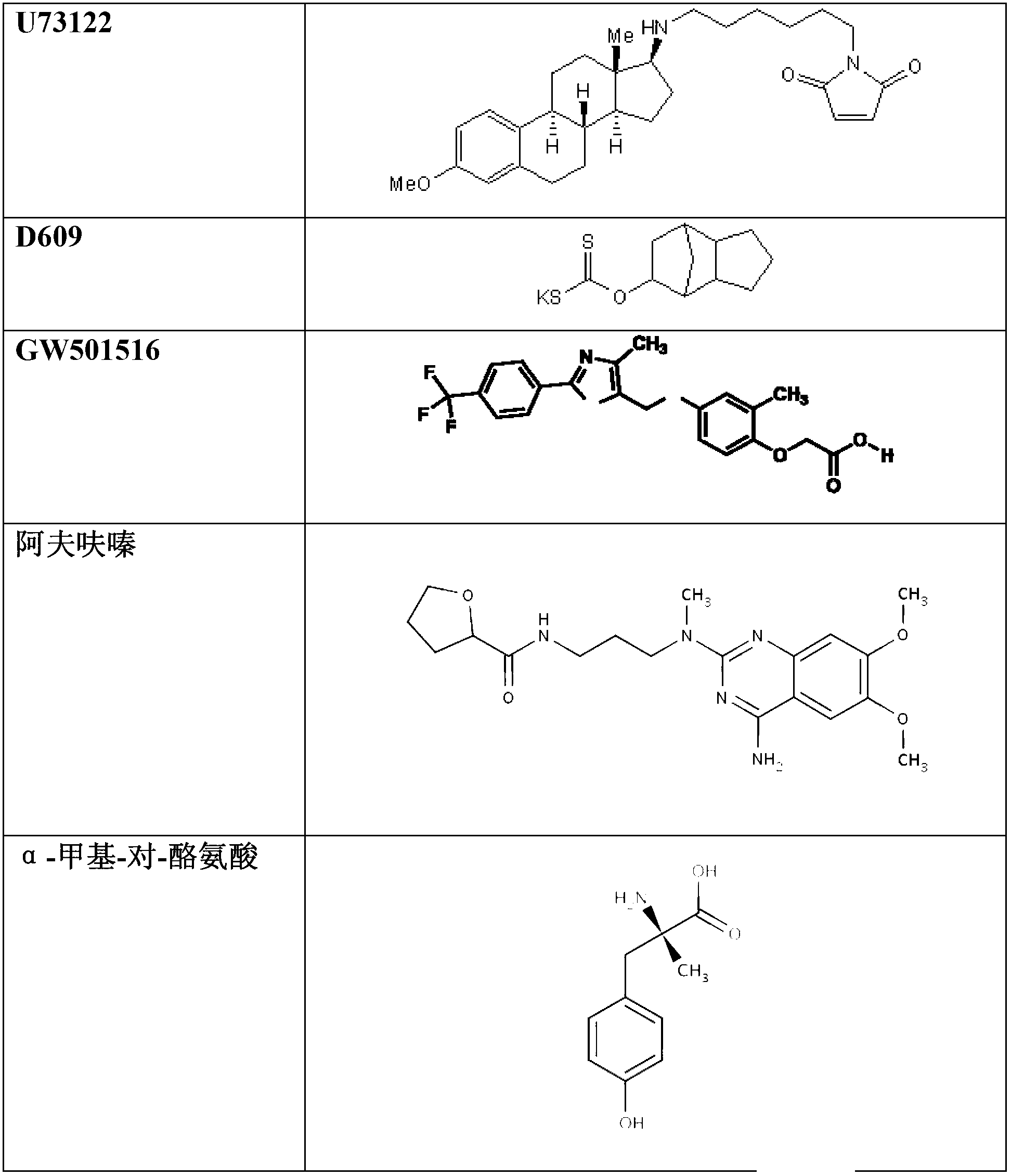
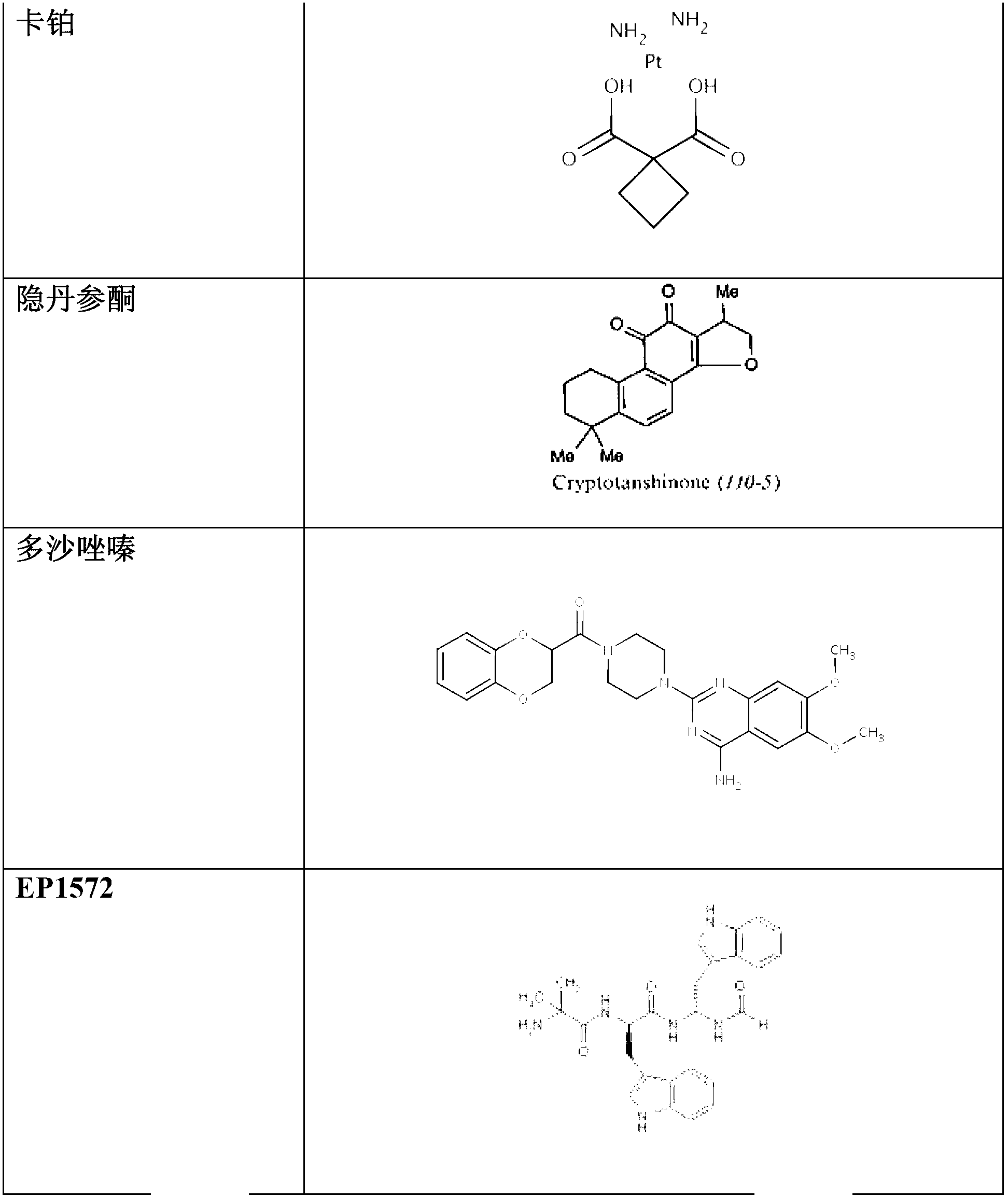
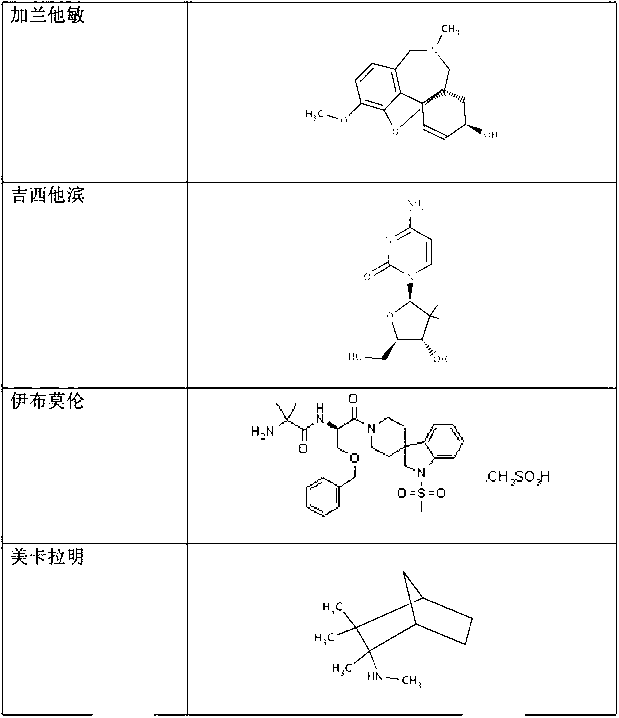
Methods for modulation of autophagy through the modulation of autophagy-inhibiting gene products
A technology for inhibiting genes and gene products, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, gene therapy, genetic engineering, etc., can solve the problem of few autophagy regulators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0215] Methods of preparation of such formulations or compositions may comprise the step of bringing into association an agent of the invention with the carrier and, optionally, one or more excipients.
[0216] Liquid formulation forms of the compounds of this invention for oral administration include pharmaceutically acceptable emulsions, microemulsions, solutions, suspensions, syrups and elixirs. In addition to the active ingredient, liquid preparations may also contain inert diluents widely used in the art, for example, water or other solvents, solubilizers and emulsifiers such as ethanol, isopropanol, ethyl carbonate, ethyl acetate, benzene Methanol, benzyl benzoate, propylene glycol, 