Method for reducing acid into alcohol by sodium borohydride
A kind of sodium borohydride, the technology of using sodium borohydride, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, organic chemistry and other directions, can solve the problems of difficult industrial production, inability to reduce acid, poor selectivity, etc., and achieve easy large-scale production. The effect of industrialized production, reduced risk and good reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014]
[0015] Add 128g of cyclohexanecarboxylic acid, 500mL of water, and 10g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide into a 1L three-necked flask, and stir at room temperature for 30min. Add 19g of sodium borohydride in batches, and cool in a water bath to control the temperature not higher than 35 degrees. After the completion, the stirring reaction was continued at room temperature for 2 h. The reaction solution was extracted with 100mL*3 ethyl acetate, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and the residue was distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 86g of the product cyclohexylmethanol, yield: 76%. MS m / z114(M+H) + 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 3.39(d, 2H), 2.99(s, 1H), 1.67-1.78(m, 3H), 1.17-1.46(m, 7H), 0.92(m, 1H).
Embodiment 2
[0017]
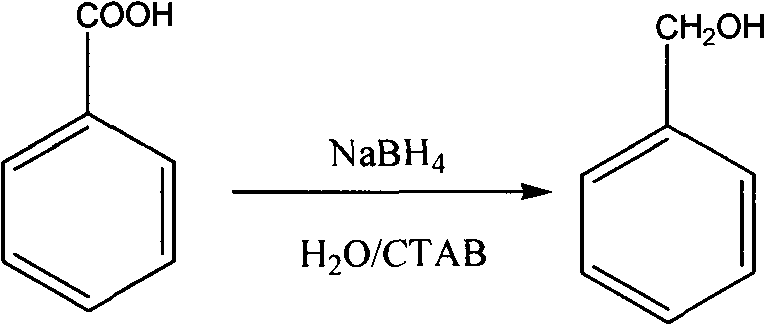
[0018] Add 122g of benzoic acid, 450mL of water, and 15g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide into a 1L three-necked flask, and stir at room temperature for 30min. Add 19g of sodium borohydride in batches, and cool in a water bath to control the temperature not higher than 35 degrees. After completion, the stirring reaction was continued at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction solution was extracted with 100mL*3 ethyl acetate, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and the residue was distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 95g of benzyl alcohol with a yield of 88%. MS m / z108(M+H) + 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 7.23-7.29 (m, 5H), 4.52 (s, 2H), 3.36 (s, 1H).
Embodiment 3
[0020]
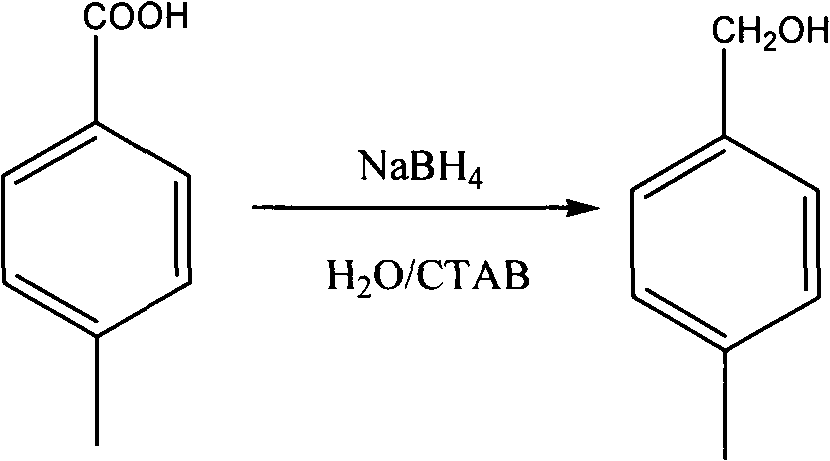
[0021] Add 136g of benzoic acid, 600mL of water, and 15g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide into a 1L three-necked flask, and stir at room temperature for 1h. Add 19g of sodium borohydride in batches, and cool in a water bath to control the temperature not higher than 35 degrees. After completion, the stirring reaction was continued at room temperature for 3 h. The reaction solution was extracted with 150 mL*3 ethyl acetate, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and the residue was distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 100 g of product 4-methylbenzyl alcohol, yield: 82%. MS m / z122(M+H) + 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 7.05-7.29(m, 4H), 4.58(s, 2H), 2.45(s, 3H), 2.23(s, 1H).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com