the solidified adhesive covers the inner wall of the through hole, tissue of interface layers such as an insulation layer, a barrier layer and a copper seed layer on a through hole base body are protected and foreign matter is prevented from entering the through hole; then, according to the position of the through hole needing to be observed, after samples are ground from the upper surfaces and the lower surfaces to be within the range of hole depths needing to be inspected through thickness measurement, according to a conventional ion thinning method, the through hole region is aligned, thinned and perforated, a plane transmission electron microscope sample of the inner wall of the through hole is obtained, and then the tissue of the interface layers at different hole depths of the through hole samples is accurately positioned and represented. According to the method, ionic contamination cannot be introduced into the samples, a sample preparation device is simple, low in cost and convenient to operate, and a feasible plane sample preparation method is provided for through hole type micro-electronic interconnected structure and semiconductor device transmission electron microscope tissue observation.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-halogen cleaning-free soldering flux
InactiveCN101690997ANo pollutionHigh insulation resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSolventTin
The invention provides a non-halogen cleaning-free soldering flux, which comprises the following compositions in percentage by weight: 0.5 to 5 percent of stannous oxalate, 0.5 to 20 percent of organic acid activator, 0.1 to 1 percent of surfactant, 0 to 3 percent of cosolvent, and the balance of solvent. Because of adopting the stannous oxalate as an activator, and having synergistic action with the organic acid activator and no halogen, the soldering flux has the advantages of no irritant odour, less smoke, no environmental pollution, strong wetting power and excellent weldability. When the soldering flux is used for welding, a printed package board has less solid residue, clean layout and low ionic contamination, and needs no cleaning after the welding; and the printed package board has high insulation resistance after the welding, which can meet the cleaning-free requirement of the printing package board.
Owner:宁波喜汉锡焊料有限公司
System and method for point-of-use filtration and purification of fluids used in substrate processing
ActiveUS7311847B2Reduce and eliminate particleReduce and eliminate and ionicIon-exchanger regenerationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityFiltration
Owner:AKRION TECH
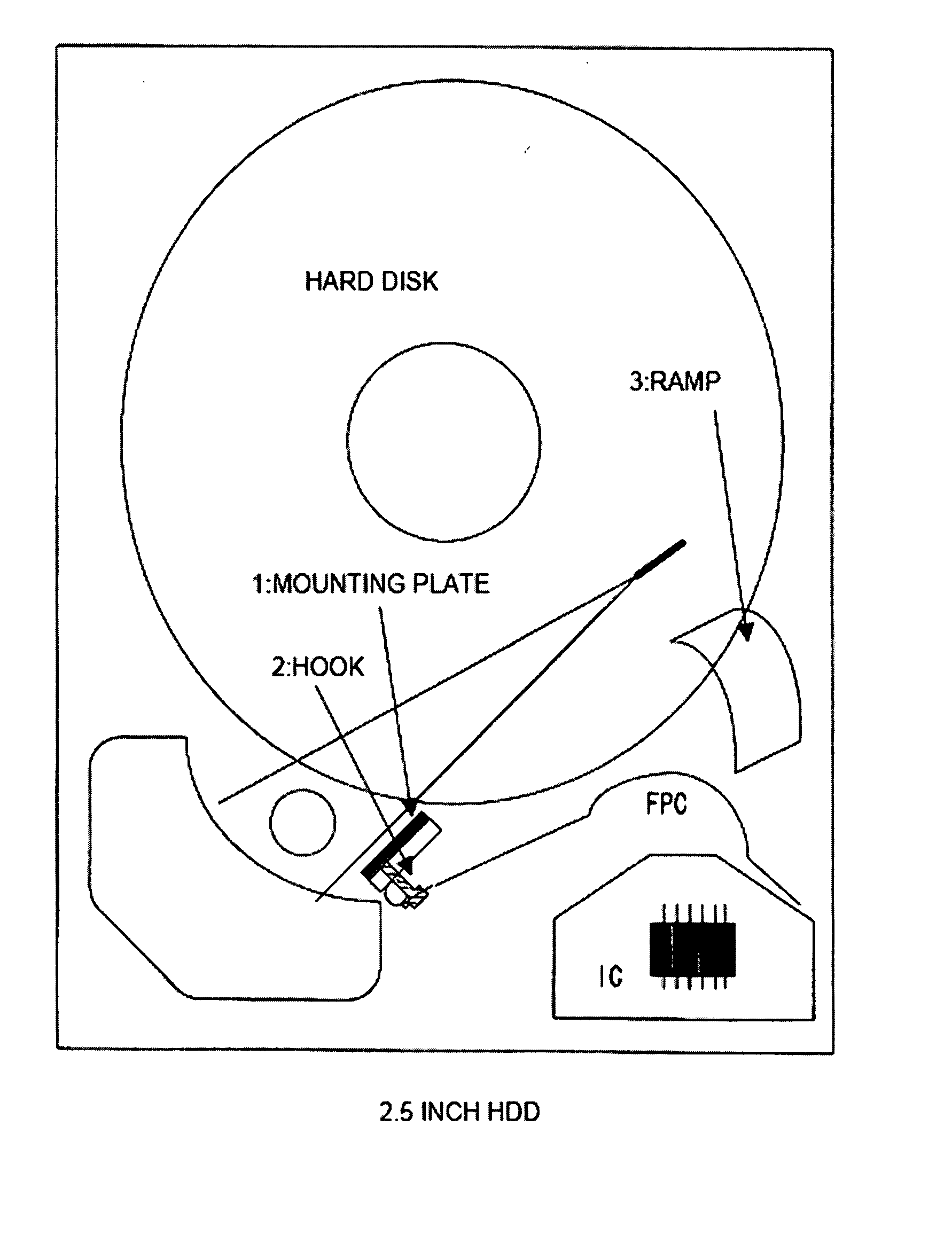
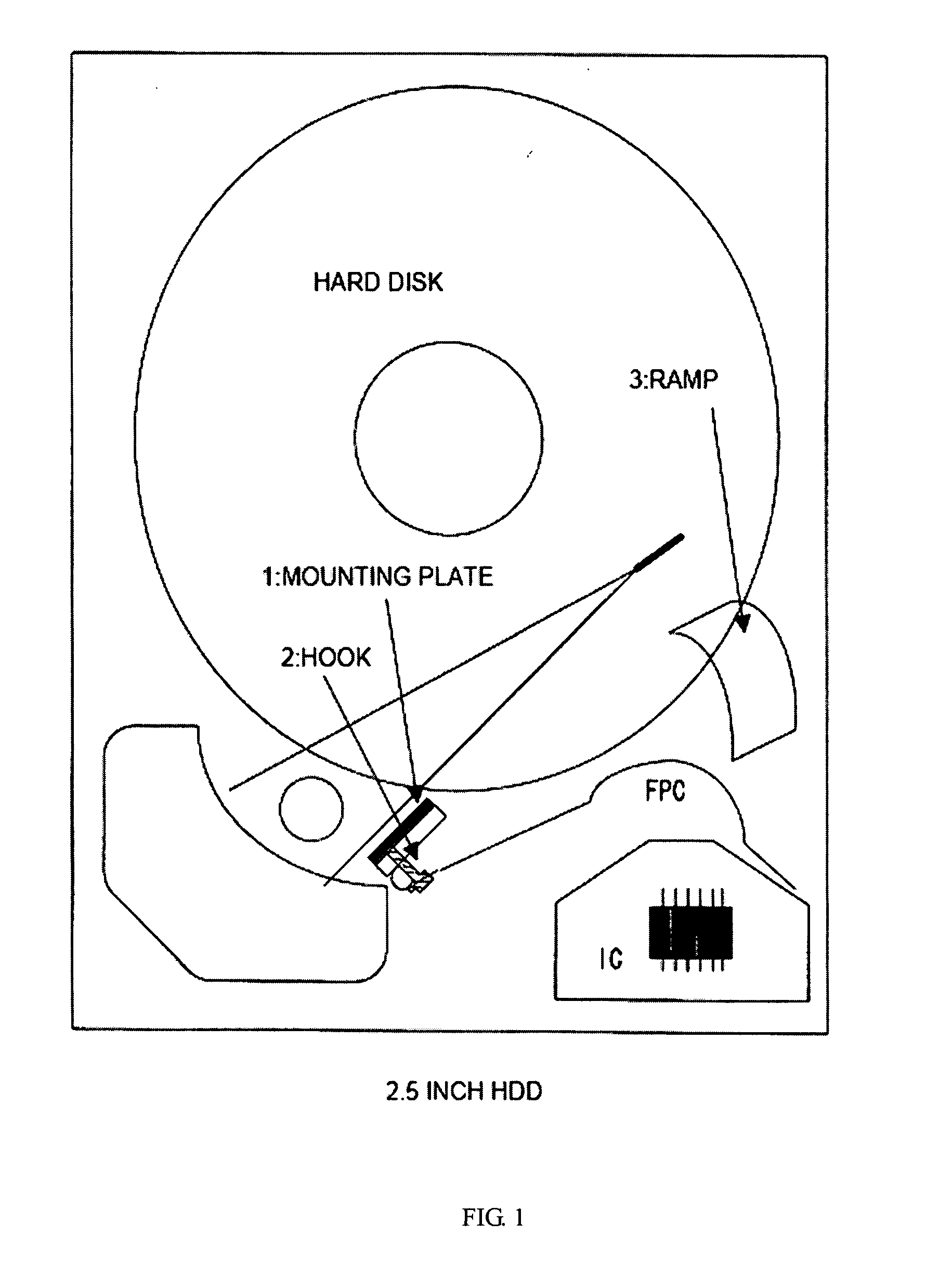
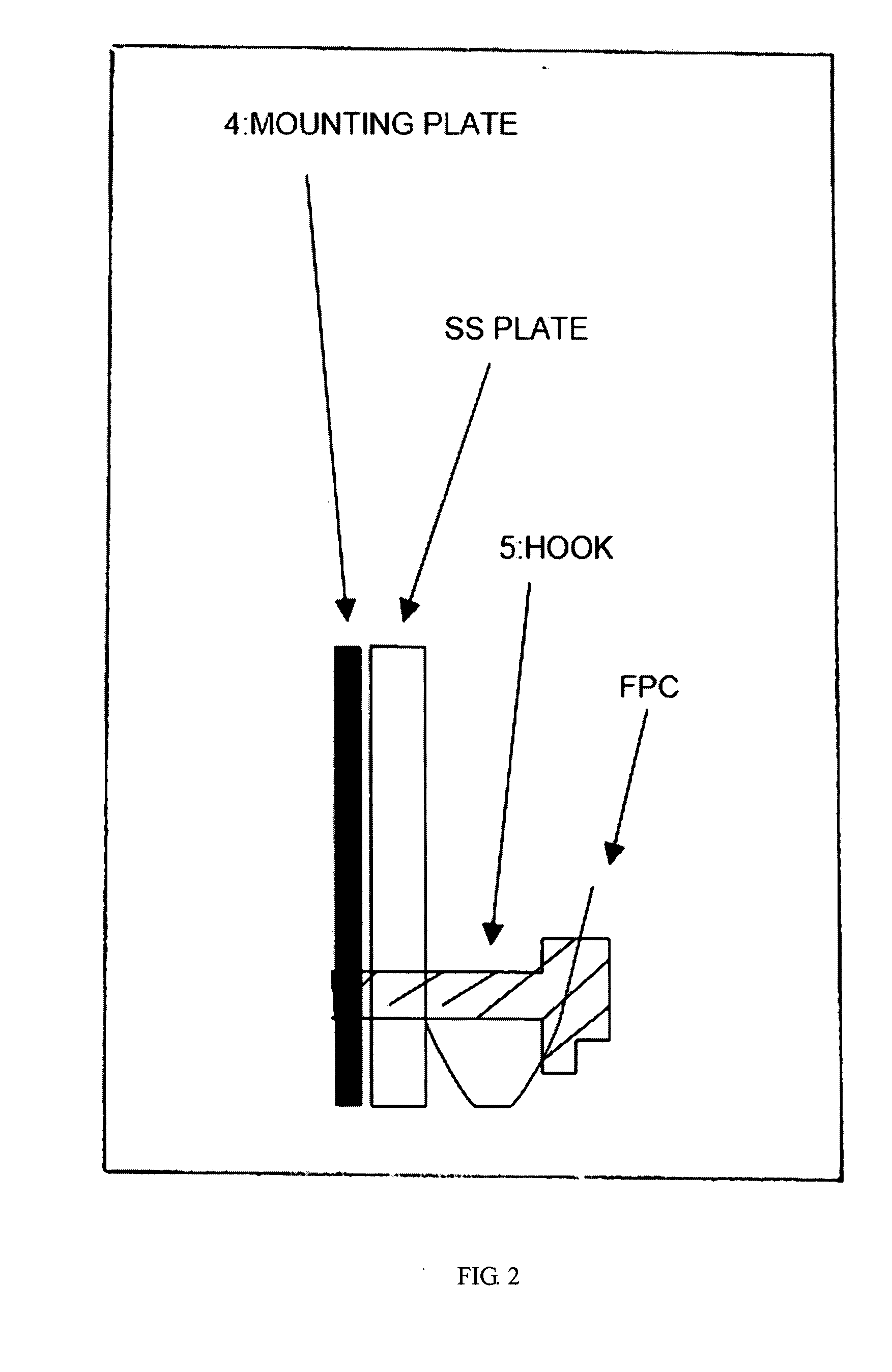
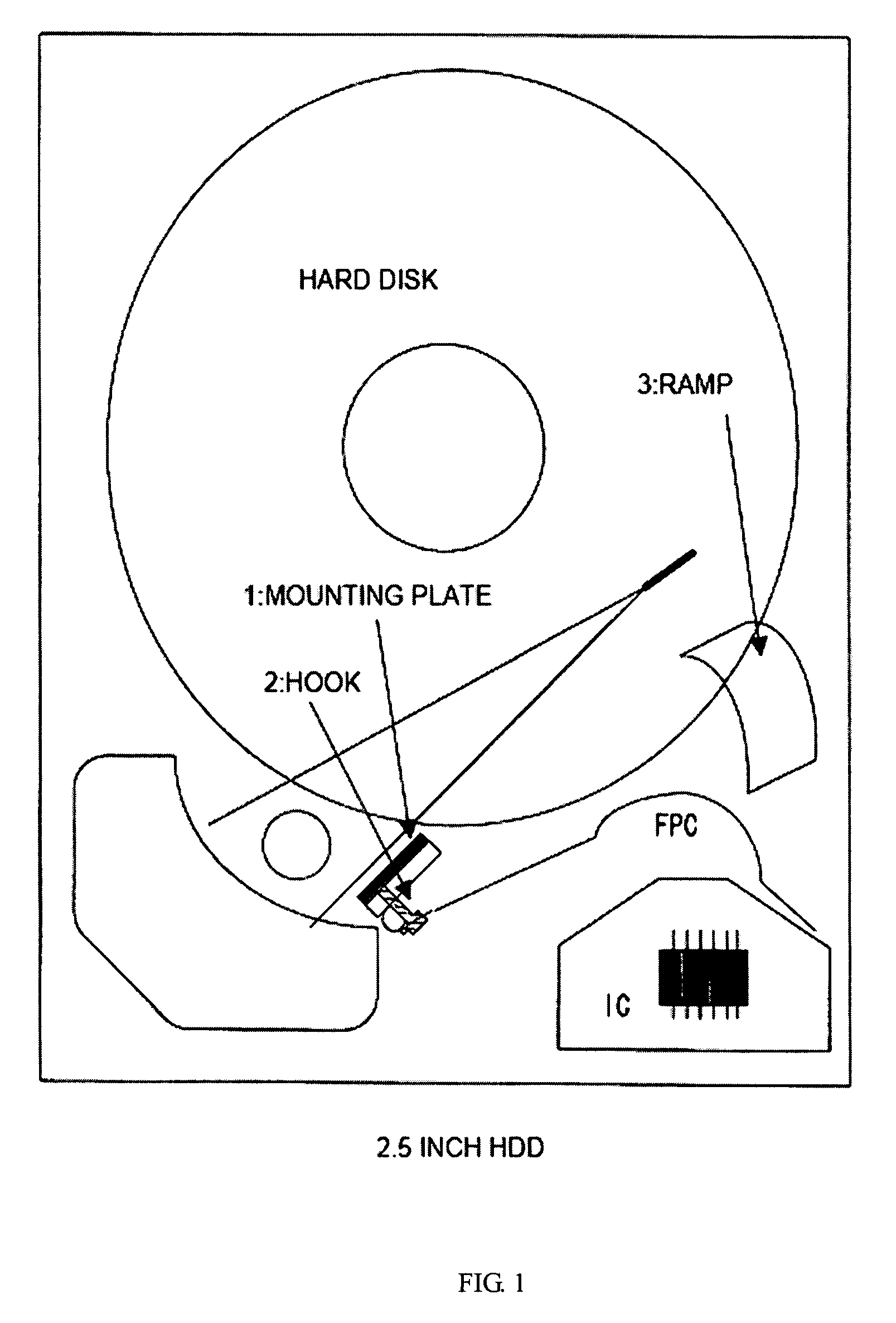
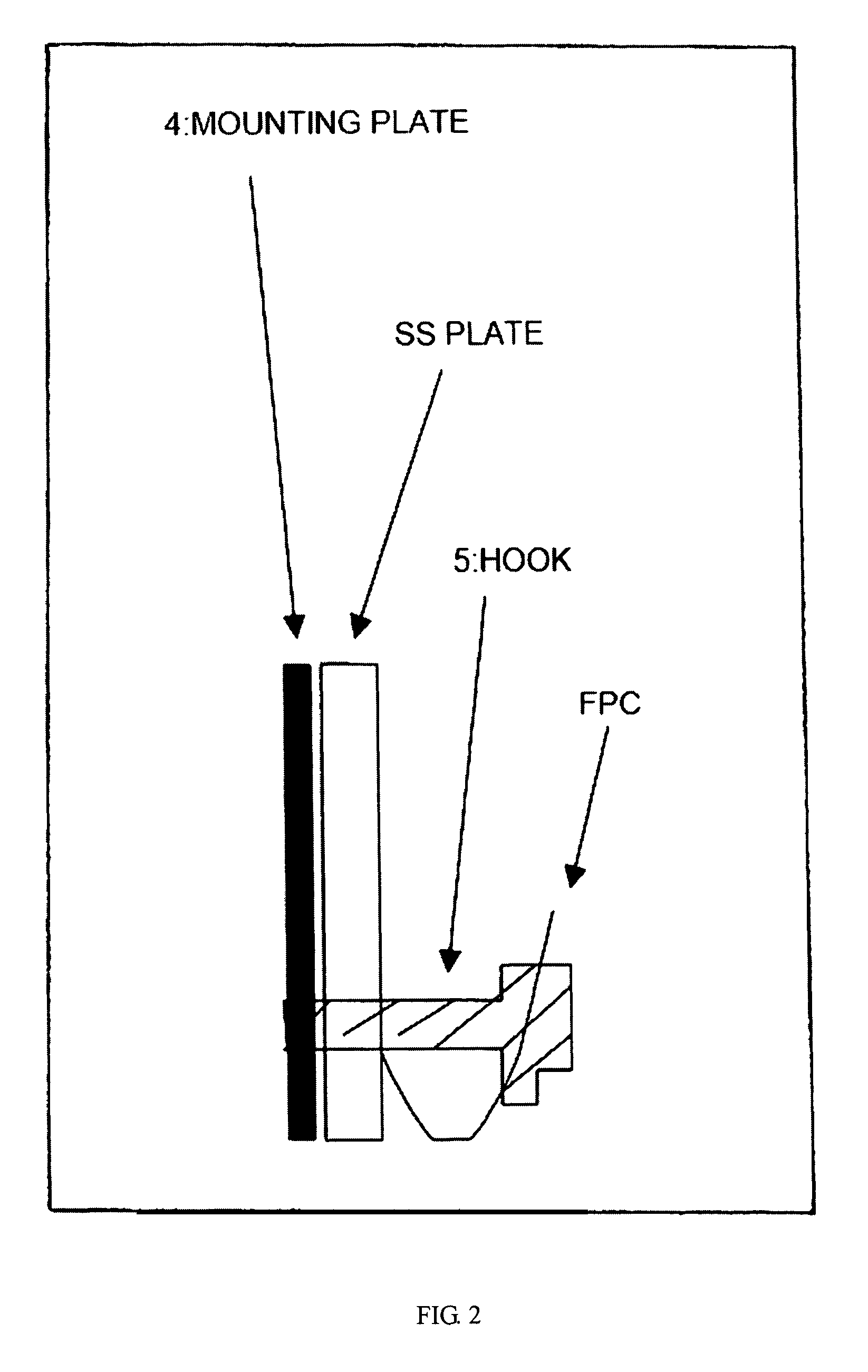
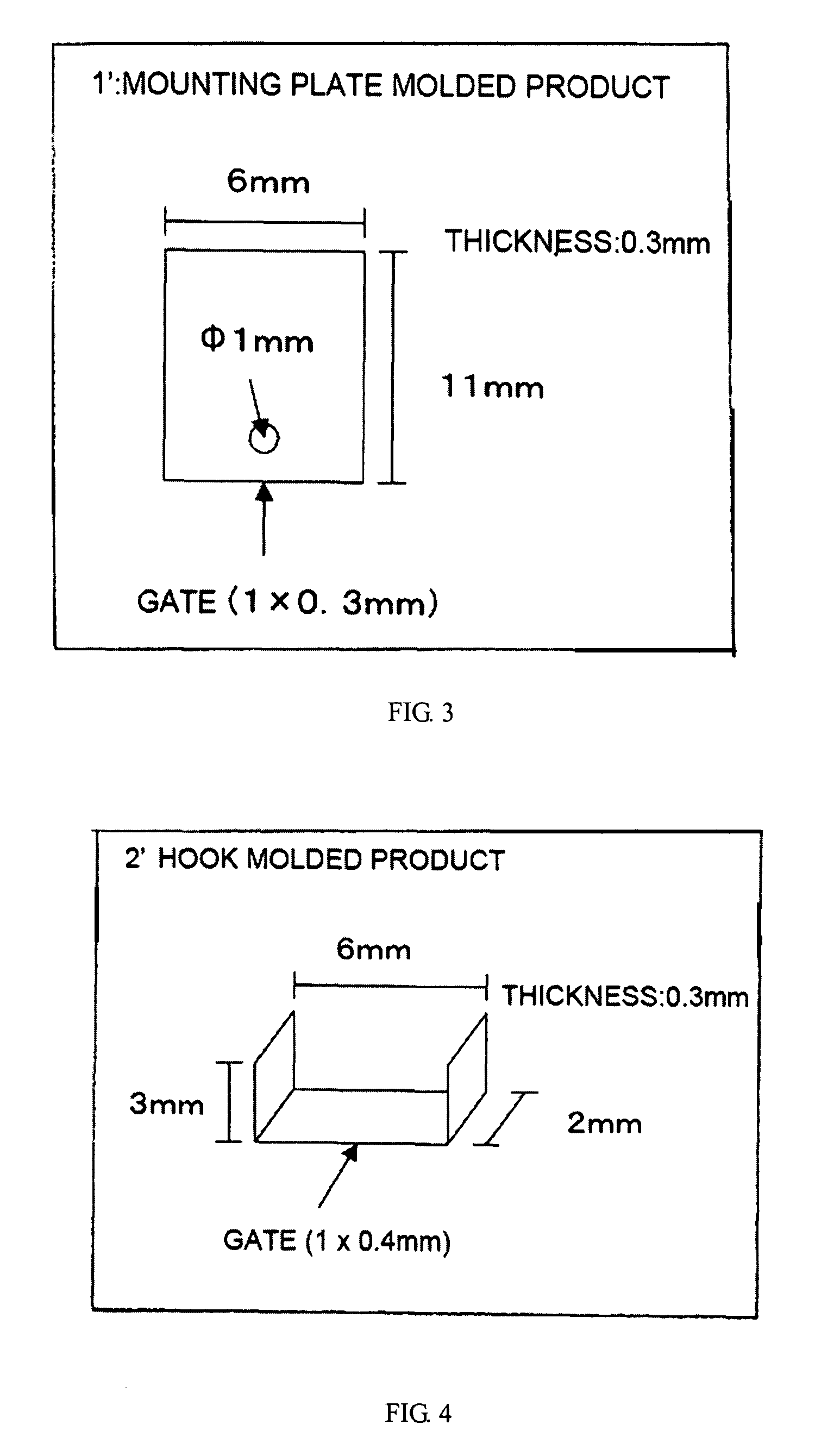
Inner Part Of Hard Disk Drive
