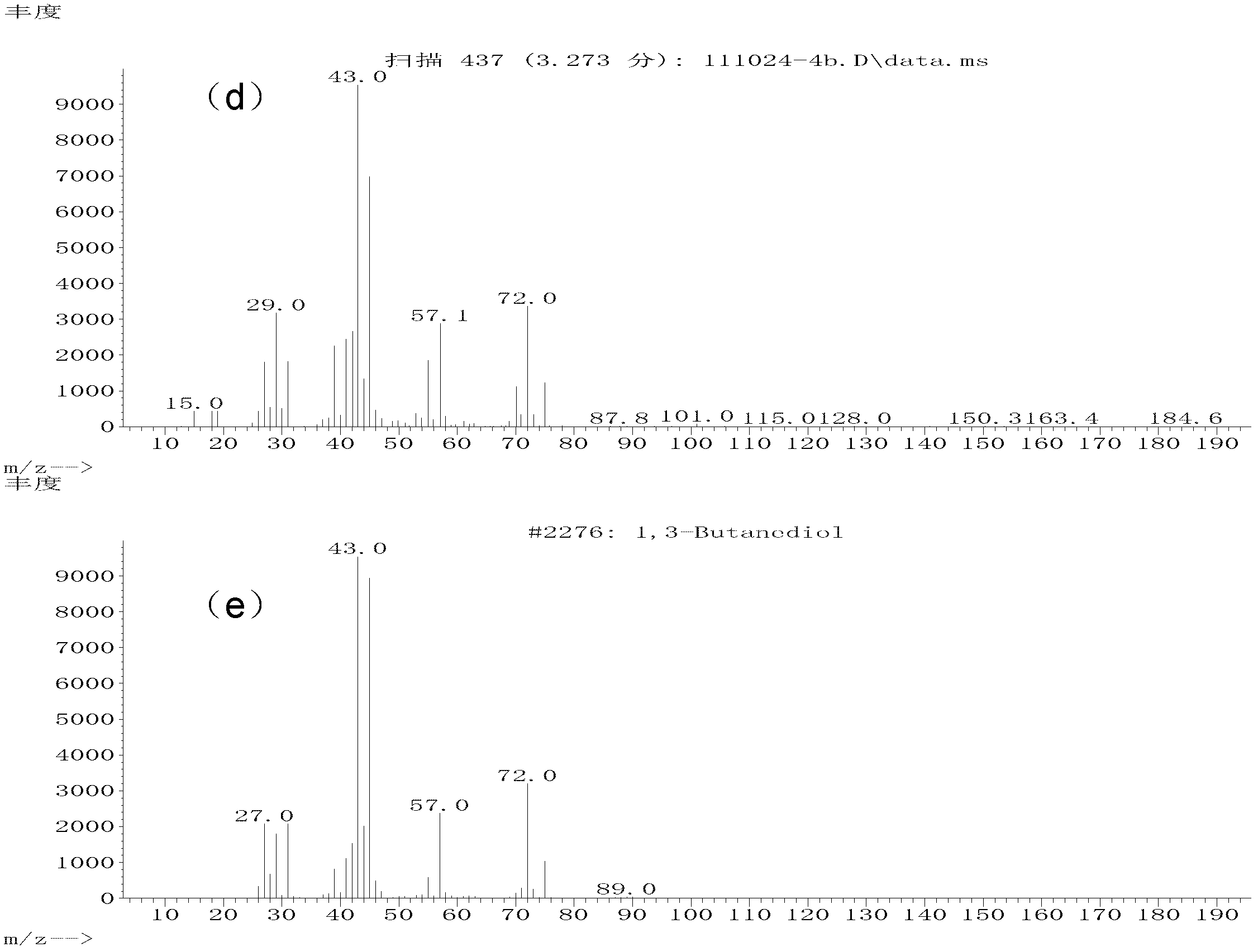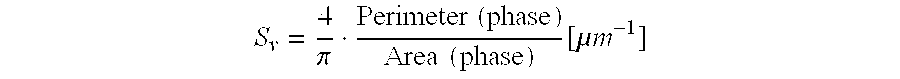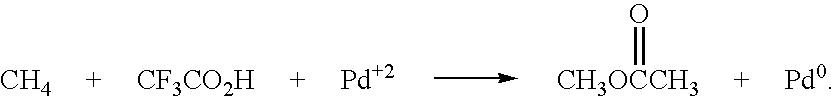Patents
Literature
413results about "Hydroxy group formation/introduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
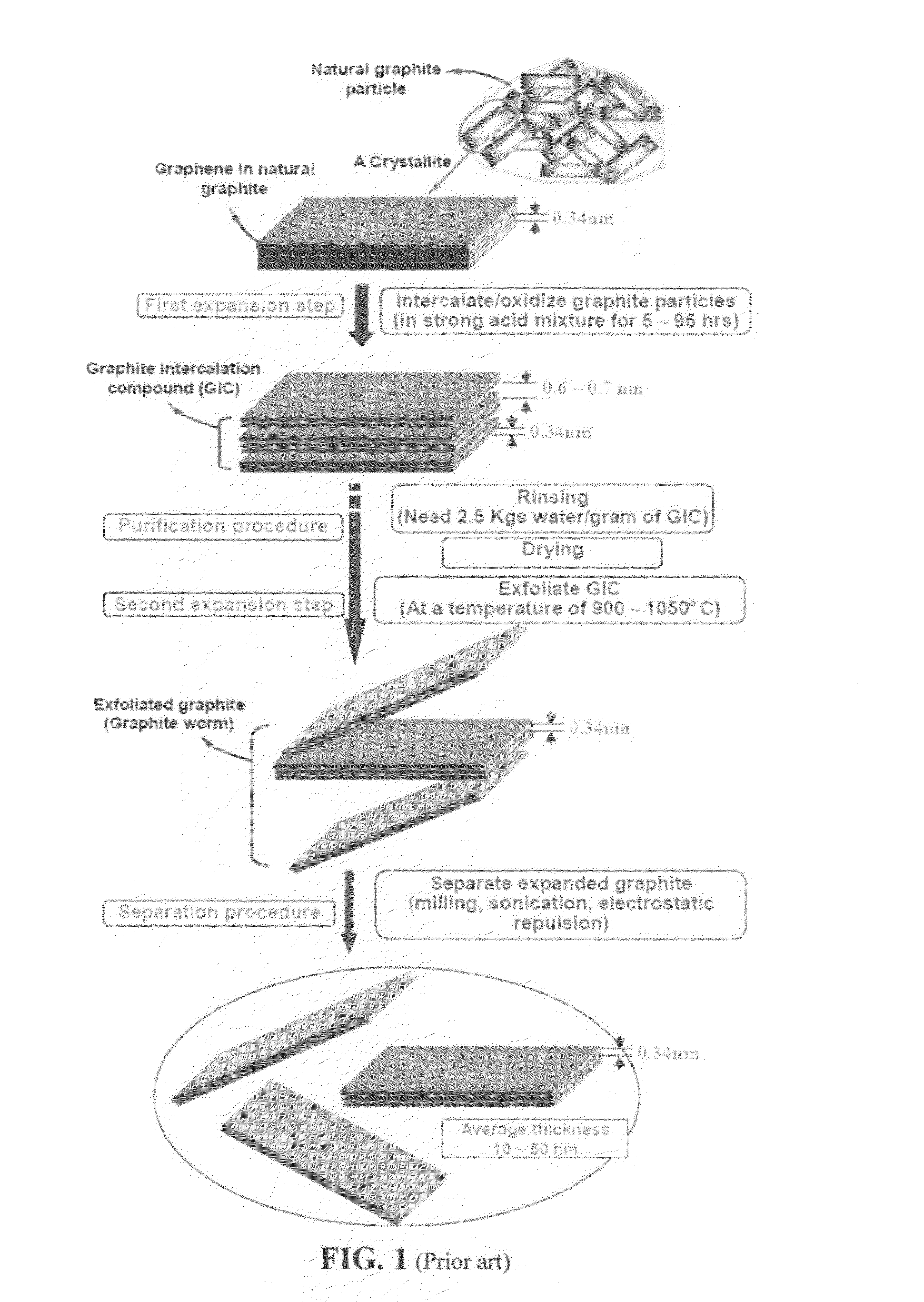
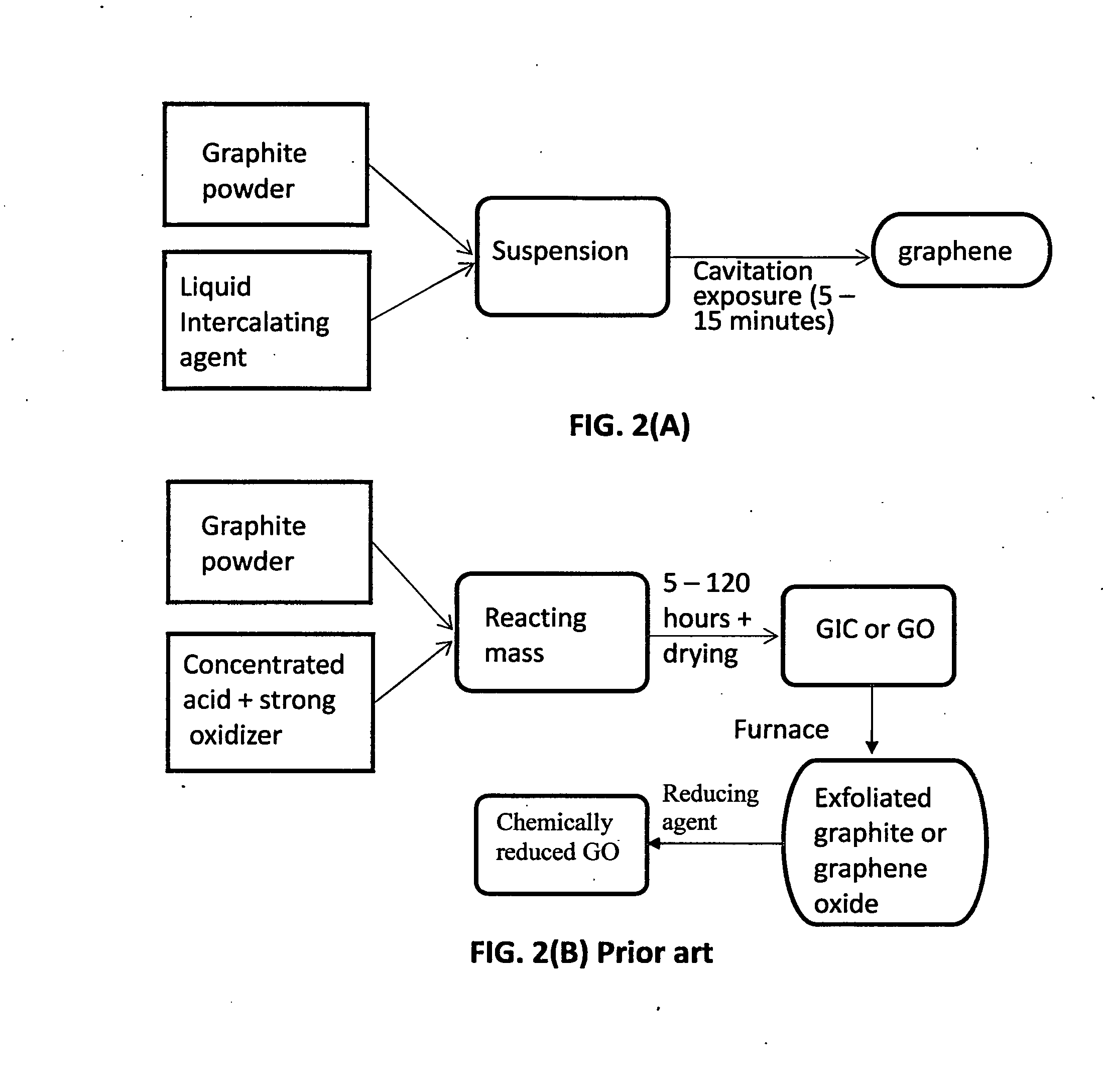
Production of graphene materials in a cavitating fluid
ActiveUS20150239741A1Shorten the timeReduce lossesCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationGraphiteCavitationLiquid medium
The invention provides a method of producing a graphene material from a starting graphitic material. In an embodiment, the method comprises: (a) dispersing the starting graphitic material in a liquid medium to form a graphite suspension; and (b) introducing the graphite suspension into a hydrodynamic