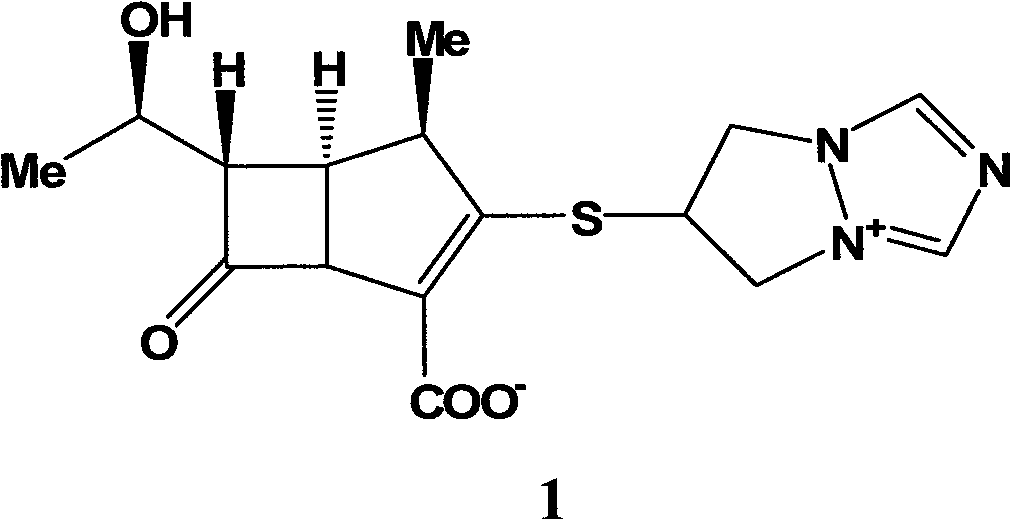
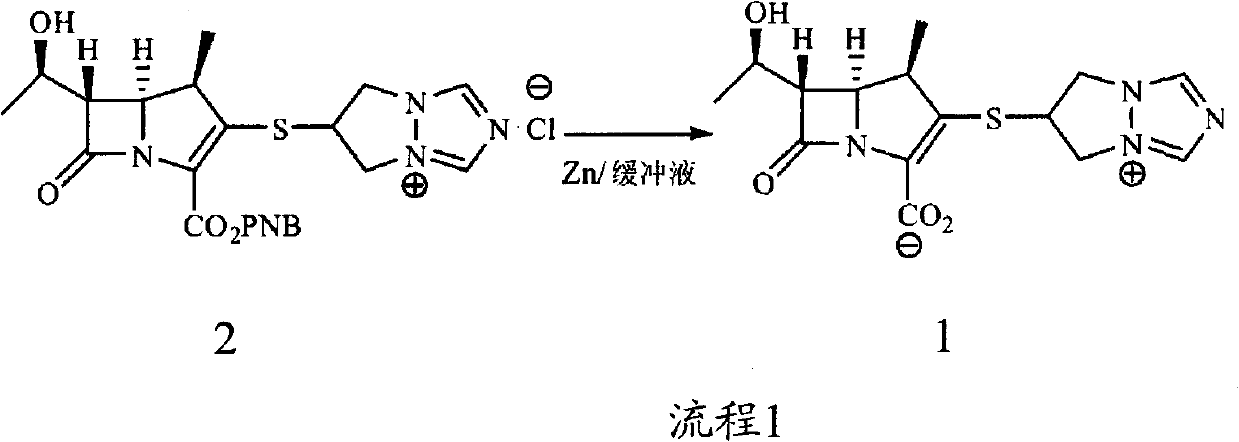
Preparation method of biapenem
A single technology of biapenem, applied in the field of preparation of biapenem, can solve the problems of product heavy metal exceeding standard, poor purity, difficult to remove, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing product degradation and improving product purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 Preparation of Biapenem
[0040] 40.0 L of deionized water, 1.0 kg (1.92 mol) of biapenem intermediate 2, 0.45 L (3.84 mol) of 2,6-lutidine, and 0.5 kg of 10% palladium on carbon were sequentially added into a 100 L hydrogenation reactor. Nitrogen was replaced several times, hydrogen was replaced several times, and finally hydrogen was passed to the pressure of 1.5MPa in the kettle, the temperature was controlled at 20°C, and stirred for 1.5h. Stirring was stopped, hydrogen was discharged and replaced with nitrogen. Filter and recover the filter cake for reuse; add 160L of acetone to the filtrate, stir and crystallize at 0°C for 4h. After filtration and vacuum drying, 0.49 kg of off-white solid was obtained, the molar yield was 73.0%, the HPLC purity was 99.1%, and the heavy metal content was <10 ppm.
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 Preparation of Biapenem
[0042] 40.0 L of deionized water, 1.0 kg (1.92 mol) of biapenem intermediate 2, 0.11 L (0.96 mol) of 3,5-lutidine, and 0.5 kg of 10% palladium on carbon were sequentially added into a 100 L hydrogenation reactor. Nitrogen was replaced several times, hydrogen was replaced several times, and finally hydrogen was passed to the pressure of 2.0 MPa in the kettle, the temperature was controlled at 40°C, and stirred for 3 hours. Stirring was stopped, hydrogen was discharged and replaced with nitrogen. Filter and recover the filter cake for reuse; add 160L of ethanol to the filtrate, stir and crystallize at 0°C for 2h. After filtration and vacuum drying, 0.45 kg of off-white solid was obtained, the molar yield was 67.2%, the HPLC purity was 98.2%, and the heavy metal content was <10 ppm.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 Preparation of Biapenem
[0044] 40.0 L of deionized water, 1.0 kg (1.92 mol) of biapenem intermediate 2, 1.1 L (9.6 mol) of 2,6-lutidine, and 0.5 kg of 10% palladium carbon were sequentially added into a 100 L hydrogenation reactor. Nitrogen was replaced several times, hydrogen was replaced several times, and finally hydrogen was passed to the pressure of 1.8MPa in the kettle, the temperature was controlled at -10°C, and stirred for 2 hours. Stirring was stopped, hydrogen was discharged and replaced with nitrogen. Filter and recover the filter cake for reuse; add 160L of acetone to the filtrate, stir and crystallize at 0°C for 4h. After filtration and vacuum drying, 0.47 kg of off-white solid was obtained, the molar yield was 69.8%, the HPLC purity was 98.8%, and the heavy metal content was <10 ppm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com