ActiveUS20070290391A1Reduce outgassingReduce pollutionLiquid crystal compositionsCarrier constructional parts dispositionHard disc driveHeat resistance
A hard disk drive inner part formed of a resin which exhibits well-balanced low outgassing properties, ultrasonic cleaning resistance, low ionic contamination properties, low particulate contamination properties, repeated removability, heat resistance, specific gravity, and water-absorbing properties. The hard disk drive inner part includes a resin composition which includes a polyphenylene ether resin (A).
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Weakly acidic copper polishing solution applicable to low downforce
InactiveCN104263248AImprove removal rateSolve pollutionPolishing compositions with abrasivesPhysical chemistryHigh surface
The invention relates to a weakly acidic copper polishing solution applicable to low downforce and belongs to the technical field of microelectronics auxiliary materials and ultra-precision machining processes. The polishing solution comprises abrasive particles, an oxidant, deionized water, an inhibitor, a complexing agent and a silica sol stabilizer; and the pH value of the polishing solution is 5-7. By adopting the weakly acidic copper polishing solution, high removal speed and high surface accuracy of copper polishing are achieved under the condition of low downforce (below 1 psi) and the surface of polished copper has less residues of abrasive particles and ionic contamination.
Owner:SHENZHEN LEAGUER MATERIAL +2
Environment-friendly soldering tin material and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN109014652AHigh purityWon't hurtWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaWelding defectAntimony
The invention discloses an environment-friendly soldering tin material and a preparation process thereof. The environment-friendly soldering tin material comprises 95.5%-97.5% of tin, 0.5%-0.9% of copper, 0.06%-0.08% of nickel, 0-0.1% of lead, 0-0.1% of silver, 0-0.1% of bismuth, 0-0.001% zinc, 0-0.1% of antimony, 0-0.03% of arsenic, 0-0.02% of ferrum, 0-0.001% of aluminum, 0-0.002% of cadmium and1%-4% of a soldering flux. The preparation process comprises the first step of pre-treatment of the raw materials. According to the environment-friendly soldering tin material and the preparation process thereof, the soldering tin material prepared from tin, copper, nickel, lead, silver, bismuth, zinc, antimony, arsenic, ferrum, aluminum, cadmium, aluminum, cadmium and the soldering flux is highin purity and environmentally friendly, welding defects can be effectively avoided when the soldering tin material is used, and the welding effect is improved; and meanwhile, the soldering flux is added into the soldering tin material in the preparation process so that ionic contamination can be avoided in use, emission can be conducted without special treatment, and the environmental friendlinessrequirement is met.
