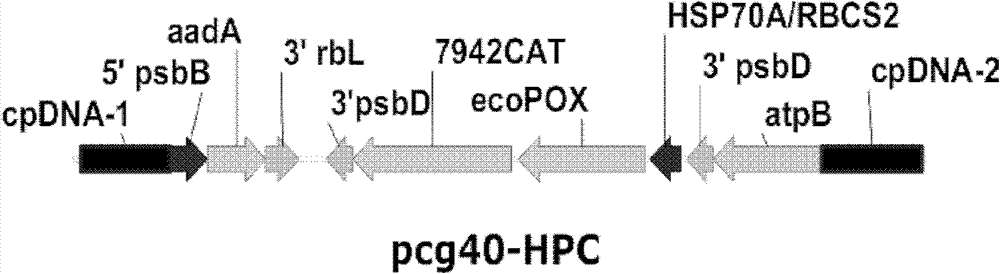
Method for improving photosynthetic hydrogen production efficiency of algae
A technology of algae and high efficiency, which is applied in the field of improving the photosynthetic hydrogen production efficiency of algae, and can solve the problems of Chlamydomonas photosynthetic hydrogen production efficiency extension duration, high cost, and Chlamydomonas photosynthetic hydrogen production cannot be industrialized, and achieve photosynthetic hydrogen production efficiency Improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0177] Embodiment 1, identification of transgenic Chlamydomonas
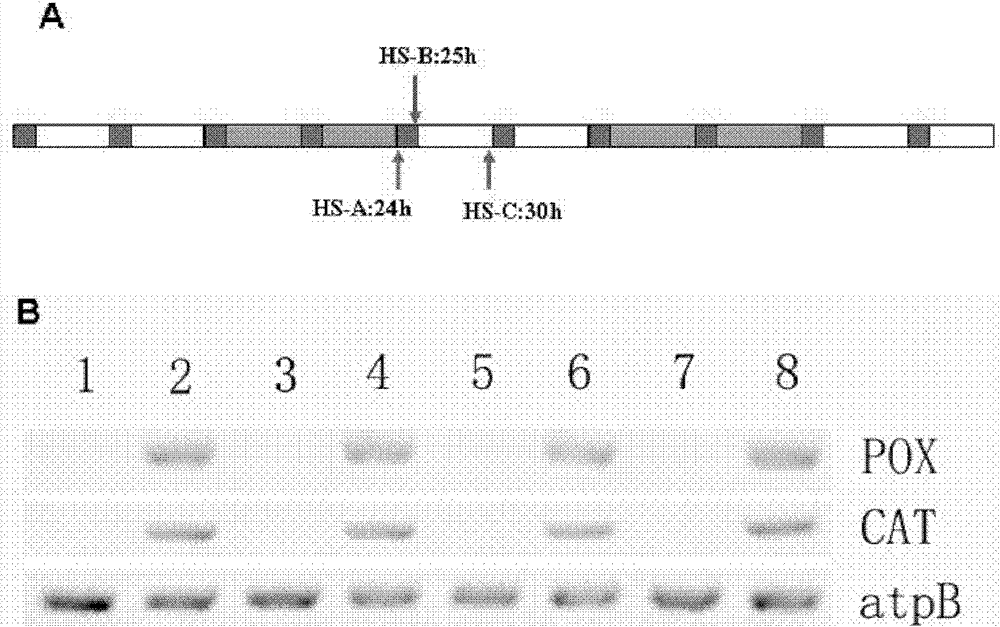
[0178] PCR method was used to detect whether the exogenous gene was integrated into Chlamydomonas chloroplast genome, and whether the exogenous gene was expressed after heat shock induction. figure 2 B shows that the expression of exogenous genes POX and CAT cannot be detected using the DNA of wild-type Chlamydomonas cc503 as a template. However, using the DNA of the transgenic Chlamydomonas ccHPC as a template, very specific bands of exogenous genes POX and CAT were detected.