cavitation reactor that generates and collapses cavitation or bubbles in the liquid medium to exfoliate and separate graphene planes from the starting graphitic material for producing the graphene material. The process is fast (minutes as opposed to hours or days of conventional processes), environmentally benign, and highly scalable. The reactor can concurrently perform the functions of graphene production, chemical functionalization, dispersion, and mixing with a polymer to make a composite.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
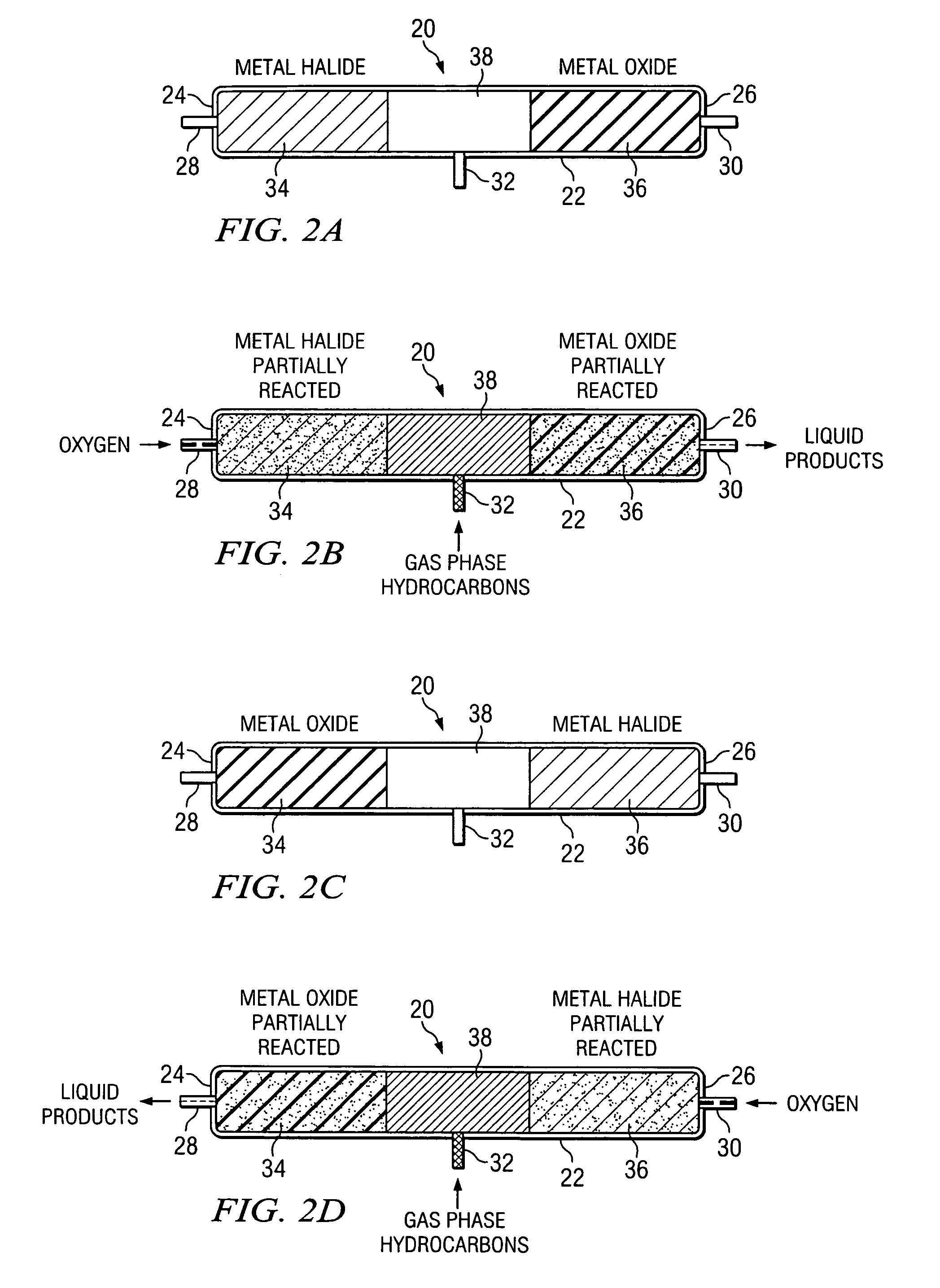
Method of hydrocarbon preservation and environmental protection
InactiveUS7019182B2Preparation by oxidation reactionsOxygen-containing compound preparationLiquid productGas phase
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