Owner:深圳市安臣焊锡制品有限公司
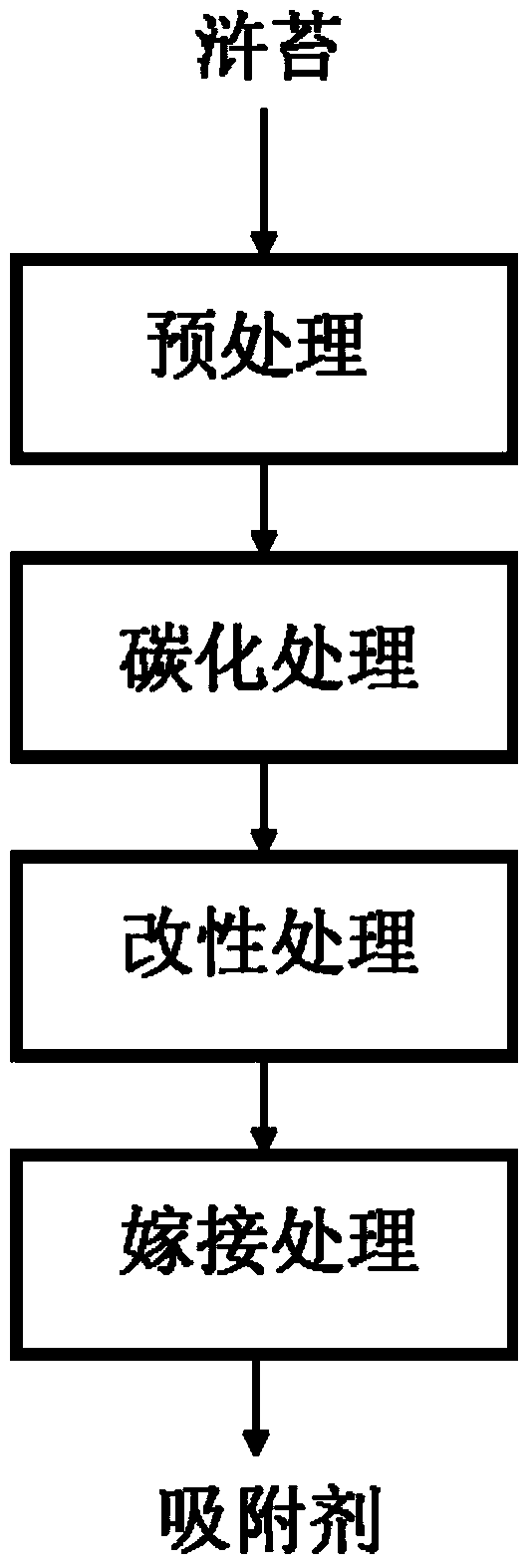
Method for preparing absorbent for preventing and treating water body pollution from enteromorpha
ActiveCN103464120AEasy to handleAvoid secondary pollutionOther chemical processesEnergy based wastewater treatmentMedicineWastewater
The invention discloses a method for preparing an absorbent for preventing and treating water body pollution from enteromorpha. The absorbent for preventing and treating the water body pollution is prepared through pretreatment, carbonization treatment, modification treatment and grafting treatment. Due to adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the enteromorpha in mass propagation can be effectively and rapidly treated, so that the secondary pollution caused by the enteromorpha is avoided. According to the method, the absorbent for absorbing water body pollutants is prepared from the enteromorpha after a series of treatment. As the reaction process is precisely controlled and optimal process parameters are selected, the absorbent prepared by using the method has a good absorption effect, and particularly has a good absorption effect on cation pollutants in wastewater, and the method disclosed by the invention has a beneficial technical effect.
Owner:山东圣克莱尔新能源有限公司
Gold-labeled test strip/card for quickly detecting mercury ions
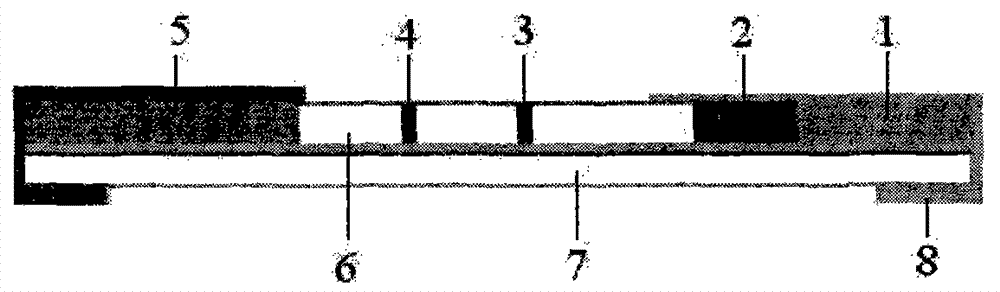
The invention discloses a gold-labeled test strip / card for quickly detecting mercury ions. The gold-labeled test strip / card comprises a bottom support plate layer (1), a sample pad (2), a gold-labeled antibody binding pad (3), a cellulose membrane (4) and an absorbent pad (5). The gold-labeled test strip / card can quickly detect the residual contamination of the mercury ions in environments, soil, water, food, drugs and cosmetics.
Owner:HENAN INST OF SCI & TECH
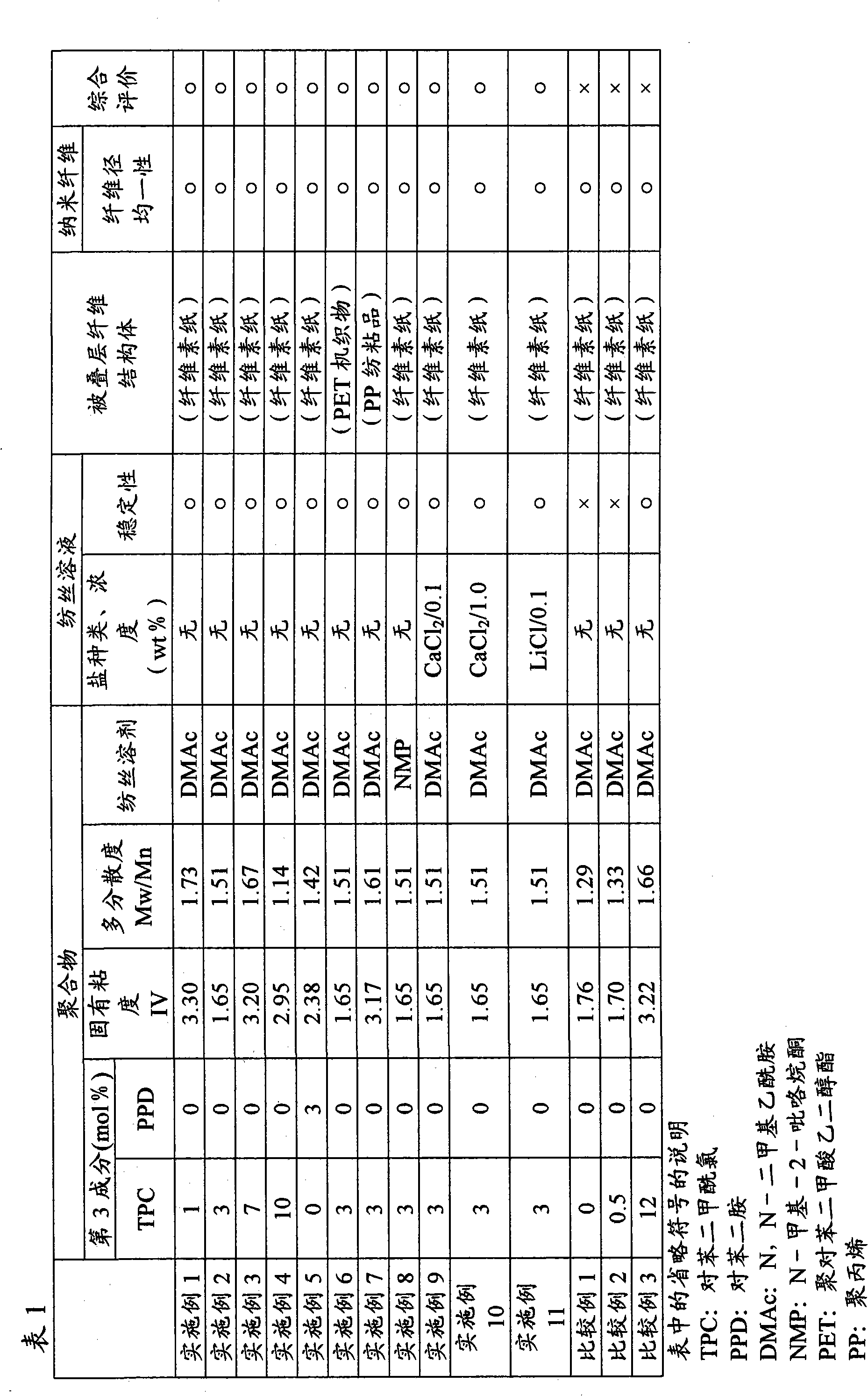
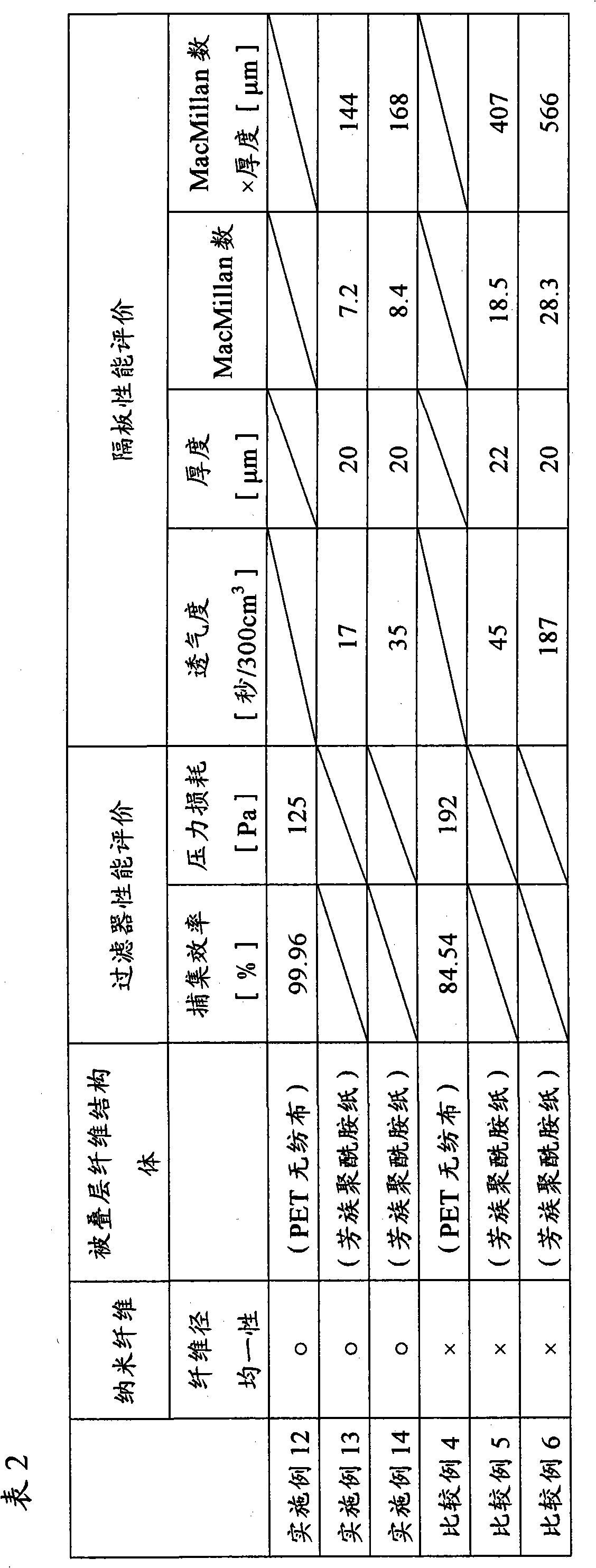
Aromatic polyamide nanofiber and fiber structure containing the same
