Solid/liquid extraction
An extraction, solid technology, applied in food extraction, oil/fat production, fatty acid preparation/refining, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory method and dangerous operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Example 1: Extraction from Dried Avocado
[0075] Extraction from dried avocado was performed with hexane (reference) and the following solvents: HMDS, MeTHF, BTF, BHF, MTBE, ETBE.
[0076] Dried avocados were crushed and added to cellulose cartouches (30 to 40 g). Extraction was performed in a Soxhlet extractor (BUCHI B-811). Four sets of extractions were then performed in parallel, and each set consisted of 20 extraction / siphon cycles. Once the extraction has been terminated, the extraction solvent is evaporated and the residue from which the solvent has been removed is weighed. The weight yields are then compared. The results are given in Table 1.
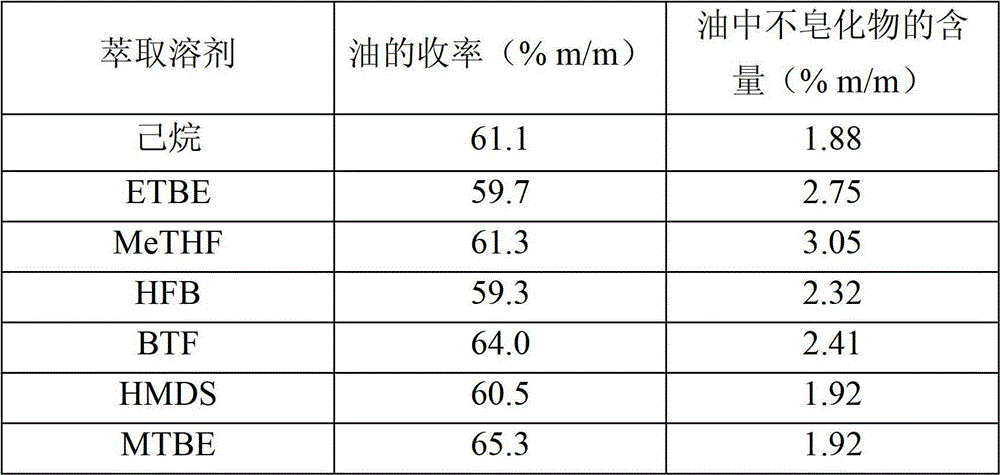
[0077] Table 1
[0078]
[0079] This result shows that the solvent according to the invention has an extraction capacity comparable to that of hexane.
[0080] The extracted oil obtained using the solvent according to the invention has a higher content of unsaponifiables relative to hexane; in the case of ETBE ...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2: Extraction from freeze-dried avocado pulp powder
[0082] Freeze-dried avocado pulp powder was extracted according to the method described in Example 1 with hexane (reference) and the following solvents: HMDS, MeTHF, BTF, MTBE, ETBE. The results are given in Table 2.
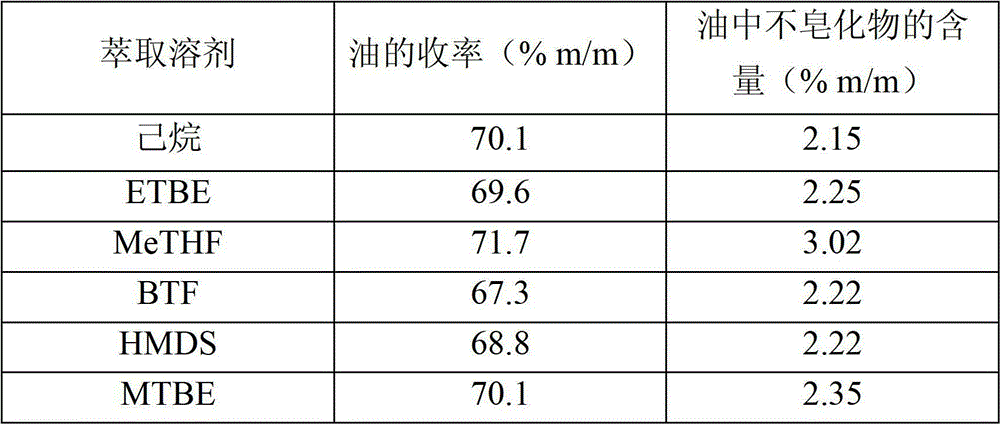
[0083] Table 2
[0084]
[0085] This result shows that the solvent according to the invention has an extraction capacity comparable to that of hexane.
[0086] The extracted oil obtained using the solvent according to the invention has a higher content of unsaponifiables relative to hexane; in the case of MeTHF the content is increased by 50%.
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3: Extraction of oil from dried avocado
[0088] Extraction from dried avocados was performed with hexane (reference) and the following solvents: BTF and ETBE.
[0089] Dried avocados were crushed and added to cellulose cylinders (30 to 40 g). Extraction was performed in a Soxhlet extractor (BUCHI B-811). Four sets of extractions were then performed in parallel, the first set consisting of 5 extraction cycles, the second set consisting of 10 cycles, the third set consisting of 15 cycles and the fourth set consisting of 20 cycles. Once the extraction has been terminated, the extraction solvent is evaporated and the residue from which the solvent has been removed is weighed. The weight yields are then compared.
[0090] The results are given in Table 3 below.
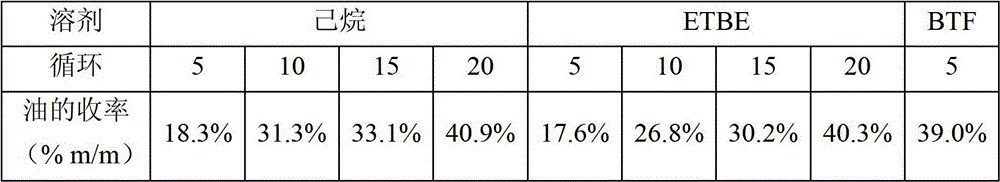
[0091] table 3
[0092]
[0093] The weight yields obtained with ETBE were similar to those obtained with the hexane reference: thus, ETBE provides an alternative to the use of hexane in solid / liq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com