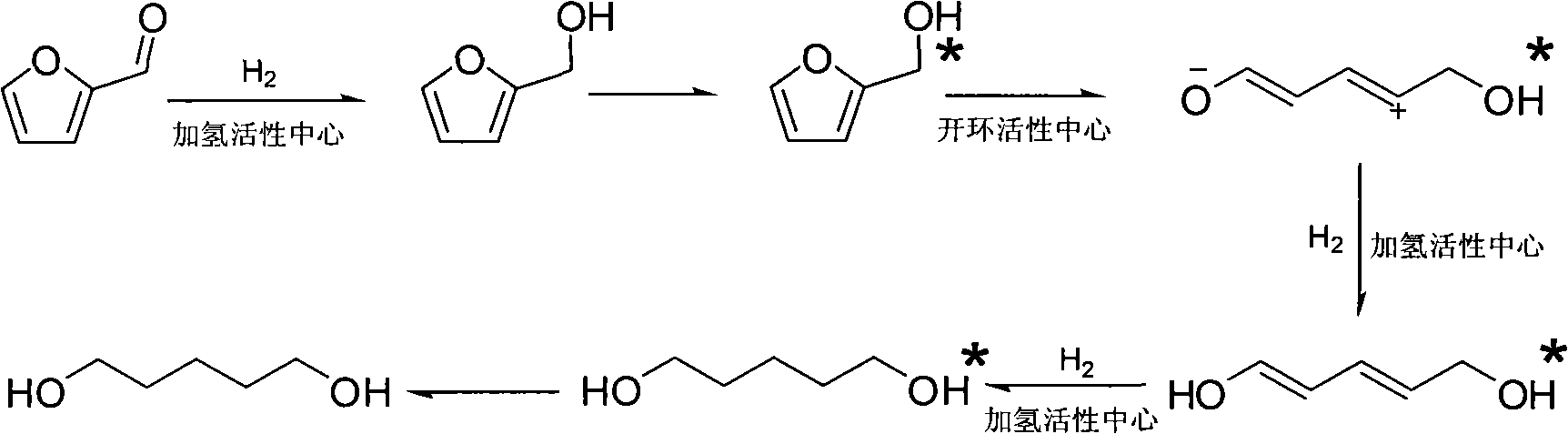
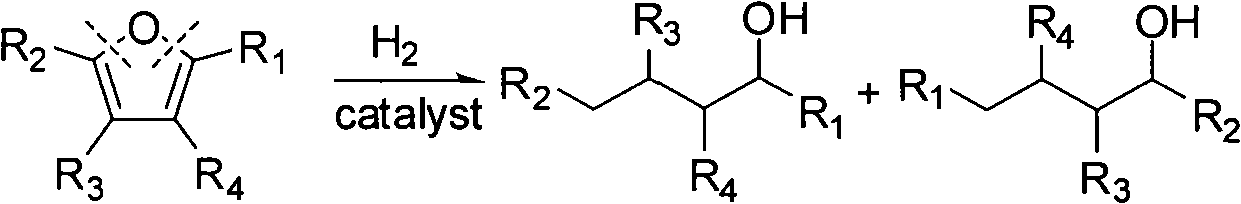
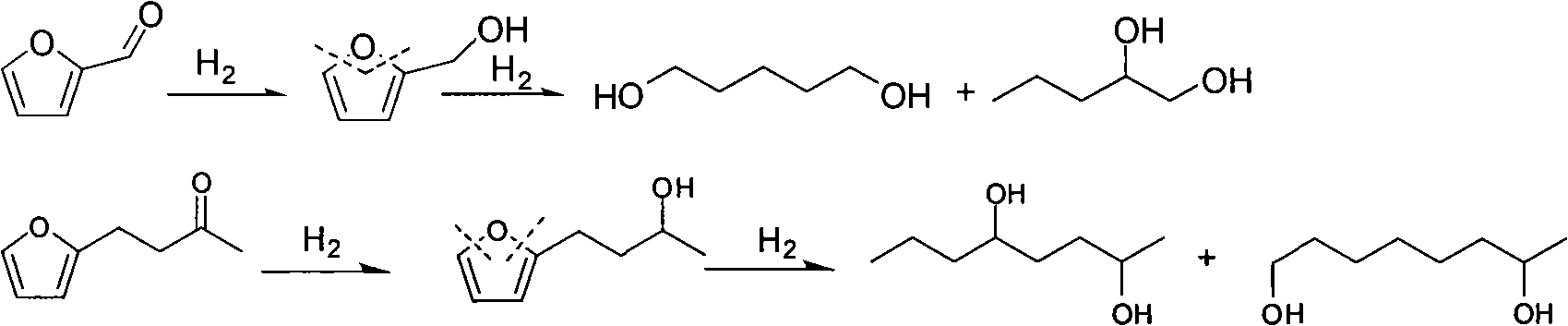
Catalyst used in ring-opening hydrogenation reaction of furan derivative
InactiveCN102068986AHigh activityGood choicePreparation by hydrogenationHydroxy group formation/introductionFuranHydrogenation reaction
The invention relates to a catalyst used in a ring-opening hydrogenation reaction of a furan derivative. The catalyst is applied to direct preparation of one-step ring-opening hydrogenation of 1,5-pentanediol and 1,2-pentanediol by taking furfural or furfuryl alcohol serving as a raw material under a mild condition. The catalyst can provide two active ingredients, namely the ring-opening active center of a transition metal oxide and the hydrogenation active center of Pt, Pd, Rh, Ru, Co