According to the invention, by preparing a solution of an aromatic copolyamide obtained by copolymerization of a specific third component, a spinning solution is stabilized even without using an alkali metal salt and a uniform aromatic copolyamide nanofiber can be obtained stably by an electrospinning method. Further, according to the invention, a fiber structure obtaining laminating a salt-free aromatic copolyamide nanofiber can be stably formed. Therefore, it can be applied to a product having no preference for ionic contamination of an alkali metal salt or the like, for example, a filter for gas or liquid filtration or an electronic component separator, and is useful in the textile industry.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Aromatic polyamide nanofiber and fiber structure containing the same
ActiveCN101827962AExcellent process stabilityFilament/thread formingMonocomponent copolyamides artificial filamentFiltrationSalt free
According to the invention, by preparing a solution of an aromatic copolyamide obtained by copolymerization of a specific third component, a spinning solution is stabilized even without using an alkali metal salt and a uniform aromatic copolyamide nanofiber can be obtained stably by an electrospinning method. Further, according to the invention, a fiber structure obtaining laminating a salt-free aromatic copolyamide nanofiber can be stably formed. Therefore, it can be applied to a product having no preference for ionic contamination of an alkali metal salt or the like, for example, a filter for gas or liquid filtration or an electronic component separator, and is useful in the textile industry.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
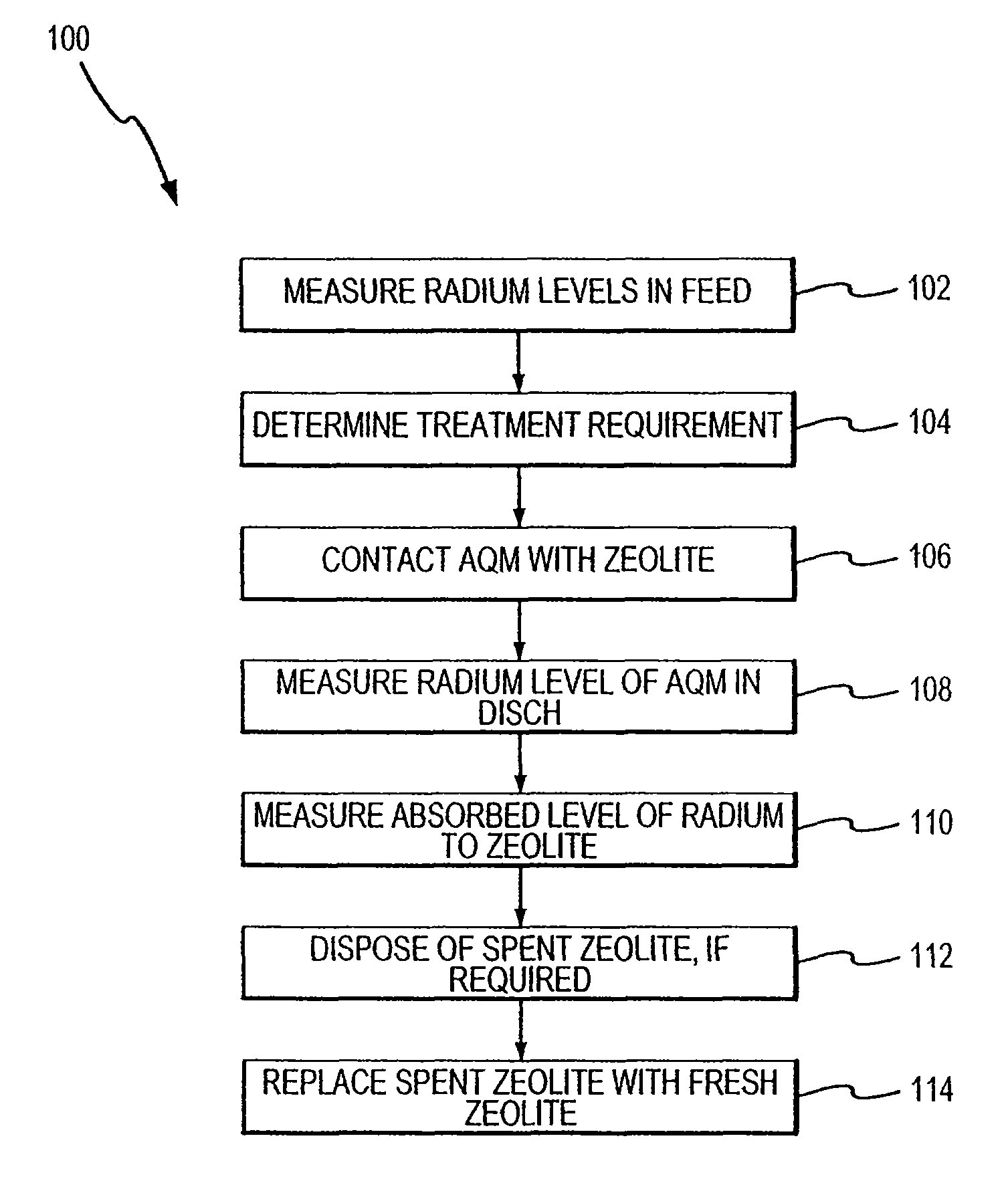
Method for removing cationic contaminants from water using natural zeolite underloaded with transition metal ions to limit leakage of intrinsic arsenic therefrom
ActiveUS8663479B2Large capacityWater treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesWater useArsenic
Owner:WRT INT
Purification process for hydrolysable organic solvent
ActiveUS20190009267A1Organic solvent is avoidedReduce capacityCation exchanger materialsIon-exchange column/bed processesOrganic solventIon exchange
