Method for extracting genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from peanuts
An extraction method and genome technology, applied in the field of peanut genomic DNA extraction, can solve the problems of harmful operators, multiple samples, complicated steps, etc., and achieve the effects of convenience, quick operability, fewer reagent varieties, and simple process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A method for extracting peanut genomic DNA, comprising the following steps:
[0038] 1) Put the peanut leaves in a centrifuge tube or mortar, add liquid nitrogen, and grind them into powder;
[0039] 2) Take 0.3-0.5g of the powder obtained in step 1), add 0.75ml of solution A and 4ul of 10mg / ml RNase to make the final concentration 1mg / ml, mix well and let stand at room temperature for 5-10 minutes;
[0040] 3) Take KAc with a volume of 0.25ml, pre-cool it to 4°C before adding it, mix well and then centrifuge at a speed of 8000-15000rpm for 8-15 minutes;
[0041] 4) Take the supernatant obtained in step 3) and add an equal volume of isopropanol, mix well, and at this time, flocculent nucleic acids appear, and then perform centrifugation at a speed of 8000-15000rpm for 8-15 minutes. Then rinse the flocculent material obtained by centrifugation with ethanol with a volume concentration of 75%, dry it after rinsing, and then use 0.05-2ml sterile ddH 2 O dissolved and drie...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A method for extracting peanut genomic DNA, comprising the following steps:
