Method for producing anhydrous lithium chloride special for electrolyzing by using lithium recovered from lithium-containing pharmaceutical waste water
A pharmaceutical wastewater and lithium chloride technology, applied in the direction of lithium halide, etc., can solve the problems of low product purity, no sodium removal, and poor product appearance, and achieve the effects of avoiding environmental pollution, avoiding waste of resources, and less investment in equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
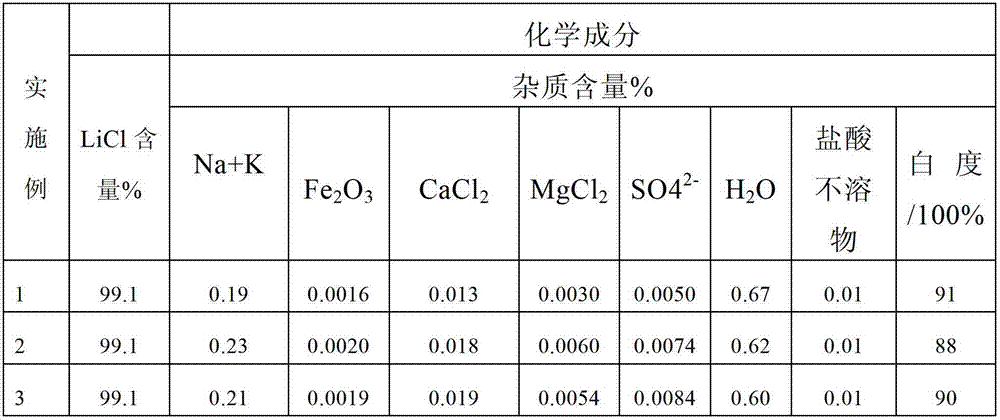
Embodiment 1
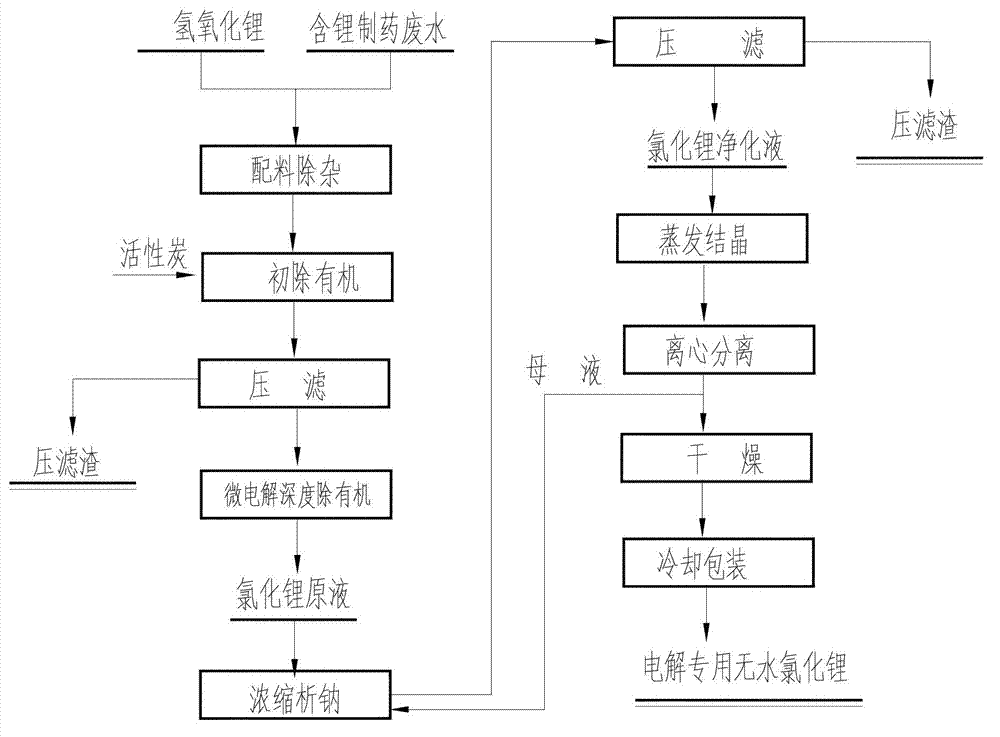
[0038] a. Ingredients removal: mix 7.6m 3 Lithium-containing pharmaceutical wastewater (contained Ca by analysis 2+ % is 0.02%, SO4 2- % is 0.07%, namely Ca 2+ The mass percentage content is 0.02%, SO4 2- The mass percentage content is 0.07%, at this time the solution density is 1070Kg / m 3 ) into the batching kettle, adjust the pH of the solution to 12 with lithium hydroxide solution, stir and react for 30 minutes, and precipitate the Mg in the waste liquid 2+ , Fe 3+ Plasma, then add 12.3Kg of BaCl 2 Stir and react with 5.0Kg ammonium oxalate for 30 minutes to remove Ca in the solution 2+ and SO 4 2- , remove the solid precipitate by pressure filtration;
[0039] b, initial organic removal: add hydrochloric acid to the filtrate obtained in step a, adjust the pH value of the solution to 8, add 8.1Kg powdered activated carbon, heat up and control it at 80°C, stir for 90 minutes, and obtain a clear solution after press filtration;
[0040] c, micro-electrolysis deep or...
Embodiment 2
[0047] a. Ingredients removal: mix 7.5m 3 Lithium-containing waste liquid (contains Ca after analysis 2+ % is 0.03%, SO4 2- % is 0.1%, then the density of the solution is 1090Kg / m 3 ) into the batching kettle, adjust the pH of the solution to 11 with lithium hydroxide solution, stir and react for 15 minutes, and precipitate the Mg in the waste liquid 2+ , Fe 3+ Plasma, then add 17.7Kg BaCl 2 Stir and react with 7.6Kg ammonium oxalate for 15 minutes to remove Ca in the solution 2+ and SO 4 2- , remove the solid precipitate by pressure filtration;
[0048] b. Initial organic removal: add hydrochloric acid to the filtrate obtained in step a, adjust the pH value of the solution to 7, add 8.2Kg powdered activated carbon, heat up and control it at 50°C, stir for 40 minutes, and obtain a clear solution after press filtration;
[0049] c, micro-electrolysis deep organic removal: pass through the solution of step b to remove organics through the micro-electrolysis organic devic...
Embodiment 3
[0056] a. Ingredients removal: mix 7.5m 3 Lithium-containing pharmaceutical wastewater (contained Ca by analysis 2+ % is 0.04%, SO42- % is 0.13%, and the density of the solution at this time is 1080Kg / m 3 ) into the batching kettle, adjust the pH of the solution to 10.5 with lithium hydroxide solution, react for 25 minutes, and precipitate the Mg in the wastewater 2+ , Fe 3+ Plasma, then add 22.8Kg BaCl 2 React with 10Kg ammonium oxalate for 25 minutes to remove Ca in wastewater 2+ and SO 4 2- , remove the solid precipitate by pressure filtration;
[0057] b, initial organic removal: add hydrochloric acid to the filtrate obtained in step a, adjust the pH value of the solution to 7.5, add 8.1Kg powdered activated carbon, heat up and control it at 65°C, stir for 65 minutes, and obtain a clear solution after press filtration;
[0058] c, micro-electrolysis deep organic removal: pass through the solution of step b to remove organics through the micro-electrolysis organic de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com