Methods for the removal of ionic contaminants from hydrolysable organic solvent by ion exchange resins are described. A mixed bed of ion exchange resin with cationic ion exchange resin and weak-base anionic ion exchange resin is used in such methods.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Material for purication anion polluted water
InactiveCN1830822AEfficient removalStrong exchange abilityWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeWhite powderIon
A laminar material for cleaning the anion-polluted water by removing the anions (F ions, arsenous radicals, or arsenic radicals) is prepared through proportionally dissolving Mg (or Zn) source and Al source in water, dissolving alkali and anions in water, quickly mixing them, stirring for 48-144 hr, pump filtering, water washing and baking to obtain white powder.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
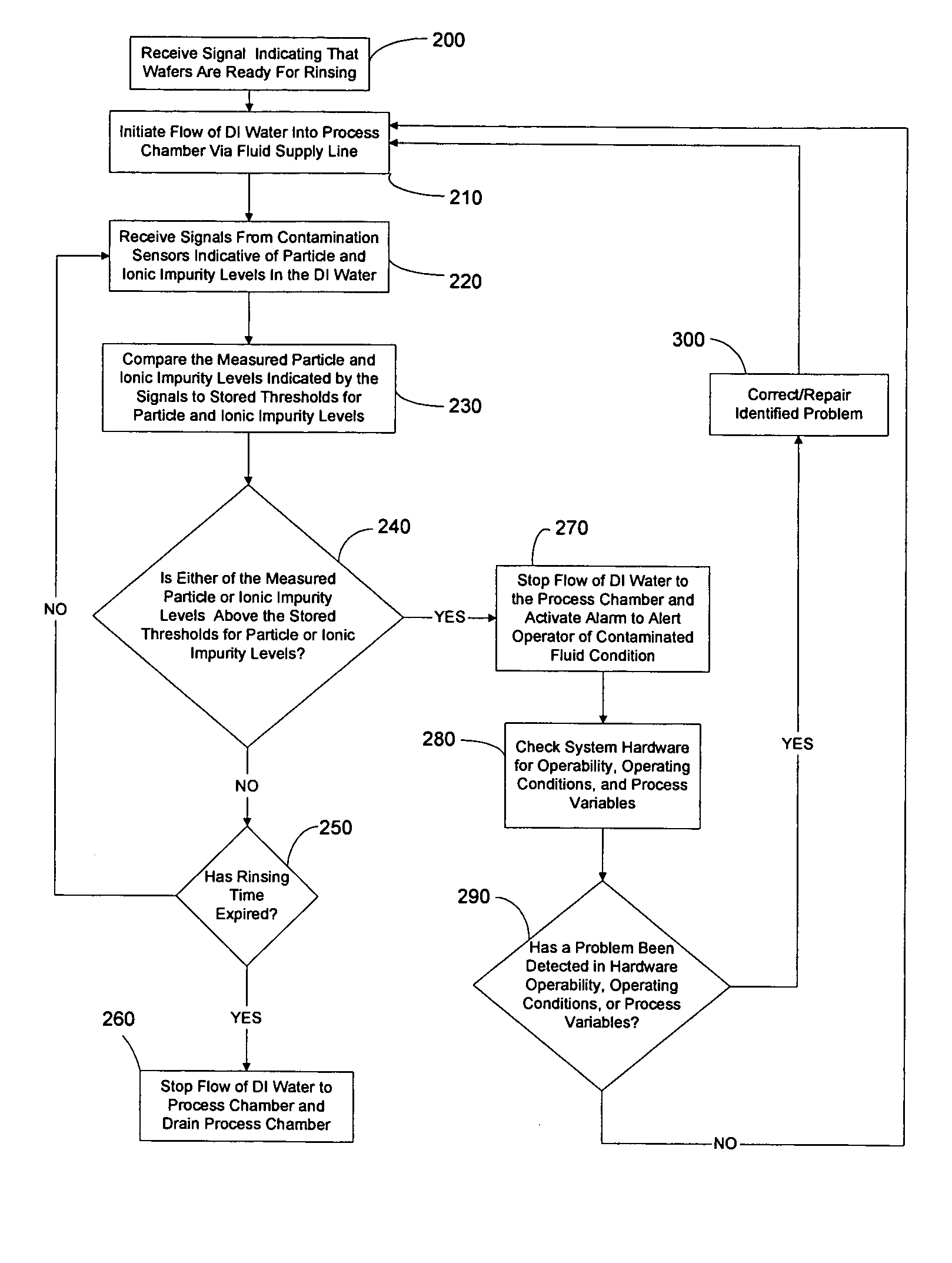
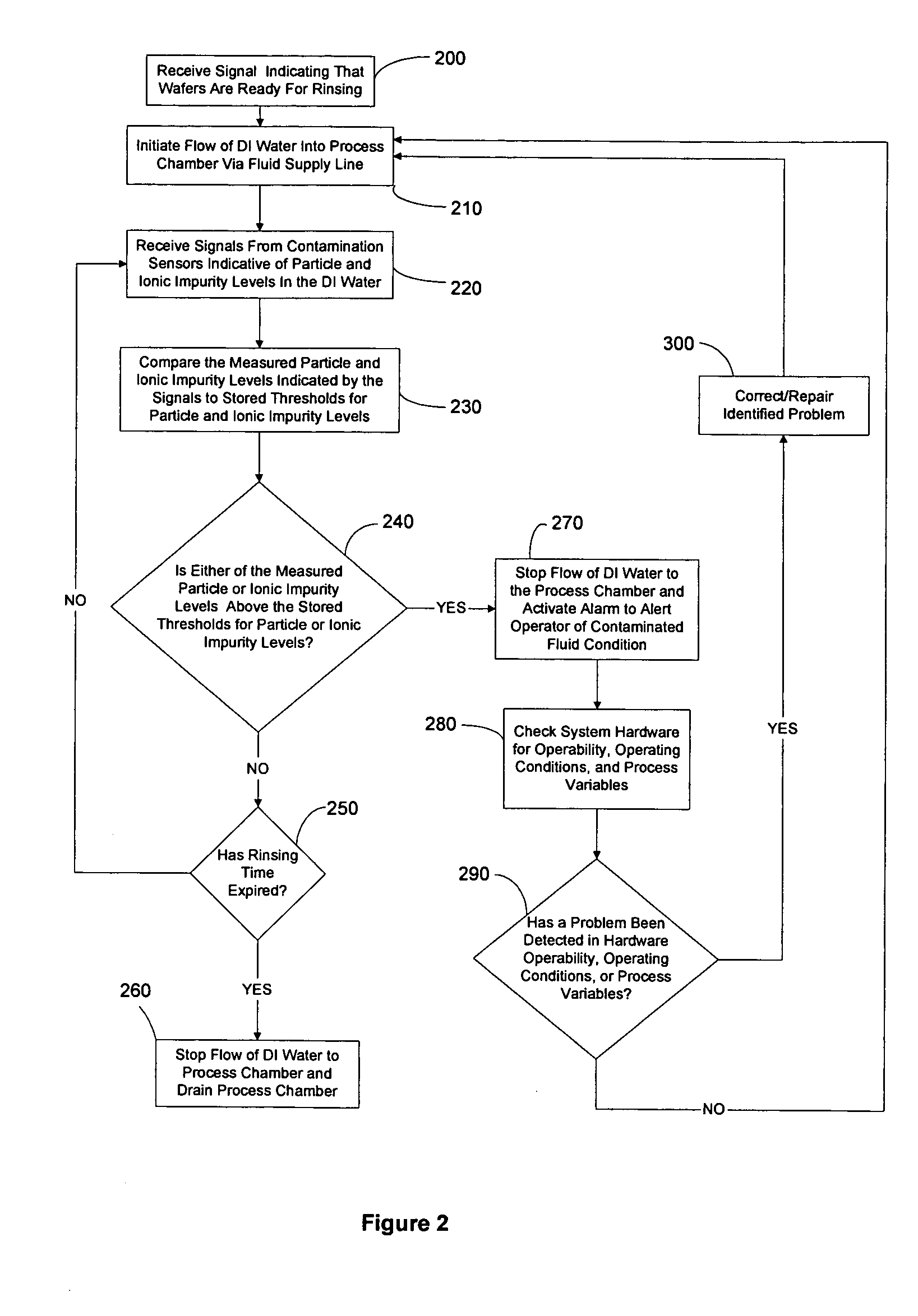
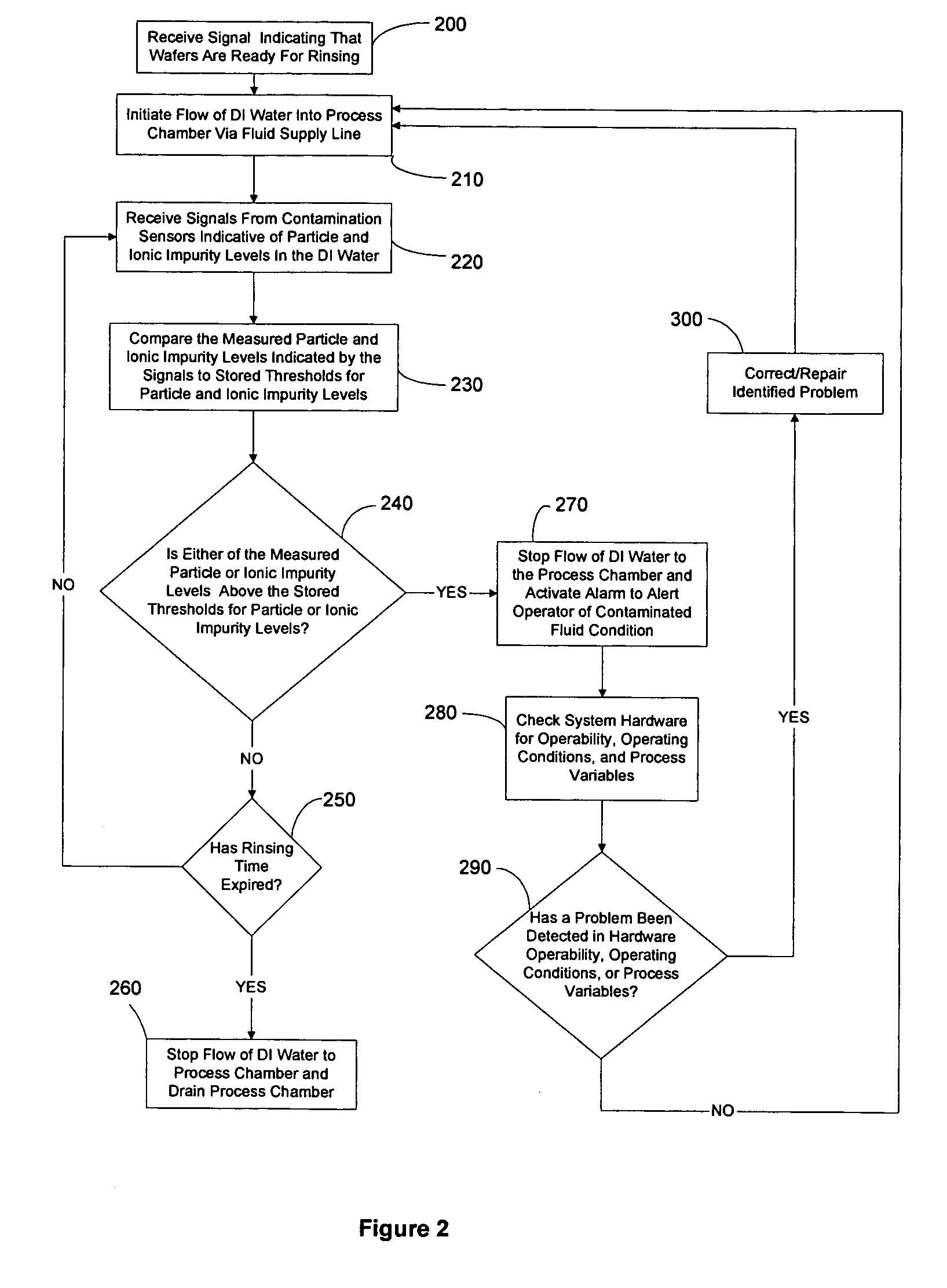
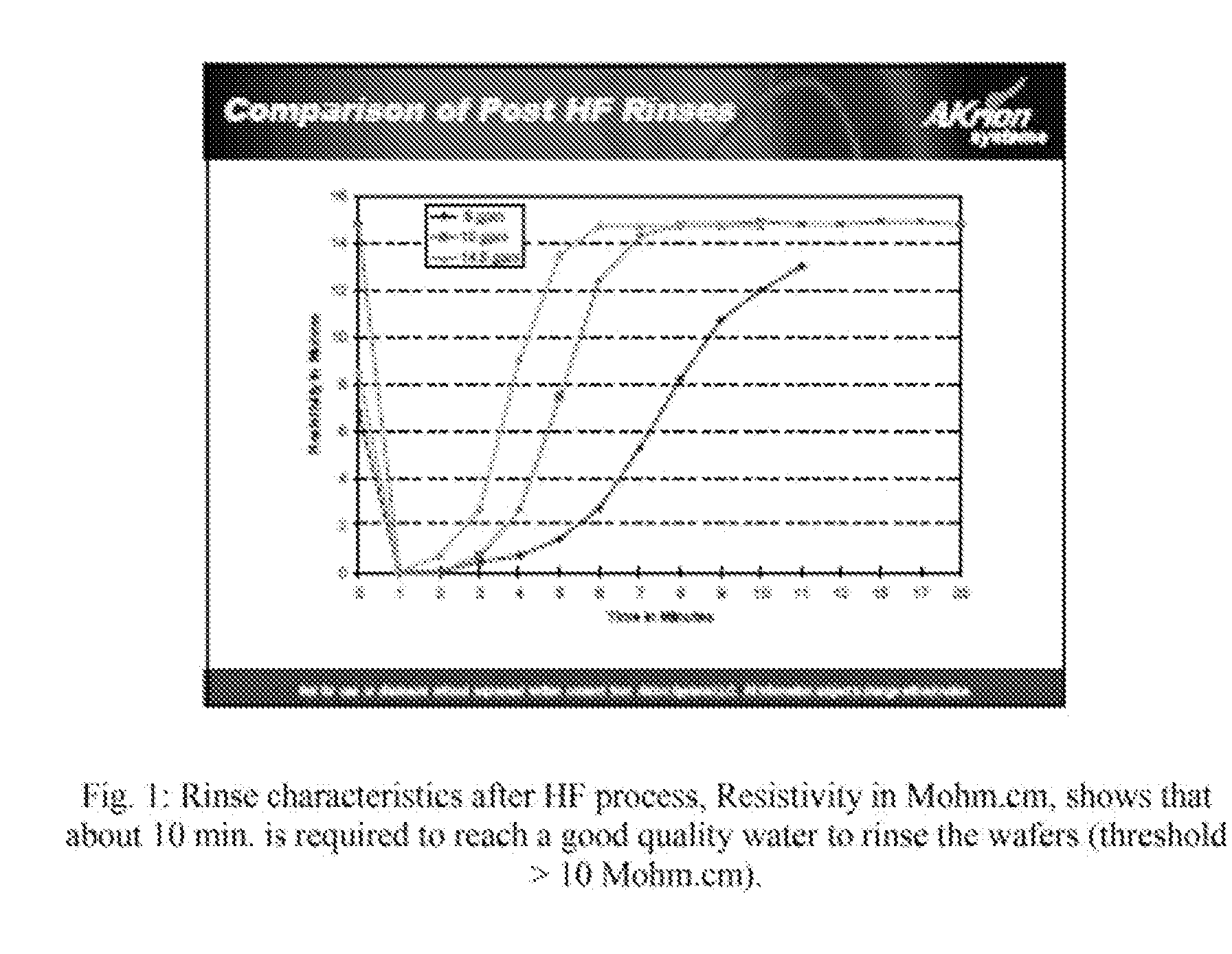
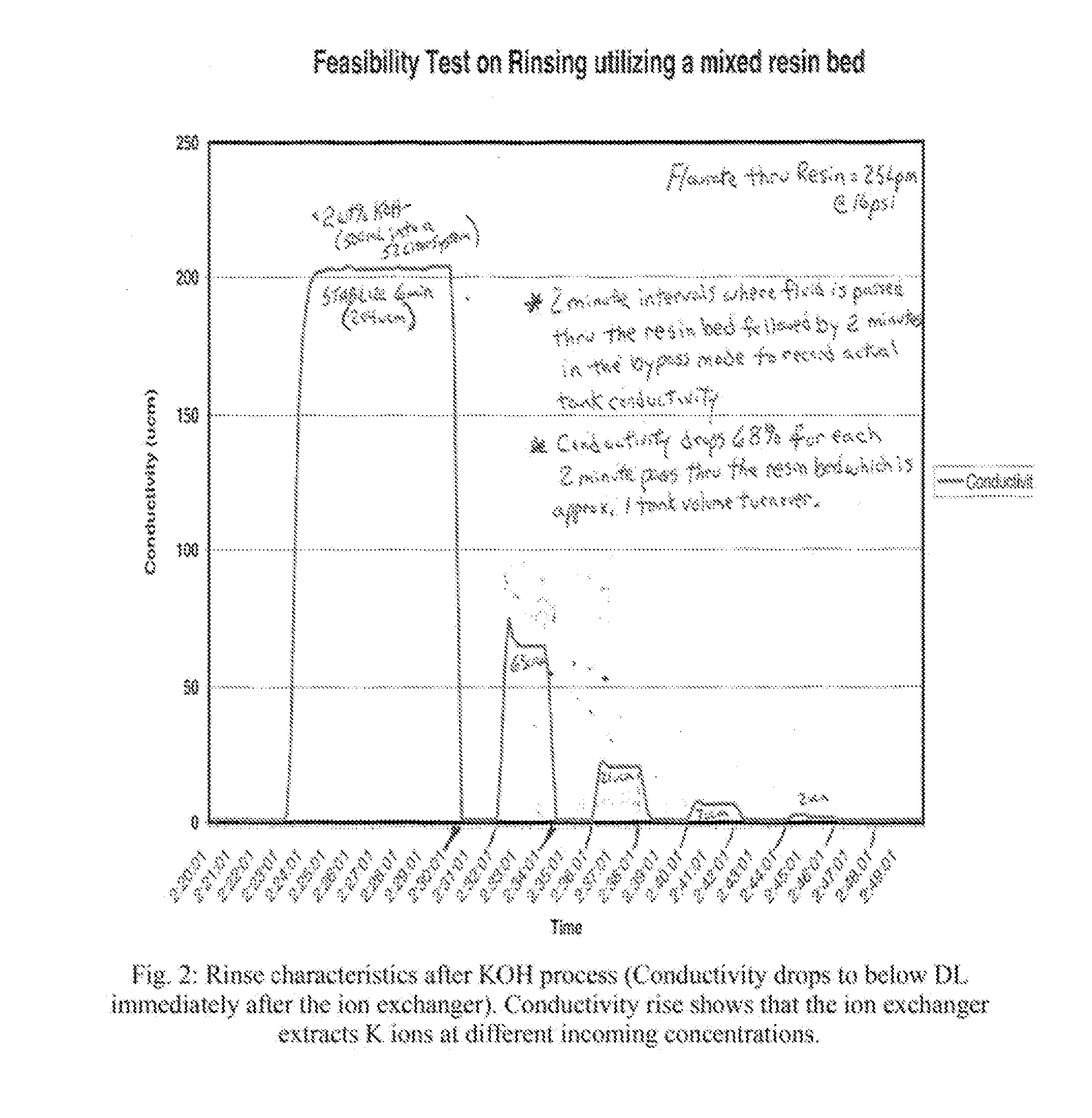
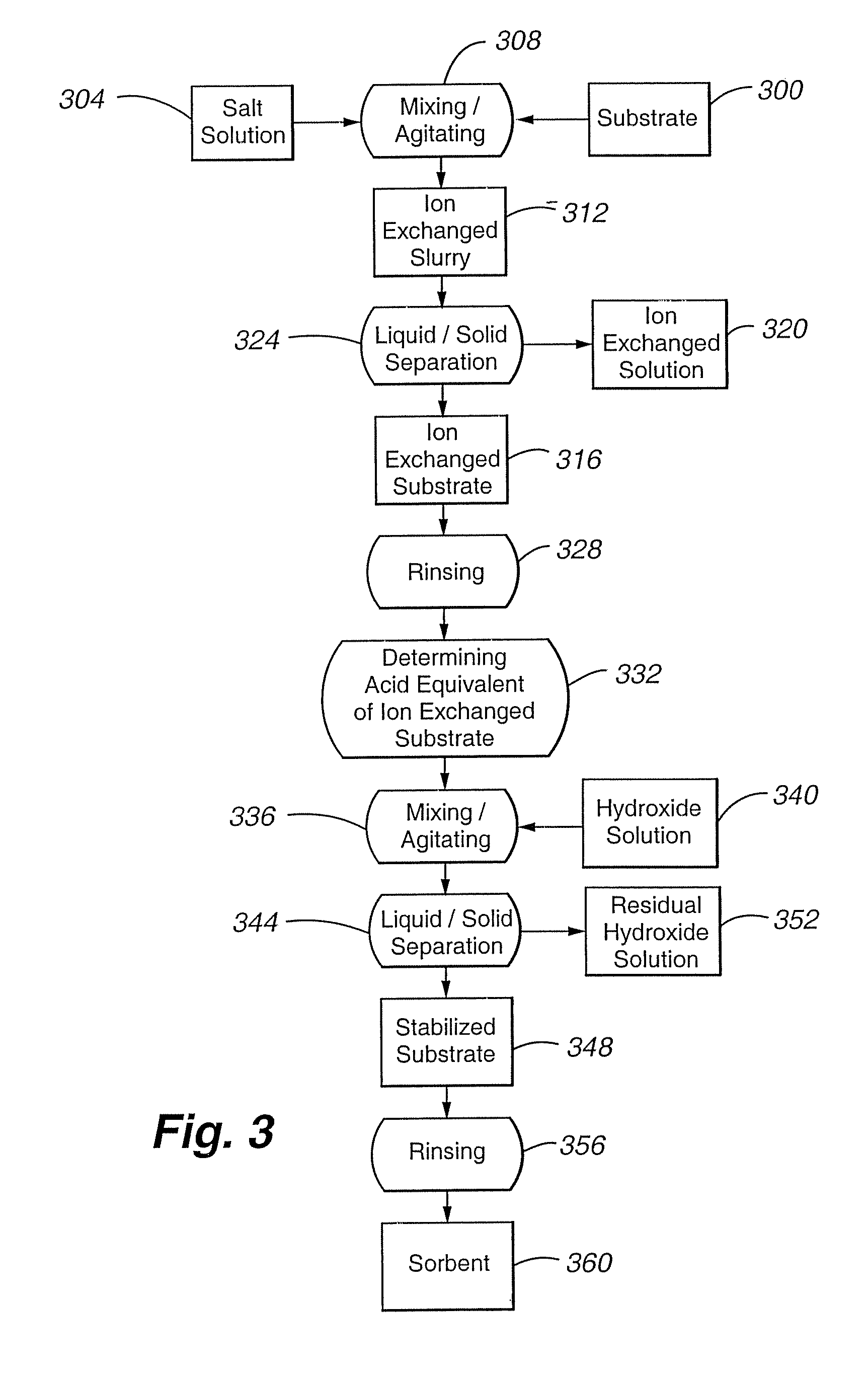
Reduced consumptions stand alone rinse tool having self-contained closed-loop fluid circuit, and method of rinsing substrates using the same
InactiveUS20140305471A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsEnvironmental engineeringIonic contamination
A system and method for rinsing substrates. In one embodiment, method comprises: a) providing a fixed volume of a rinse fluid in a rinse tool comprising a closed-loop fluid-circuit comprising a rinse tank, a deionizer, a pump, and a recirculation line fluidly coupled to an outlet of the rinse tank and an inlet of the rinse tank; and b) performing a plurality of rinse cycles in the rinse tool, each of the plurality of rinse cycles including: b-1) positioning a batch of substrates in the rinse tank; b-2) circulating the fixed volume of the rinse fluid through the fluid circuit for a rinse time, wherein during said circulation the rinse fluid contacts the batch of substrates, thereby becoming ionically contaminated rinse fluid, the deionizer removing ionic impurities from the ionically contaminated rinse fluid to produce deionized rinse fluid; and b-3) removing the batch of substrates from the rinse tank.