or Ni, wherein the active center of the transition metal oxide is mainly used for adsorbing furfural or furfuryl alcohol and directly hydrogenating a furan ring for opening the furan ring; and the hydrogenation active center of a noble metal or Co, Ni and the like is mainly used for quickly hydrogenating an intermediate material and hydrogenating subsequent enol so as to obtain 1,5-pentanediol and 1,2-pentanediol. An environmentally-friendly, reproducible, low-cost, mild and effective method is provided for producing 1,5-pentanediol and 1,2-pentanediol. The high-performance ring-opening hydrogenation catalyst is also suitable for the ring-opening hydrogenation reaction of other furan derivatives.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process for the production of synthesis gas
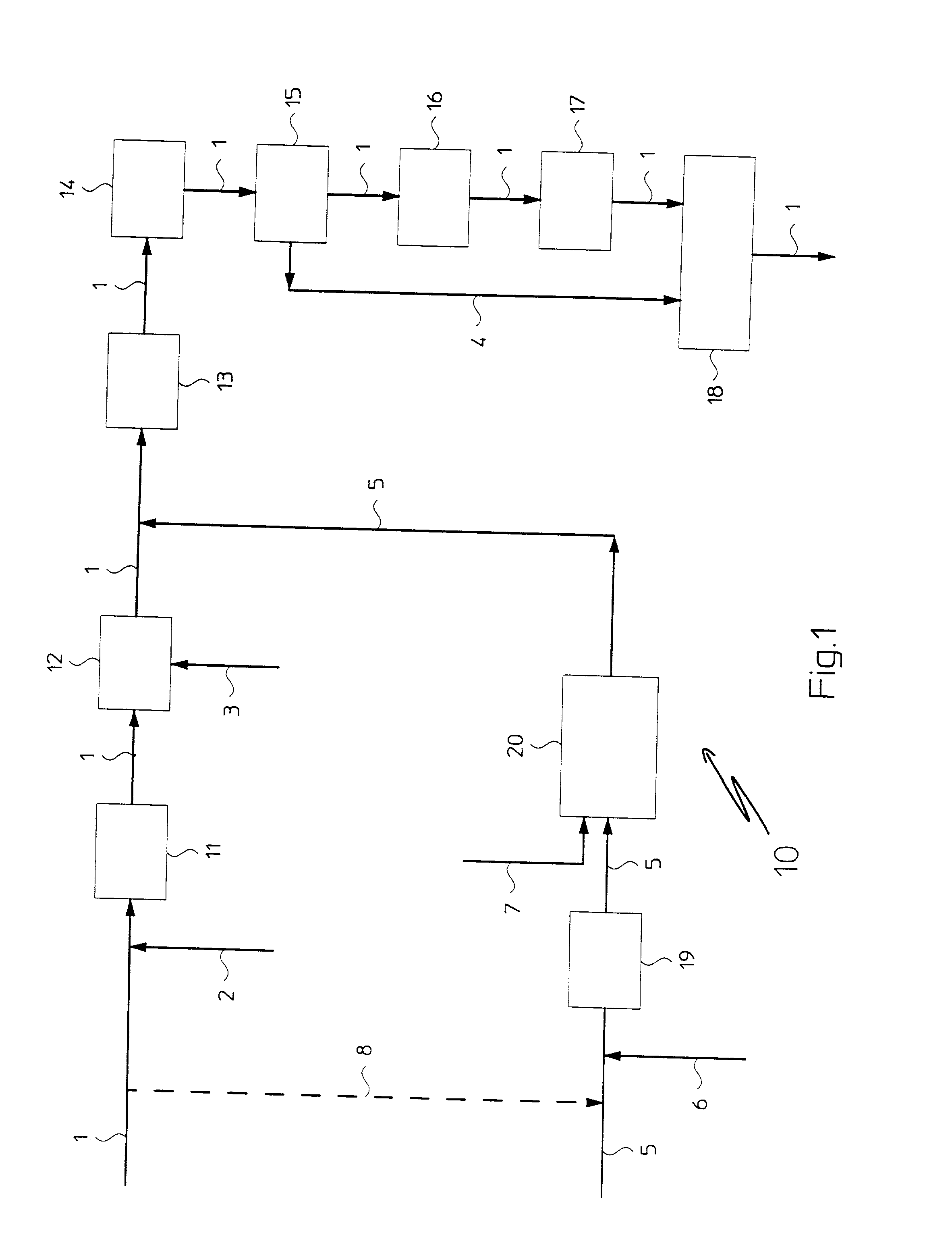
InactiveUS20010006615A1Improve conversion yieldOxygen-containing compound preparationPreparation by oxidation reactionsSyngasThermodynamics
A process for the production of synthesis gas for obtaining compounds such as ammonia or methanol, in which hydrocarbons and steam are reacted first in a primary reforming section (11) and then-together with oxygen-in a secondary reforming section (12), thus obtaining CO, CO2, H2 and possibly N2 which are then fed to a carbon monoxide conversion section (13, 14), is distinguished by the fact of reacting hydrocarbons, steam and oxygen in an autothermal reforming section (20) provided in parallel with respect to other reforming sections (11, 12), and feeding the so produced CO, CO2, H2 and possibly N2 to the carbon monoxide conversion section (13, 14).
