Coconut tree branch and leaf fiber based wood-plastic composite material and preparation method of coconut tree branch and leaf fiber based wood-plastic composite material
A wood-plastic composite material, coconut tree technology, applied in the field of coconut branch and leaf fiber-based wood-plastic composite material and its preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
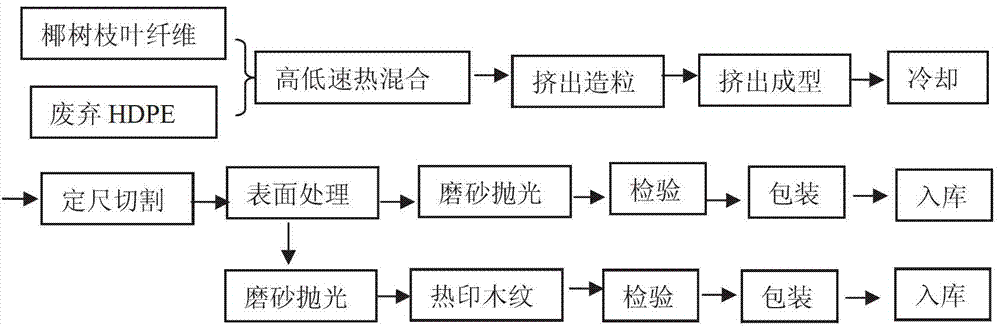
[0026] Manufacturing steps of coconut tree branch and leaf fiber-based wood-plastic composite board:
[0027] (1) Raw material preparation: crush waste PE bottle caps into 40-100 mesh granules and dry them to obtain waste PE granules; the naturally falling coconut tree branches and leaves are cut, dried and dehydrated, hammered, and ground to prepare a particle size of 50-100 mesh. 100 mesh coconut tree branch fiber.
[0028] (2) High mixing: Mix the coconut tree branch and leaf fibers, waste PE particles and additives in the ratio of 55:25:20 by weight in a high-speed mixer to obtain a high mixing material. Auxiliaries include 2.5% solubilizer, 2.2% coupling agent, 2.4% lubricant, 2.1% colorant, 2.5% antibacterial agent, 2.3% UV stabilizer, 2.0% dispersant, 2.0% antioxidant, crosslinking agent 2.0%.
[0029] (3) Granulation: Use a conical twin-screw granulator to granulate the high-mixed material described in step (2).
[0030] (4) Input the granulated particles into the c...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Manufacturing steps of coconut tree branch and leaf fiber-based wood-plastic composite board:
[0034] (1) Raw material preparation: crush waste PE bottle caps into 40-100 mesh granules and dry them to obtain waste PE granules; the naturally falling coconut tree branches and leaves are cut, dried and dehydrated, hammered, and ground to prepare a particle size of 50-100 mesh. 100 mesh coconut tree branch fiber.
[0035] (2) High mixing: Mix the coconut tree branch and leaf fibers, waste PE particles and additives in the ratio of 75:15:10 by weight percentage in a high-speed mixer to obtain a high mixing material. Auxiliaries include 1.0% solubilizer, 1.2% coupling agent, 1.2% lubricant, 1.1% colorant, 1.2% antibacterial agent, 1.2% UV stabilizer, 1.1% dispersant, 1.0% antioxidant, crosslinking agent 1.0%.
[0036] (3) Granulation: Use a conical twin-screw granulator to granulate the high-mixed material described in step (2).
[0037] (4) Input the granulated particles...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Manufacturing steps of coconut tree branch and leaf fiber-based wood-plastic composite board:
[0041] (1) Raw material preparation: crush waste PE bottle caps into 40-100 mesh granules and dry them to obtain waste PE granules; the naturally falling coconut tree branches and leaves are cut, dried and dehydrated, hammered, and ground to prepare a particle size of 50-100 mesh. 100 mesh coconut tree branch fiber.
[0042] (2) High mixing: Mix 55.01% to 74.99% of the coconut tree branch and leaf fiber described in step (1), 15.01% to 24.99% of waste PE particles and 10.01% to 19.99% of additives in a high-speed mixer to obtain High mix. Auxiliaries include 1.01%-2.49% solubilizer, 1.21%-2.19% coupling agent, 1.21%-2.39% lubricant, 1.11%-2.09% colorant, 1.21%-2.49% antibacterial agent, and 1.21% ultraviolet stabilizer ~2.29%, dispersant 1.11%~1.99%, antioxidant 1.01%~1.99%, crosslinking agent 1.01%~1.99%,
[0043] (3) Granulation: Use a conical twin-screw granulator to gr...
PUM
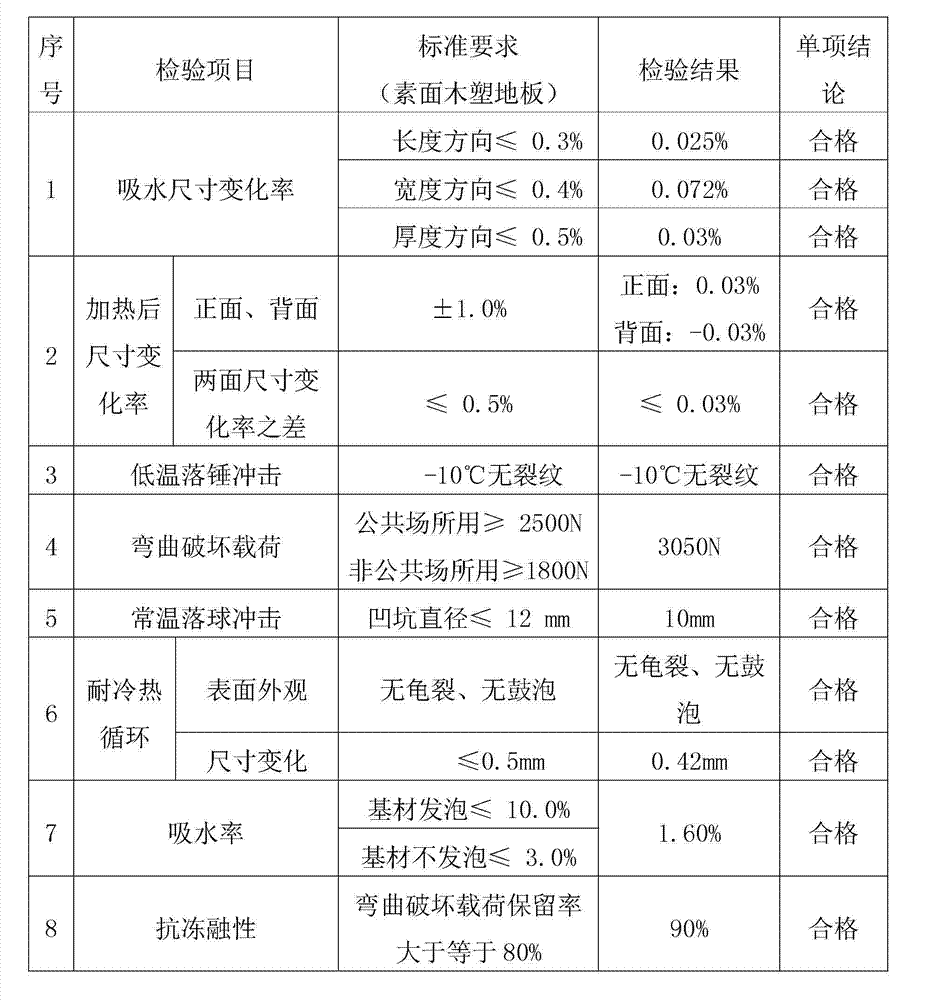
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com