Owner:NAURA AKRION INC
High capacity regenerable sorbent for removal of arsenic and other toxic ions from drinking water
InactiveUS20060293170A1Improved and cost-effective controlPrevent qualitySolid sorbent liquid separationWaterSorbentMontmorillonite
The present invention is directed to a sorbent comprising a disordered polyvalent metal oxide on the surface of an inert substrate. The substrate can be a layered silicate, such as vermiculite, an aluminosilicate such as montmorillonite, or a nonlayered silicate such as a zeolite. The sorbent removes ionic contaminants, such as arsenic, from process streams.
Owner:ADA TECH
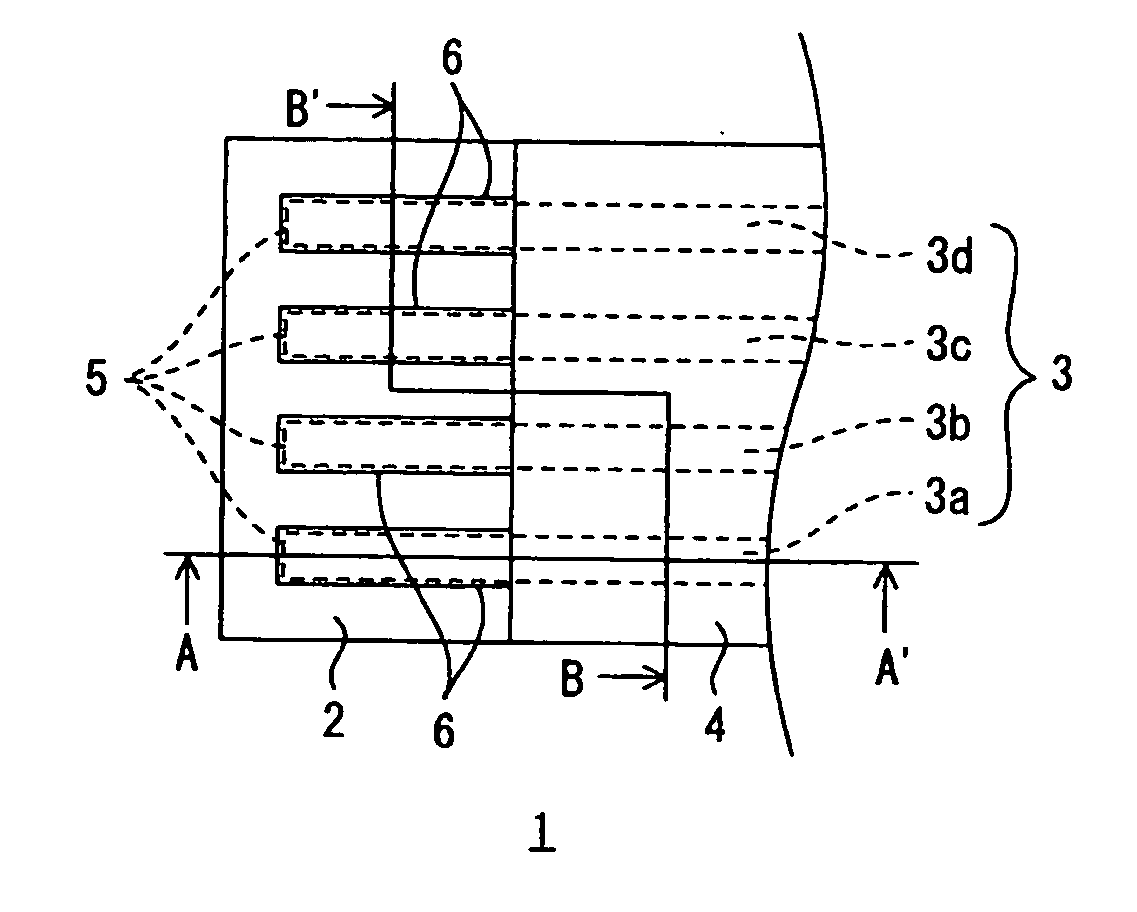
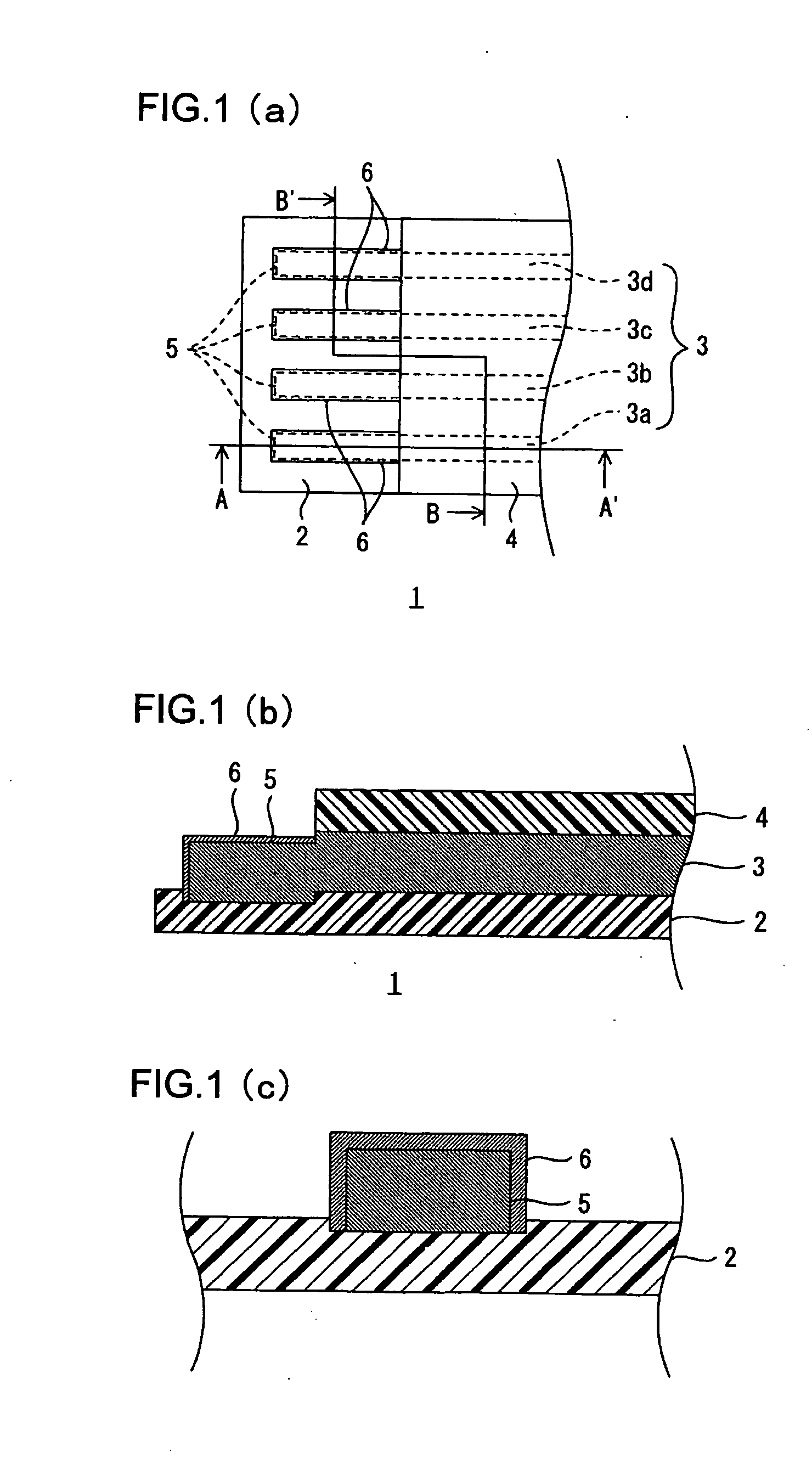
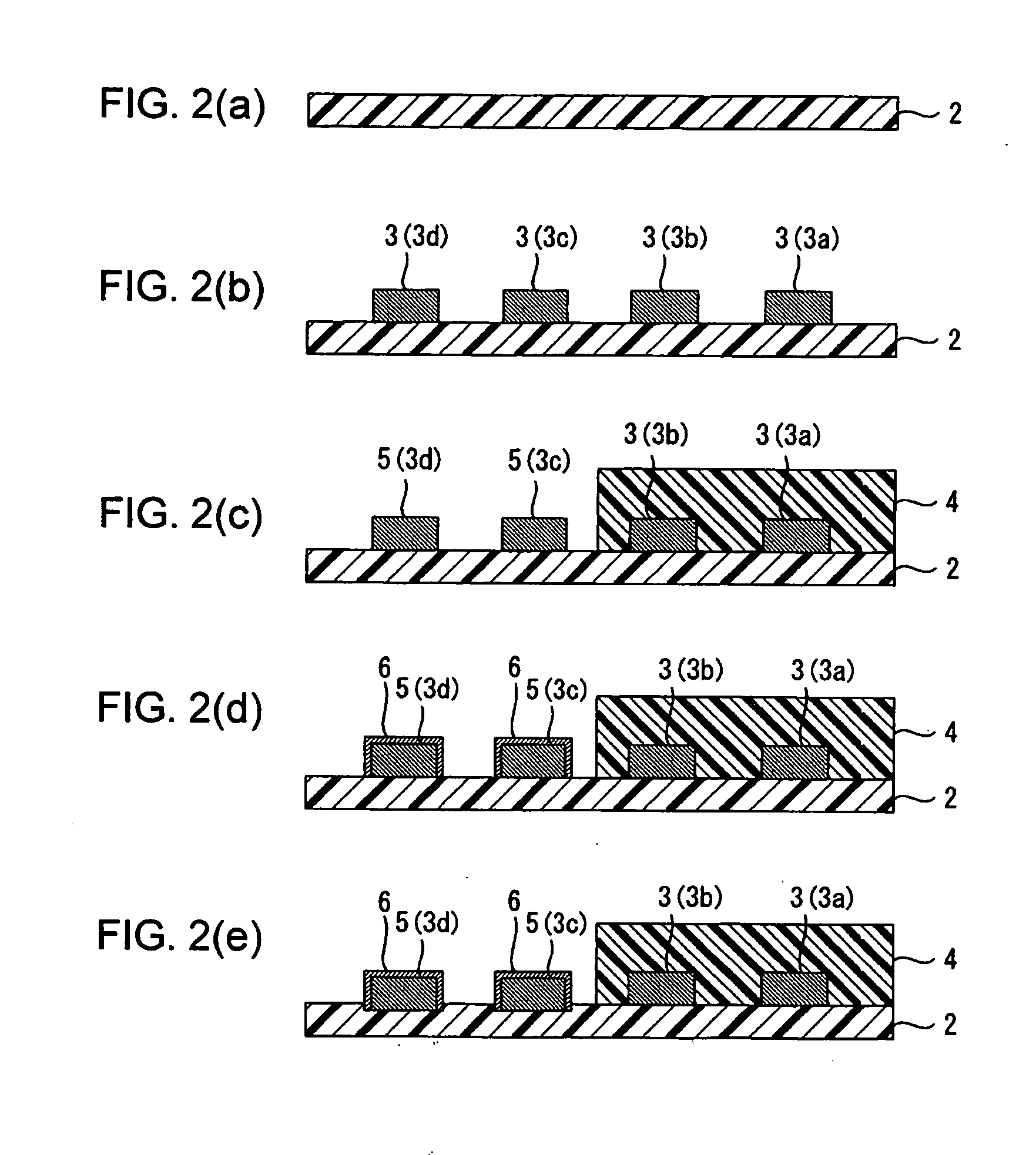
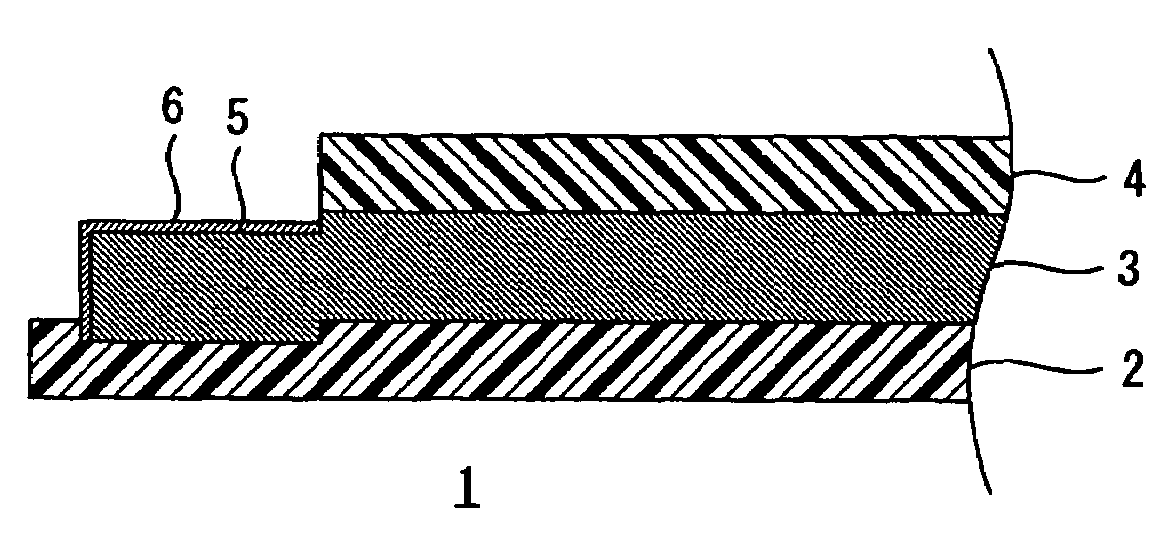
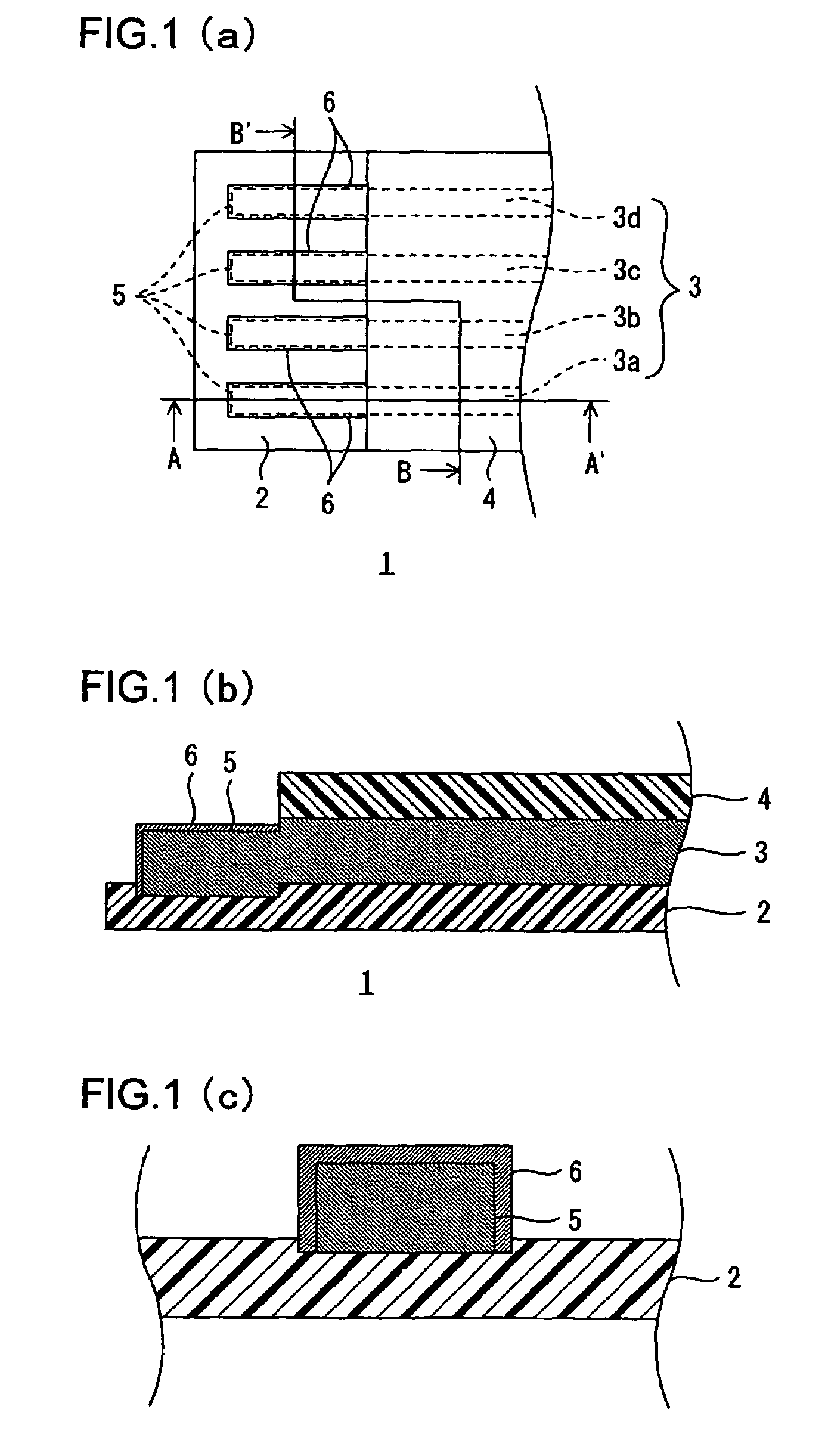
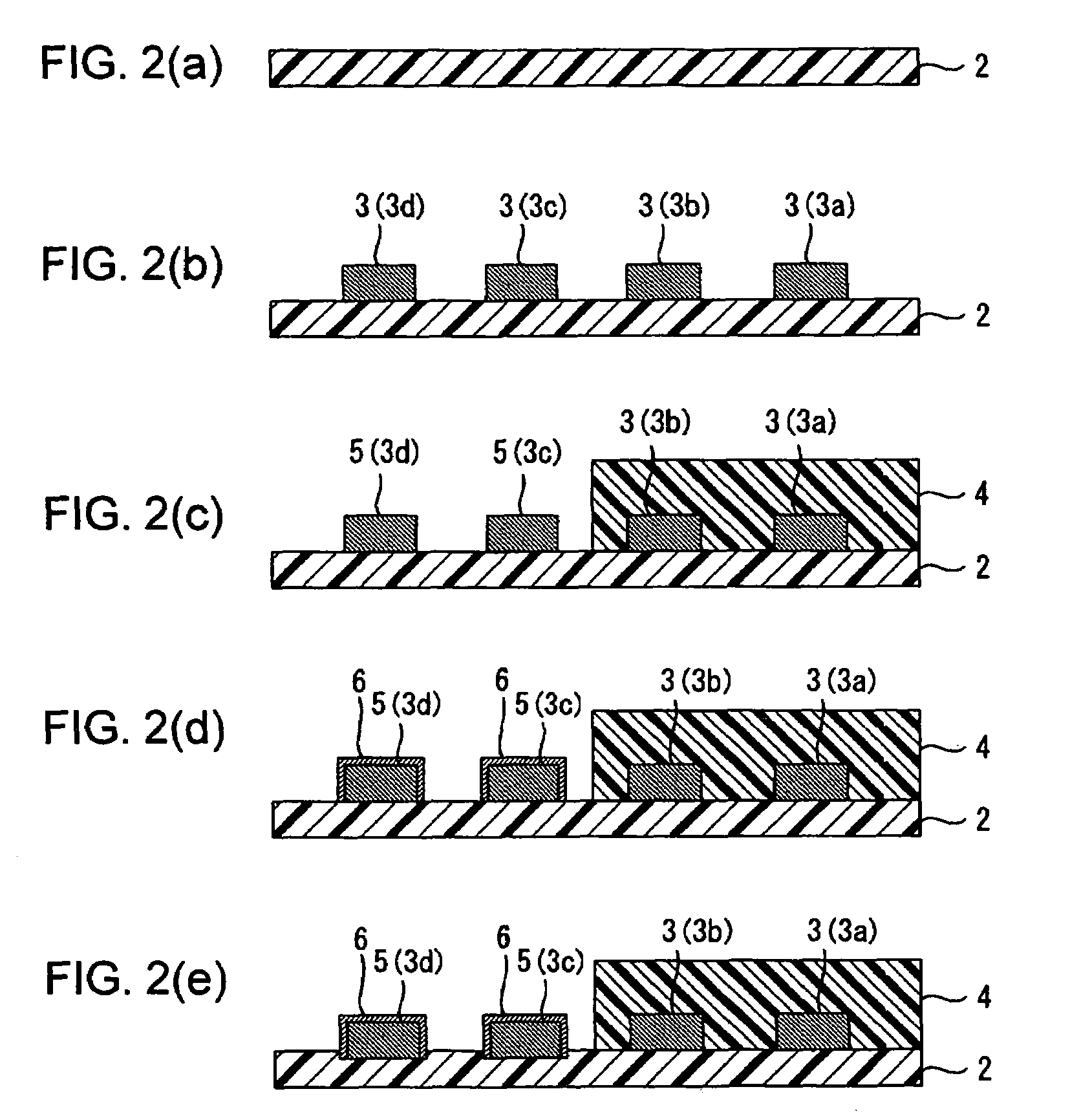
Wired circuit board
InactiveUS20060042823A1Improve adhesionAvoid residuePrinted circuit aspectsComponent plug-in assemblagesHigh humidityEngineering
A wired circuit board which even when a conductive pattern is formed in the form of fine pitch can provide improved adhesion between the conductive pattern and an insulating layer to prevent a plating solution from remaining between a metal plating layer and the insulating layer, so as to prevent ionic impurities in the plating solution from remaining as residual or ionic contamination, whereby even when electric current flows through the circuit under a high temperature and high humidity environment over a long term, a short circuit from ionic migration can be prevented to suppress insulating failure. Lower end portions of terminal portions 5 formed on an insulating base layer 2 and lower end portions of side surfaces and metal plating layers 6 covering over the terminal portions 5 are embedded in the insulating base layer 2 in a flexible wired circuit board 1 at one longitudinal end portion thereof exposed from an insulating cover layer 4. This can provide the result of preventing infiltration of the plating solution in between the metal plating layers 6 and the insulating base layer 2 when the metal plating layer 6 is formed.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Aqueous solution and method for removing ionic contaminants from the surface of a workpiece
ActiveCN101253258AReduce pollution valueLess quantityPrinted circuit aspectsDetergent mixture composition preparationResistAlcohol