1,3-butanediol, oils (especially cottonseed oil, peanut oil, corn oil, germ oil, and castor oil), glycerin, THF, polyethylene glycol, and sorbitan Fatty acid esters, or mixtures thereof.
[0217] Besides diluents, the oral compositions can also include adjuvants such as wetting agents, emuls...
Embodiment 1
[0302] Example 1. High-throughput image-based siRNA screening of genes involved in autophagy regulation
[0303] Genes involved in the regulation of autophagy in mammals were identified using human neuroblastoma H4 cells stably expressing the LC3-GFP reporter. Under normal growth conditions, LC3-GFP in the cells is diffusely distributed in the cytosol. When autophagy is induced, LC3-GFP is recruited in the cytosol and can be observed to present spots corresponding to autophagosomes. To confirm this system, cells were transfected with siRNA against the essential autophagy mediator ATG5 or against mTOR, a suppressor gene of starvation-induced autophagy. After culturing for 72 h under normal nutritional conditions, the cells were transfected with ATG5 siRNA. This resulted in a marked downregulation of autophagy via a decrease in the number and intensity of LC3-GFP positive autophagosomes ( figure 1 A) and the decreased ratio of LC3II to LC3I in Western blot assay ( figure...
Embodiment 2
[0306] Example 2. Secondary high-throughput characterization of candidate genes
[0307] To elucidate the molecular pathways by which newly identified genes are involved in the regulation of autophagy, additional high-throughput assays were used to characterize these hit genes ( Figure 4 ). In one experiment, the function of mTORC1, an essential mediator of starvation-induced autophagy, was investigated. To identify candidate genes that regulate autophagy by altering mTORC1 activity, in situ immunoblotting assays were used to evaluate phosphorylation levels of ribosomal S6 protein (rpS6), a downstream target of mTORC1 signaling. To confirm this system, H4 cells were transfected with mTOR siRNA. Compared with the non-targeting siRNA control, the phosphorylation level of rpS6 was significantly decreased in mTOR siRNA-transfected cells ( Figure 5 ). Knockdown of only 14 (6%) of 219 validated genes induced autophagy by in situ immunoblotting assays in cells, and was strong...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com