Owner:BADANO MARCO
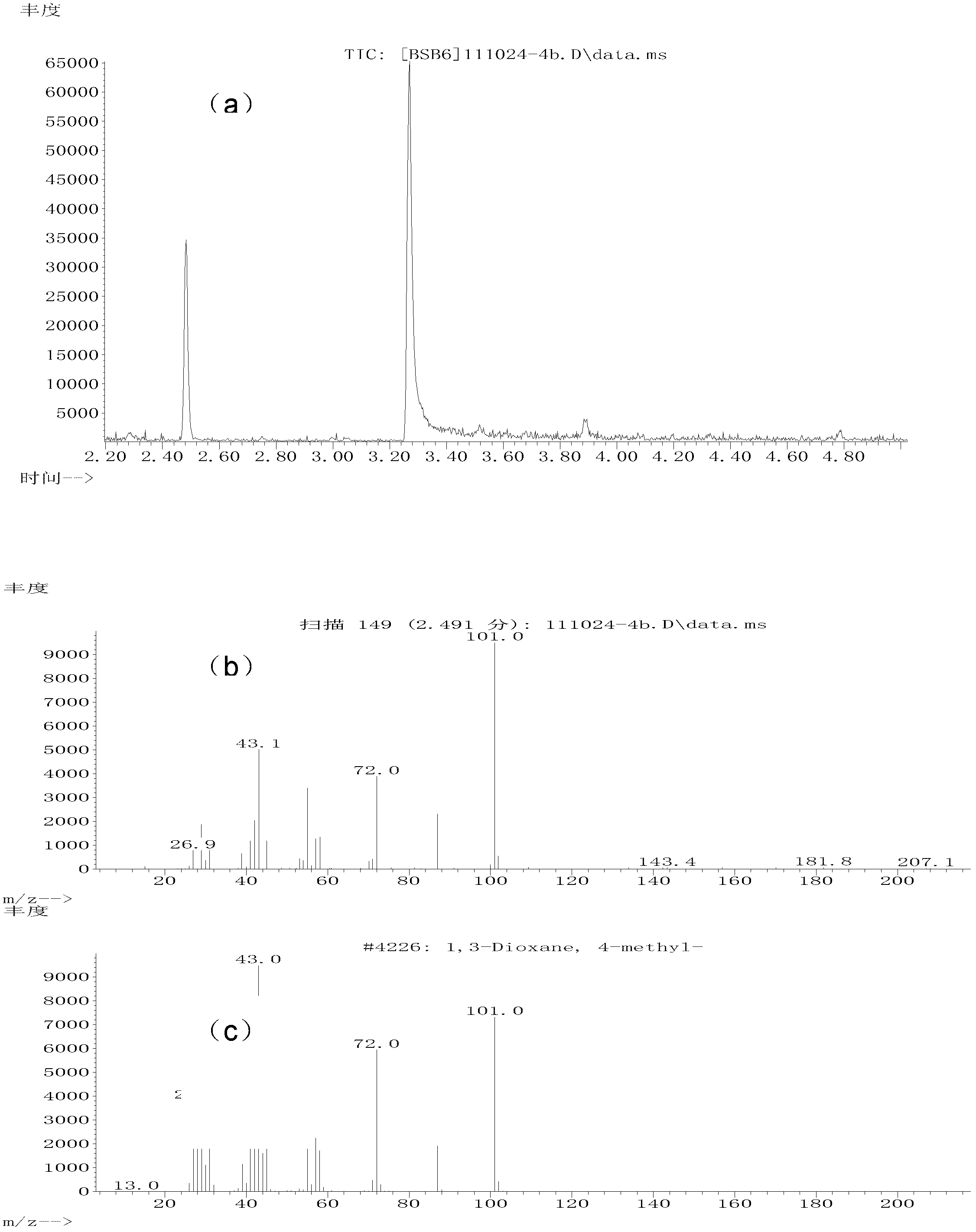
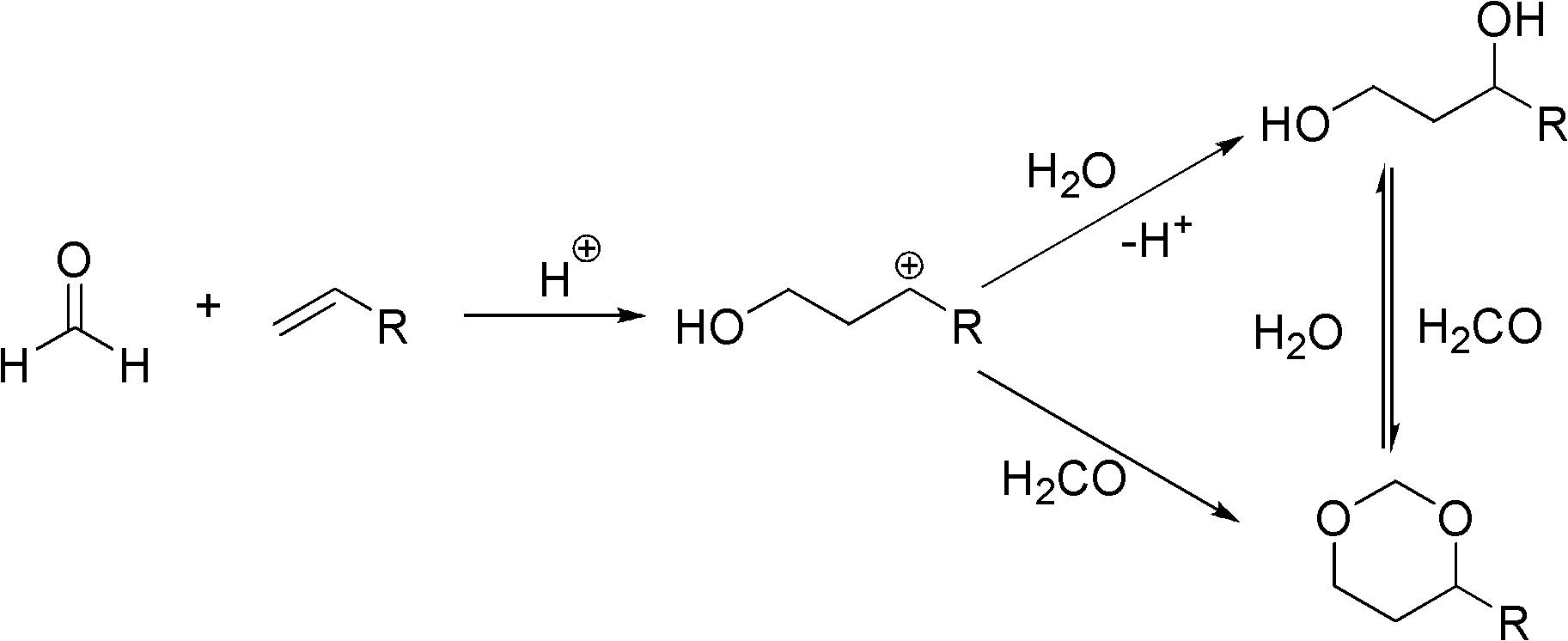
Method for preparing 1,3-dihydric alcohol directly from olefin
ActiveCN103102229AEasy to makeIncrease varietyOrganic compound preparationHydroxy group formation/introductionDiolAlkane synthesis
The invention relates to a method for preparing 1,3-dihydric alcohol directly from olefin. The method employs formaldehyde, olefin and water as reaction substrates to directly prepare 1,3-dihydric alcohol under the effect of an acid catalyst. The process is as follows: mixing formaldehyde, olefin and water with the catalyst; placing the mixture into a pressure vessel for sealing; stirring; and