To reduce ionic contaminants on printed circuit boards that are at least partially covered with a solder resist mask and are provided with top layers on the copper structures, an aqueous cleaning solution is used, which contains at least one ethanolamine compound and / or the salt thereof, at least one alcoholic solvent and, at need, at least one guanidine compound and / or the salt thereof.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Wired circuit board
InactiveUS7355128B2Improve adhesionAvoid residuePrinted circuit aspectsComponent plug-in assemblagesHigh humidityIonic contamination
A wired circuit board having improved adhesion between the conductive pattern and an insulating layer to prevent a plating solution from remaining between a metal plating layer and the insulating layer. The invention prevents ionic impurities in the plating solution from remaining as residual or ionic contamination, thereby preventing a short circuit from developing when electric current flows through the circuit under a high temperature and high humidity environment. Lower end portions of the terminal portions that are formed on an insulating base layer and lower end portions of side surfaces and metal plating layers that cover the terminal portions are embedded in the insulating base layer in a flexible wired circuit board.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Non-halogen cleaning-free soldering flux
InactiveCN101690997BNo pollutionHigh insulation resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSolventTin
The invention provides a non-halogen cleaning-free soldering flux, which comprises the following compositions in percentage by weight: 0.5 to 5 percent of stannous oxalate, 0.5 to 20 percent of organic acid activator, 0.1 to 1 percent of surfactant, 0 to 3 percent of cosolvent, and the balance of solvent. Because of adopting the stannous oxalate as an activator, and having synergistic action withthe organic acid activator and no halogen, the soldering flux has the advantages of no irritant odour, less smoke, no environmental pollution, strong wetting power and excellent weldability. When thesoldering flux is used for welding, a printed package board has less solid residue, clean layout and low ionic contamination, and needs no cleaning after the welding; and the printed package board has high insulation resistance after the welding, which can meet the cleaning-free requirement of the printing package board.
