Solid-liquid separation device for organic carbon sources in excess sludge
A technology for separation of excess sludge and solid-liquid, applied in sludge treatment, biological sludge treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as limited separation capacity and influence on downstream microbial operation, and achieve the goal of reducing clogging Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The experimental methods used in the following examples are conventional methods unless otherwise specified.
[0030] The materials and reagents used in the following examples can be obtained from commercial sources unless otherwise specified.
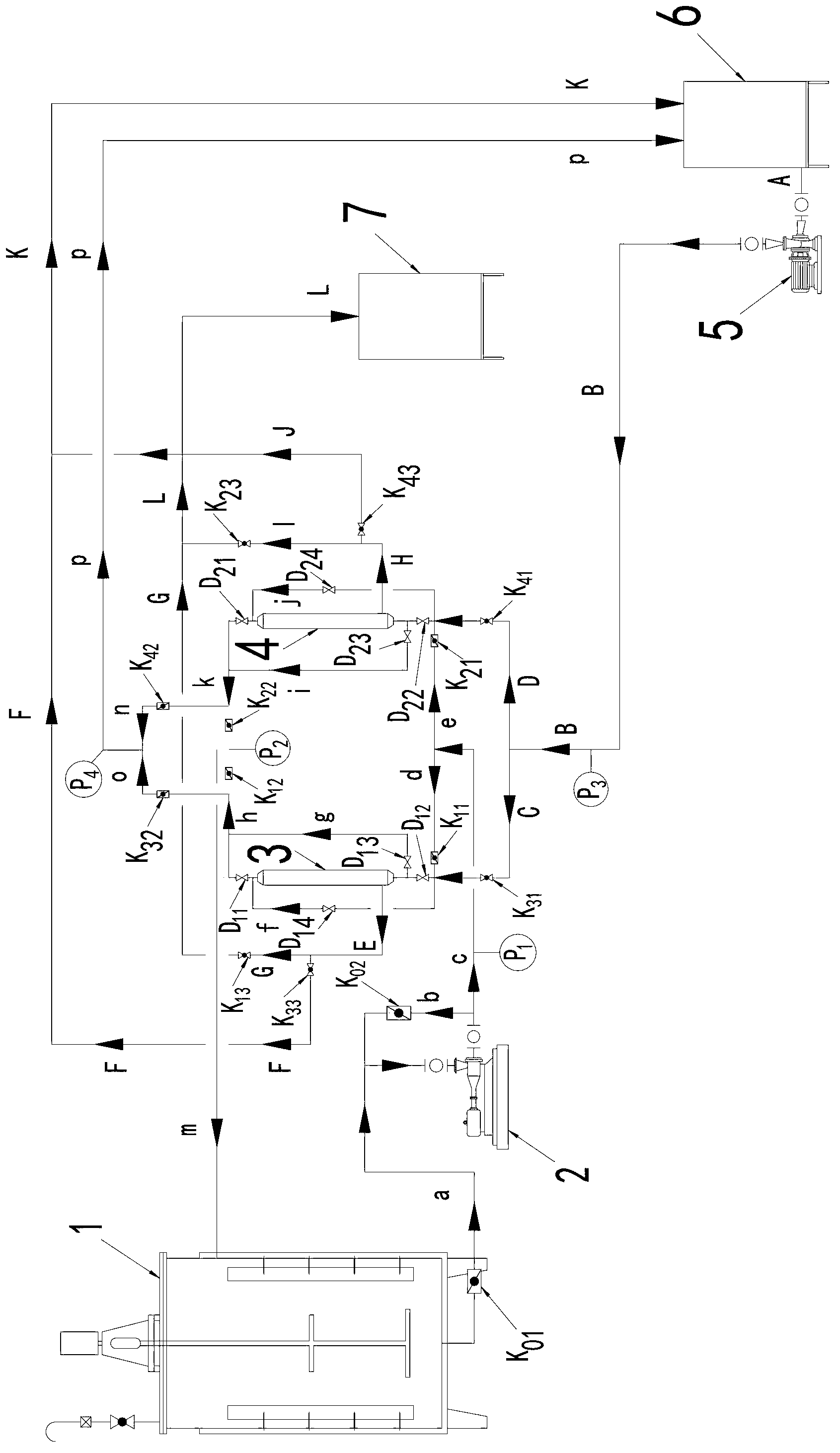
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, the surplus sludge organic carbon source solid-liquid separation device provided by the present invention comprises anaerobic hydrolysis reactor 1, screw pump 2, chemical cleaning tank 6, chemical cleaning pump 5, ceramic membrane microfiltration device I3 and ceramic membrane microfiltration Device II4;
[0032] The bottom of the anaerobic hydrolysis reactor 1 is connected to the screw pump 2 through the excess sludge pipeline a, and the excess sludge pipeline a is equipped with a ceramic membrane operating valve K 01 ; The screw pump 2 communicates with the ceramic membrane microfiltration device I3 and the ceramic membrane microfiltration device II4 through the excess sludge pipeline b, c, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com