[0045] 1) Put the peanut leaves in a centrifuge tube or mortar, add liquid nitrogen, and grind them into powder;
[0046] 2) Take 5-7g of the powder obtained in step 1), add 9ml of solution A and 45ul of 10mg / ml RNase, mix well and let stand at room temperature for 5-10 minutes;
[0047] 3) Take KAc with a volume of 3ml, pre-cool it to 4°C before adding it, mix well and then centrifuge at a speed of 8000-15000rpm for 8-15 minutes;
[0048] 4) Add an equal volume of isopropanol to the supernatant obtained in step 3), and mix thoroughly. At this time, flocculent nucleic acids appear. Pick out the flocculents and rinse the flocculents with ethanol with a volume concentration of 75%. , rinsed and dried, then 0.05-2ml sterile ddH 2 O dissolved and dried the resulting precipitate to obtain a DNA extract.
[0049] Solution A described in the above steps is 1M Tris-HCl, 0.5M EDTA, 5M NaCl, mass con...
Embodiment 3
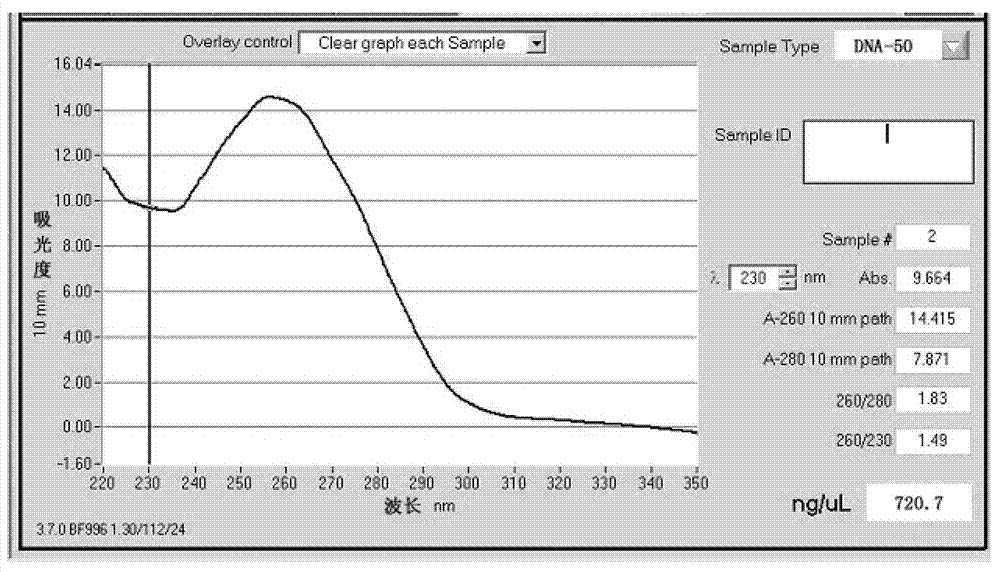
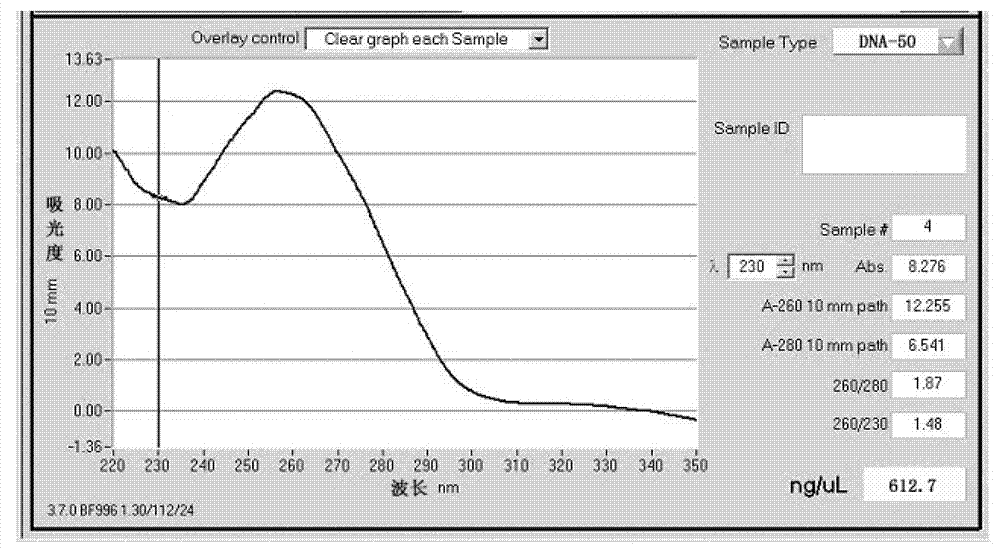
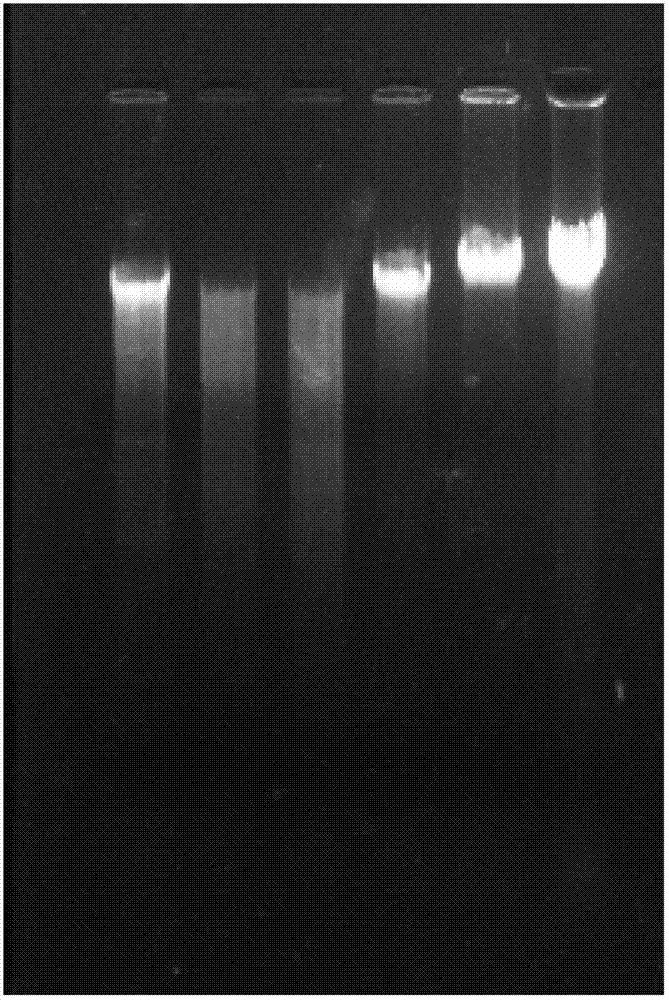
[0051] Detect the quality of the peanut gene DNA that embodiment 1 makes with NanoDrop-1000 ultra-micro nucleic acid protein assay instrument, the result is as follows figure 1 shown. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the values of D260 / D280 are all between 1.8-2.0, and the measured concentration is above 600ng / ul, indicating that this method is feasible for extracting peanut genomic DNA.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com