Owner:宁波喜汉锡焊料有限公司
A Weak Acid Copper Polishing Fluid for Low Downforce
InactiveCN104263248BImprove removal rateSolve pollutionPolishing compositions with abrasivesLiquid copperPhysical chemistry
Owner:SHENZHEN LEAGUER MATERIAL +2
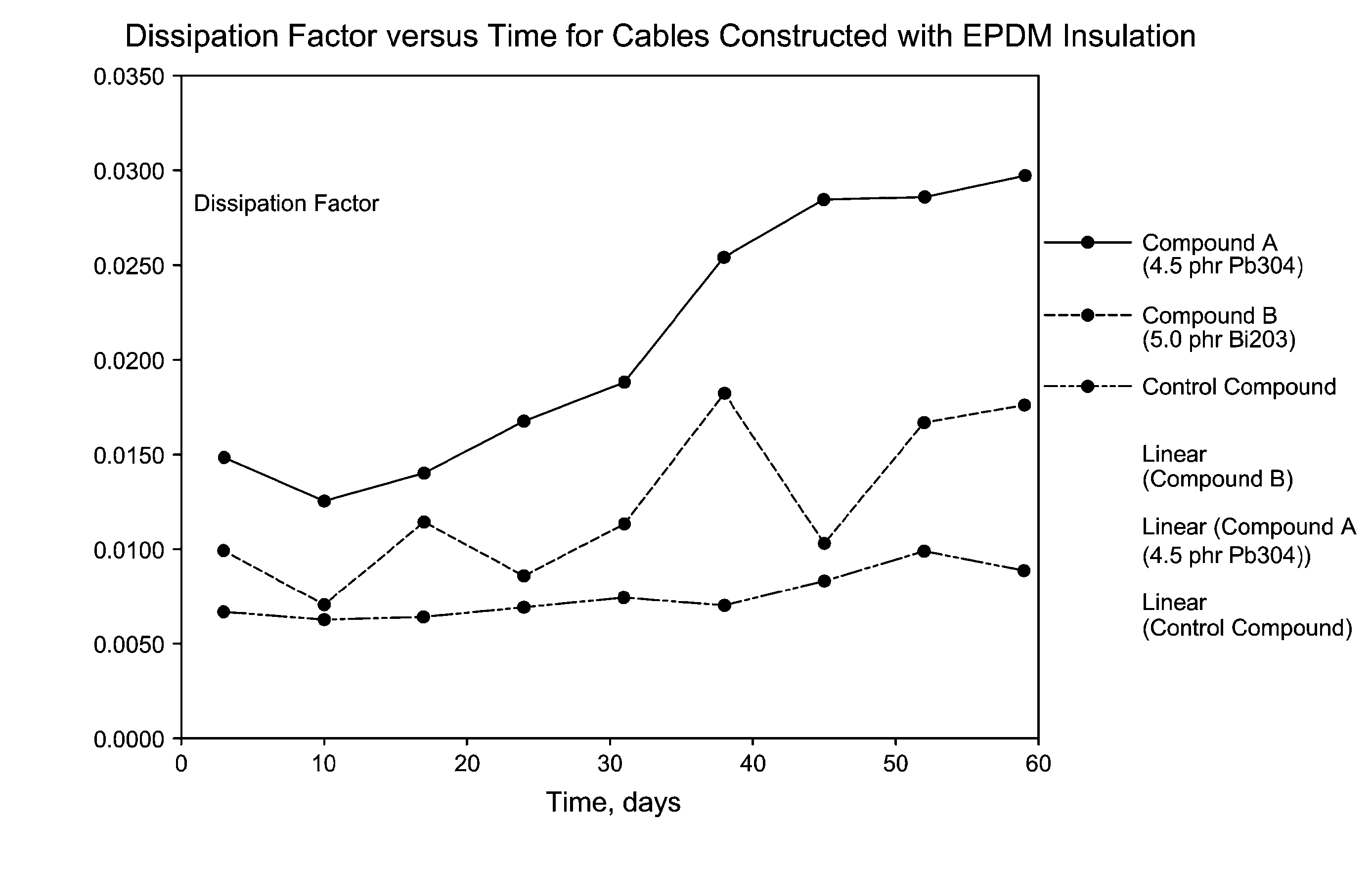
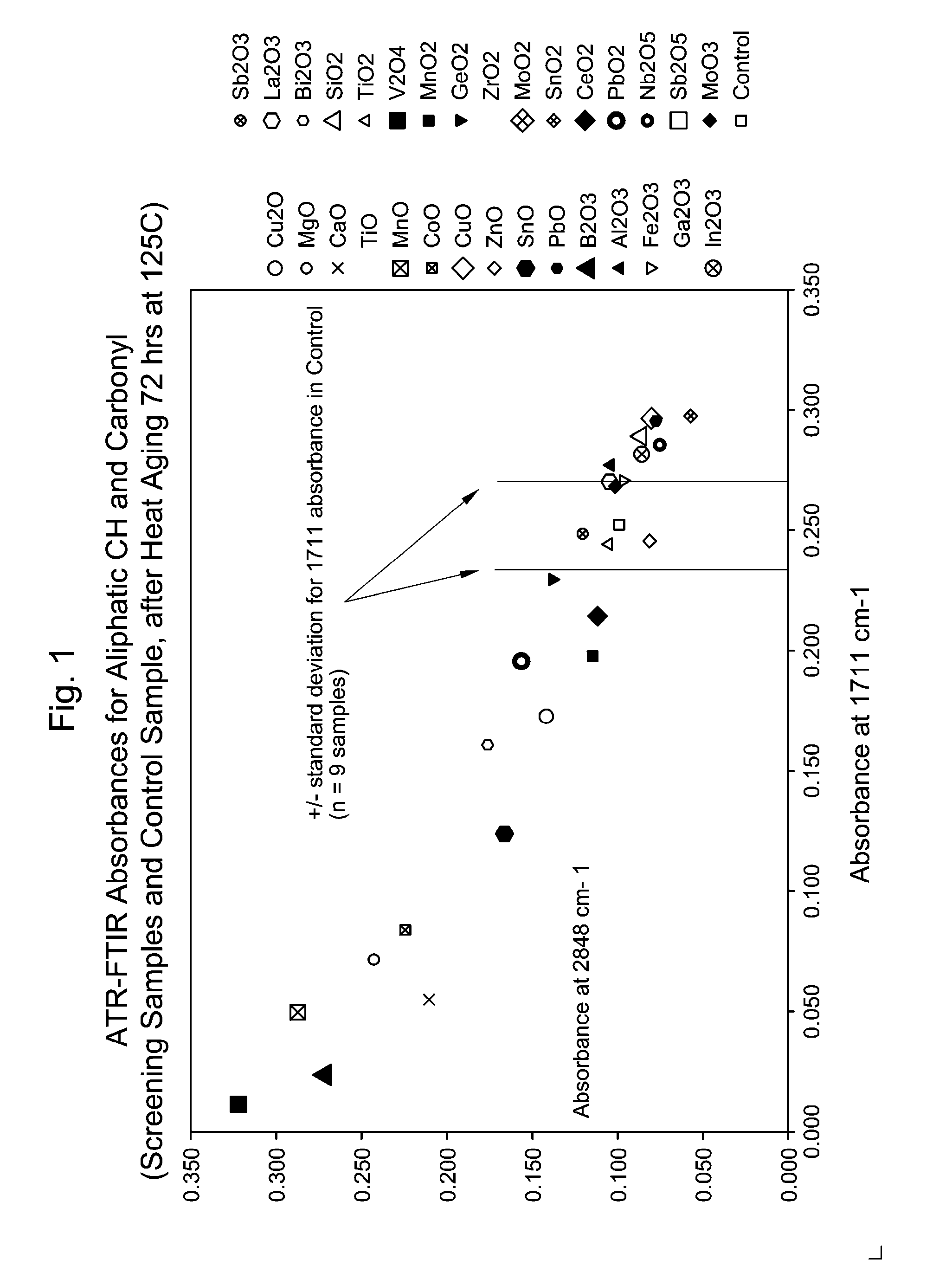
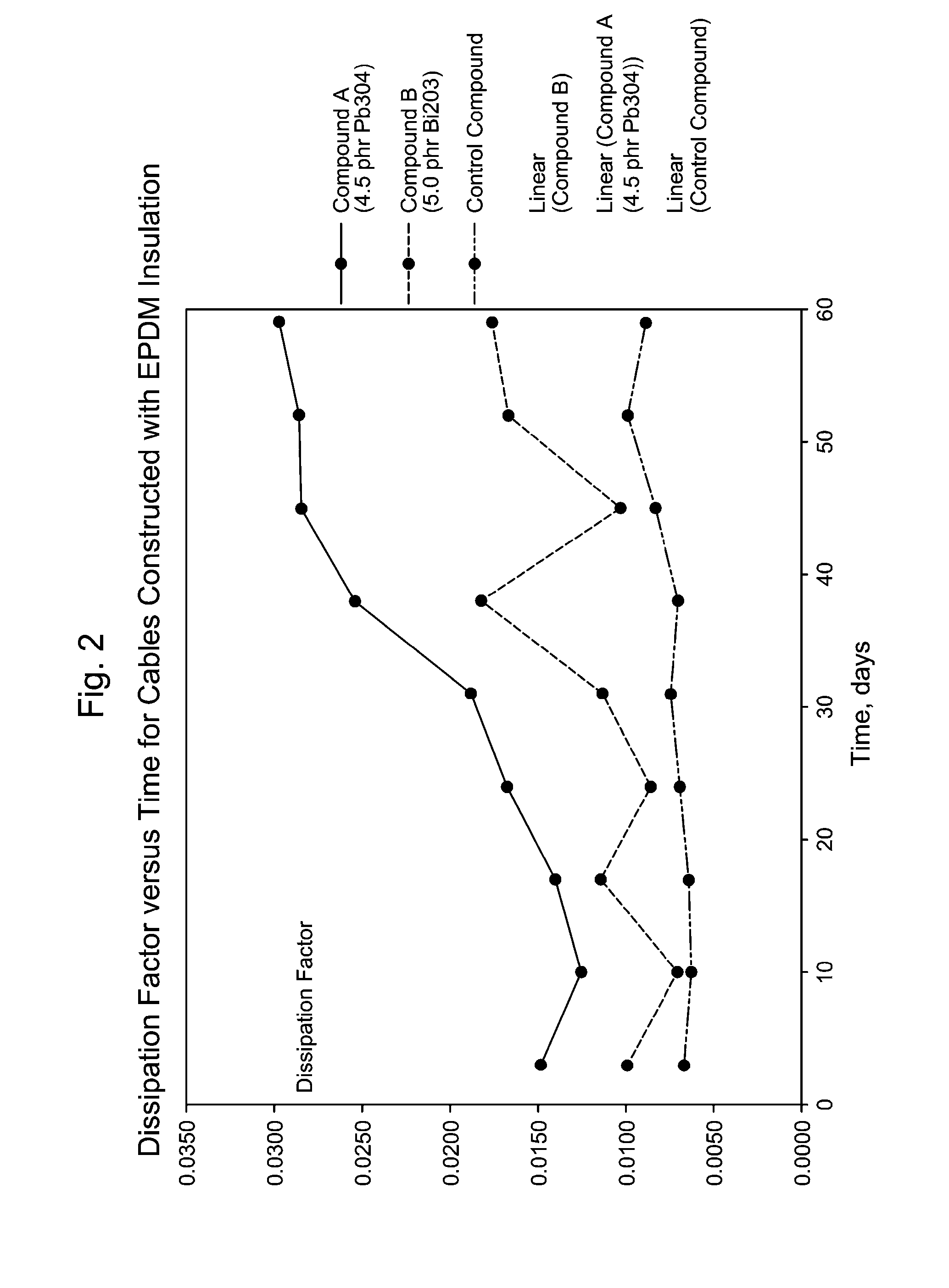
Oxides for Protection Against Electrochemical Oxidation and Ionic Contamination in Medium-Voltage Power-Cable Insulation
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Cleaning process and device for removing ionic contamination from PCB (printed circuit board)
PendingCN110238111ARealize fully automatic operationImprove cleaning efficiencyCleaning using liquidsConductive pattern polishing/cleaningEngineeringIonic contamination
The invention discloses a cleaning process and a cleaning device for removing ionic contamination from a PCB (printed circuit board). The cleaning process includes following flow paths of acid pickling, first multistage overflow water cleaning, ion removal cleaning, second multistage overflow water cleaning, drying and cooling. The cleaning device comprises a running roller conveyor belt used for conveying the PCB, wherein an automatic board placing machine is connected with the head end of the running roller conveyor belt, an acid pickling segment, a first multistage overflow water cleaning segment, an ion removal cleaning segment, a second multistage overflow water cleaning segment, a drying segment and a cooling segment are sequentially arranged on a passing path of the running roller conveyor belt, and an automatic board collection device is connected with the tail end of the running roller conveyor belt. The cleaning process and the cleaning device for removing the ionic contamination from the PCB improve cleaning effects of removing the ionic contamination from the PCB, and save labor cost, and the cleaning device can perform accurate parameter control, and the cleaning effects of the cleaning process for removing the ionic contamination from the PCB are further improved, and then ionic contamination degree of the PCB is further reduced, and furthermore PCB industry development is promoted.
Owner:江门市奔力达电路有限公司
Method for removing moisture and chloride ions in fluoroethylene carbonate
PendingCN113845507AAvoid problems with high moisture contentEfficient removalOrganic chemistryDesiccantEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a method for removing water and chloride ions in fluoroethylene carbonate, which comprises the following steps of: removing water by using an alkaline drying agent until the water content is less than or equal to 30ppm, so that no metal cation pollution is generated after the reaction, removing the chloride ions, and dynamically cooling and crystallizing, so that the obtained crystal is uniform in size and can be prevented from being adhered to the wall in a large area; the method is easy to operate in the subsequent filtering process, heating is not adopted in the whole water removal process, operation is easy and convenient, and the problems that a traditional heating distillation method is large in energy consumption, tedious in step, low in efficiency and high in water content are solved.
Owner:ZHUHAI LEE & MAN MATERIALS SCI CO LTD
Inner part of hard disk drive
ActiveUS7932315B2Reduce outgassingReduce pollutionReducing carrier contaminationRecord information storageHard disc driveHeat resistance
A hard disk drive inner part formed of a resin which exhibits well-balanced low outgassing properties, ultrasonic cleaning resistance, low ionic contamination properties, low particulate contamination properties, repeated removability, heat resistance, specific gravity, and water-absorbing properties. The hard disk drive inner part includes a resin composition which includes a polyphenylene ether resin (A).
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com