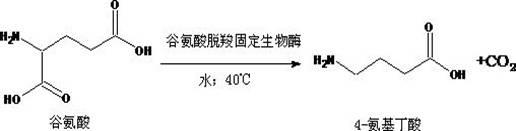
Method for catalytically synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid from glutamate biological solid-phase enzyme
A technology of aminobutyric acid and biosynthesis, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, botany equipment and methods, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as the safety of Escherichia coli, achieve short cycle, low energy consumption, and high reaction single-minded effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Weigh 14.7g of glutamic acid, add 1000ml of purified water and 10kU of solid-phase enzyme to make the substrate concentration 100mmols / L, heat in a water bath, and keep stirring at 37°C for reaction. Samples were taken every 30 minutes to detect the content of glutamic acid to determine the conversion rate of the reaction; when the conversion rate of γ-aminobutyric acid reached 99% (usually 180-240 minutes), the reaction solution was separated from the solid-phase enzyme by filtration.
[0059] Add 0.5 g of activated carbon to the filtrate of the reaction liquid, stir for 30 minutes, and decarburize by filtering through a 0.22 μm filter membrane. The filtrate was transferred to a rotary thin-film concentrator, and concentrated in vacuum at 60°C until the content of γ-aminobutyric acid was 230-240g / 100ml.
[0060] Add 100ml of 95% alcohol, the white precipitate of γ-aminobutyric acid precipitates, stir and cool to room temperature, filter with suction, wash with 95% alco...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Weigh 73.5g of glutamic acid, add 500ml of water and dilute 50kU of solid-phase enzyme to 1000ml with pure water to make the substrate concentration 500mmols / L, heat in a water bath, and keep stirring at 37°C for reaction. Samples were taken every 30 minutes to detect the content of glutamic acid to determine the conversion rate of the reaction; when the conversion rate of γ-aminobutyric acid reached 99% (usually 180-240 minutes), the reaction solution was separated from the solid-phase enzyme by filtration.
[0063] Add 2.0 g of activated carbon to the filtrate of the reaction liquid, stir for 30 minutes, and decarburize by filtering through a 0.22 μm filter membrane. Transfer the filtrate to a rotary thin-film concentrator; concentrate in vacuum at 60°C until the content of γ-aminobutyric acid is 230-240g / 100ml.
[0064] Add 250 ml of 95% alcohol, and white precipitate of γ-aminobutyric acid precipitates out. The filtrate is stirred and cooled to room temperature, fil...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Weigh 147.0g of glutamic acid, add 500ml of water and dilute 50kU of solid-phase enzyme to 1000ml with pure water, so that the substrate concentration is 1000mmols / L, heat in a water bath, and keep stirring at 37°C for reaction. Samples were taken every 30 minutes to detect the content of glutamic acid to determine the conversion rate of the reaction; when the conversion rate of γ-aminobutyric acid reached 99% (usually 180-240 minutes), the reaction solution was separated from the solid-phase enzyme by filtration.
[0067] Add 5.0 g of activated carbon to the filtrate of the reaction liquid, stir for 30 minutes, and decarburize by filtering through a 0.22 μm filter membrane. The filtrate is transferred to a rotary thin-film concentrator; concentrated in vacuum at 60°C until the content of γ-aminobutyric acid is 230-240g / 100ml.
[0068] Add 1000 ml of 95% alcohol, and white precipitate of γ-aminobutyric acid precipitates out. The filtrate is stirred and cooled to room te...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com