Link application of protein tag
A protein and protease technology, applied in the field of protein labeling and its application, can solve the problems of enzyme protein denaturation, affecting the purity of reaction products, reducing and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0290] Preparation of RbCl Competent Cells:
[0291] (1) Streak the DH5α strain on the LB plate, 37°C, 10-12h;
[0292] (2) Pick a single clone in 30ml S.O.B and culture overnight at 37°C;
[0293] (3) Inoculate the overnight bacteria into 200ml S.O.B at 1:100, culture at 37°C until OD550=0.35, about 2 hours;
[0294] (4) Quickly transfer the bacterial solution to an ice-salt bath (-3~-5°C), pre-cool for 15 minutes (shake gently once every ~3 minutes), and pre-cool the 500ml centrifuge cup at the same time;
[0295] (5) pre-cooling centrifuge;
[0296] (6) Quickly transfer the bacterial solution to a 500ml centrifuge cup;
[0297] (7) 4500rpm×5min, 4°C, discard the supernatant;
[0298] (8) Add 4×16ml Buffer1, lightly mix, suspend, and put in ice-salt bath for 15min;
[0299] (9) 4000rpm×5min, 4°C, discard the supernatant;
[0300] (10) Add 4×4ml Buffer2, suspend the cells, and place on ice;
[0301] (11) Immediately aliquot into 200 μl / tube (tube pre-cooled);
[0302]...
Embodiment 1
[0346] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of SBD fragment
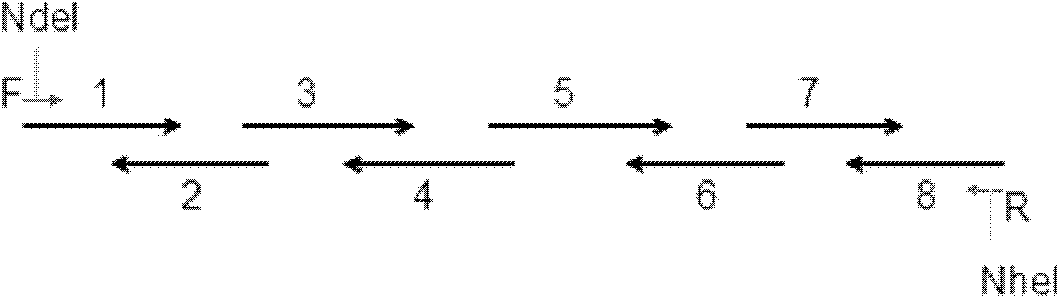
[0347] Such as figure 1 Synthetic primers were designed for the coding sequence of the starch binding domain (SBD).
[0348] In the case that there is no template for gene amplification or the template is difficult to obtain, overlapping PCR technology is currently an effective method and approach for synthesizing genes. The present inventors artificially synthesized SBD gene fragments by stepwise overlapping PCR technique. A total of 10 primers were designed according to the sequence of the SBD, and there was a certain length of complementary overlapping sequence (20bp) between each two primers of 1-8. Use the middle two primers as templates (such as primer 2, primer 3), and the two sides as amplification primers (such as primer 1, primer 4), amplify 1-4, 5-8 by PCR, and compare the two sections. Long DNA fragments, and then these two fragments (SBD1-4, SBD5-8) after purification and recovery were used as templates, u...
Embodiment 2
[0350] Example 2. Purification application of fusion expression of SBD and solubilizing tag SUMO
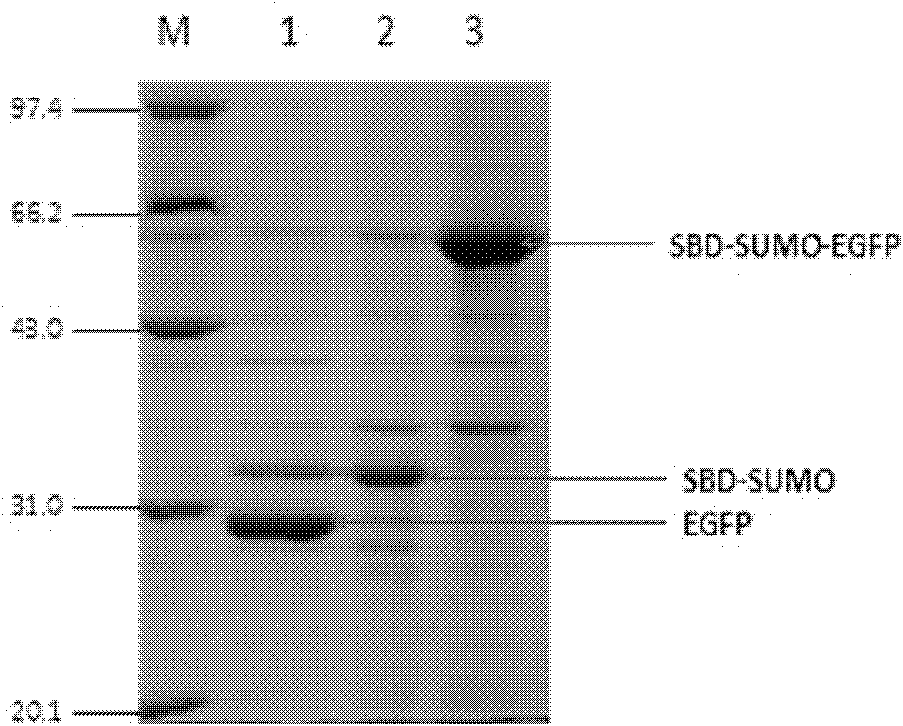
[0351] The previously constructed pET28a His-SBD-SUMO-EGFP and pET28a His-SBD-SUMO-JNK2 were induced and expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3) by 0.5mM IPTG at 22°C for 20 hours, and the bacterial liquid was collected for sonication After centrifugation, the obtained supernatant protein crude extract was mixed with starch beads at 4° C. for 1 hour, and the solution was eluted twice to remove foreign proteins. Then Ulp1c enzyme (catalytic domain of Ulp1) was used for enzyme cleavage reaction.
[0352] Such as Figure 3-4 As shown, it can be seen that the SBD-SUMO-EGFP and SBD-SUMO-JNK2 fusion proteins are well bound to starch beads in one step, and can be effectively purified to the target protein after cleavage by Ulp1c enzyme. SBD itself, as a solid-phase label, can specifically bind to starch beads. This affinity binding is stronger than that of general anions and cations, and it is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com