[0179] The results showed that exogenous genes POX and CAT had been integrated into the genome of the transgenic Chlamydomonas.
Embodiment 2
[0180] Embodiment 2, the expression of exogenous gene of transgenic Chlamydomonas
[0181] At the beginning, the inventors adopted a culture method of heat shock once a day, and found that the expression level of the exogenous gene was relatively low.
[0182] Therefore, the induction method of heat shock at 40°C every 6 hours was adopted. For the specific procedure, see figure 2 A, The expression of exogenous genes POX and CAT has been at a high level throughout the culture period.
Embodiment 3
[0183] Embodiment 3, the detection of growth rate
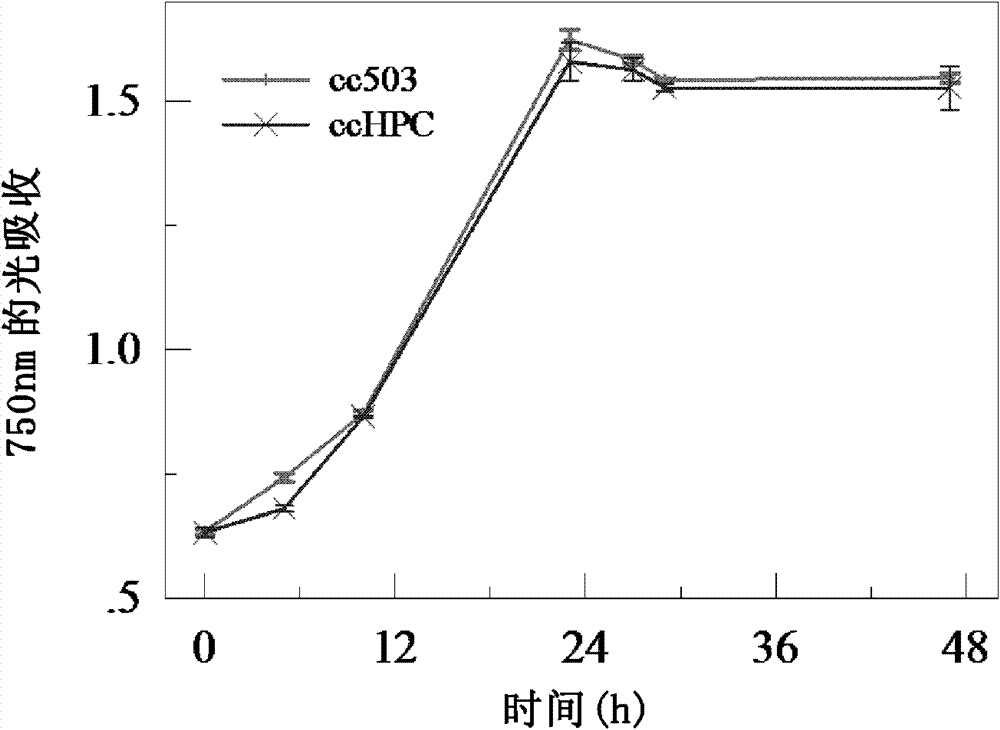
[0184] Since the transgenic Chlamydomonas introduced two exogenous genes, in order to detect whether the expression of the exogenous genes affects the growth rate of Chlamydomonas itself, the inventors tested the growth rate of Chlamydomonas at the same initial concentration. image 3 (Experimental conditions are: continuous low light (light intensity is 75umol photons m -2 the s -1 ) culture and heat shock every 6 hours) showed that the growth rate of the transgenic Chlamydomonas ccHPC was only slightly lower than that of the wild-type Chlamydomonas cc503, and there was no significant difference between the two. This indicated that although the expression of the exogenous gene changed the metabolic response of Chlamydomonas itself, it did not cause a significant inhibitory effect.
[0185] In the practice of metabolic engineering transformation, the growth of many transgenic species is lower than that of wild-type species,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com