reacting for longer than 2 h at a reaction temperature higher than 80 DEG C. After the reaction, the catalyst is easily separated from the reaction system and can be reused for many times, and yield of 1,3-dihydric alcohol is up to 95%.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
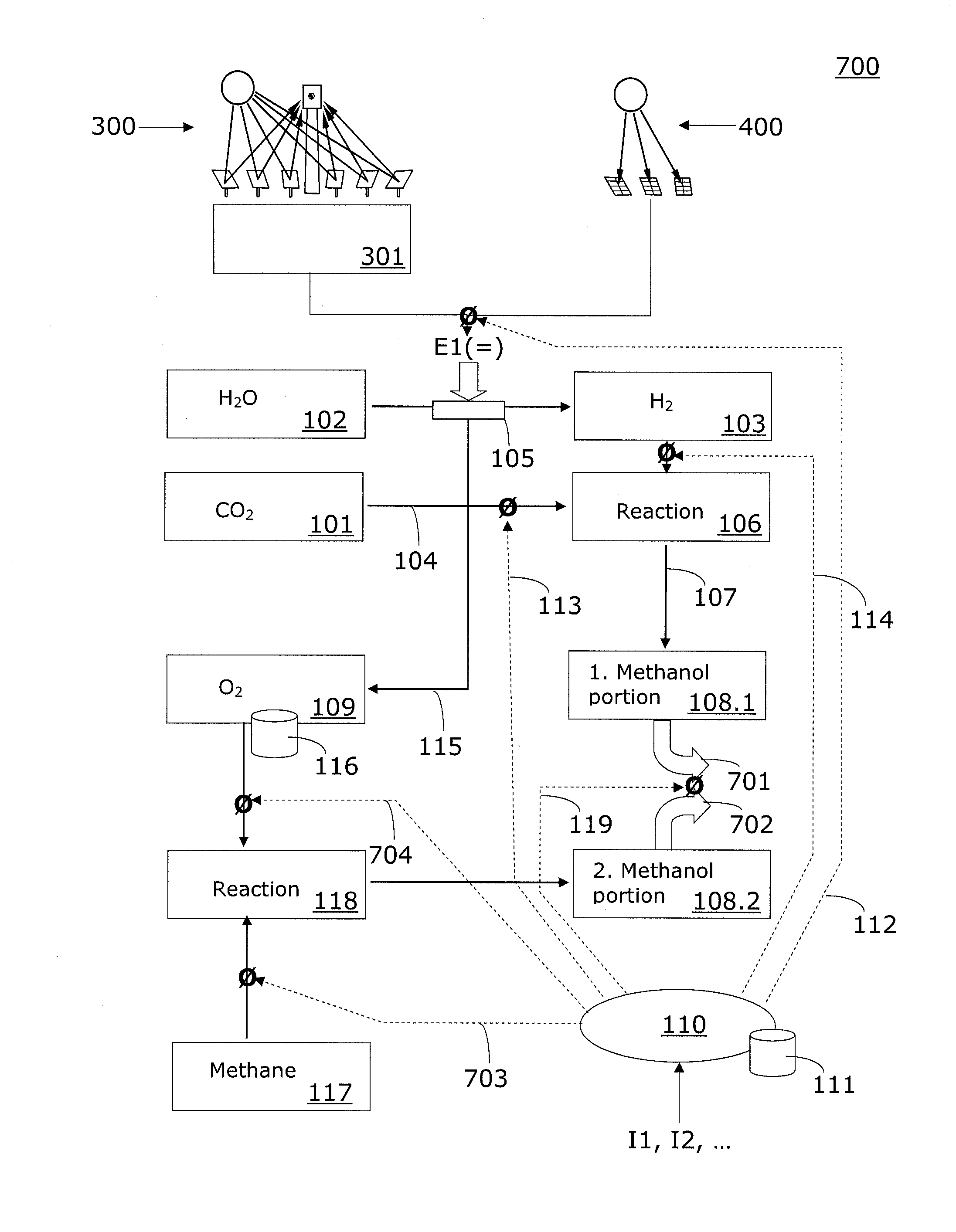
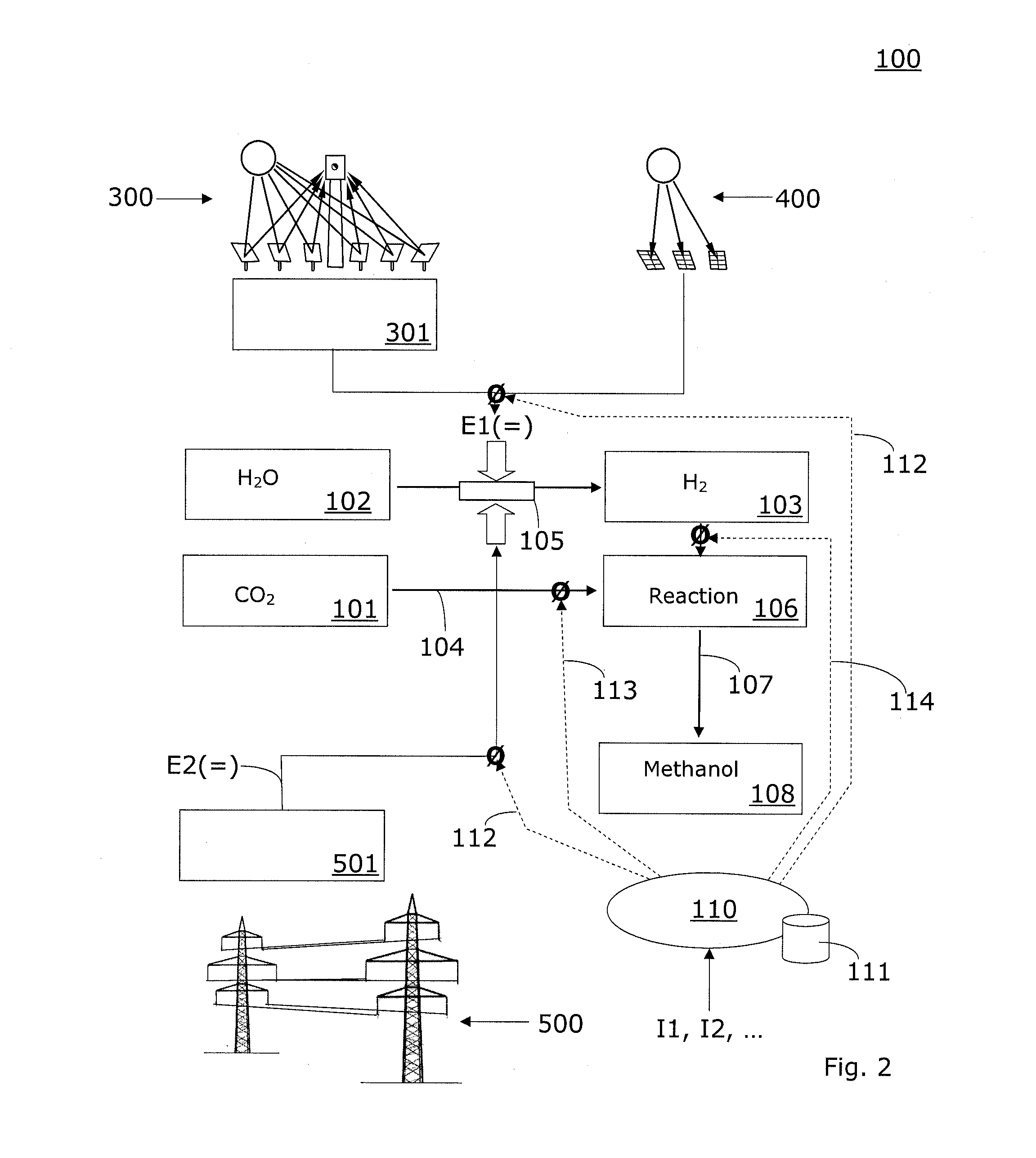
Method and system for providing a hydrocarbon-based energy carrier using a portion of renewably produced methanol and a portion of methanol that is produced by means of direct oxidation, partial oxidation, or reforming
InactiveUS20120226080A1Reduction of worldwide emissionImprove balanceOxygen-containing compound preparationPreparation by oxidation reactionsPartial oxidationWind power
Methanol is produced as a storable and transportable carbon-based energy carrier using at least two different methods. To produce a first methanol portion, water is electrolyzed, preferably using energy from renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power, to produce hydrogen. The hydrogen is then reacted with carbon dioxide to produce the first methanol portion. To produce a second methanol portion, methane is reacted with oxygen. A controller can advantageously be used to control the amount of chemicals in each reaction.
Owner:SILICON FIRE AG
Oxyfunctionalization of polyolefins
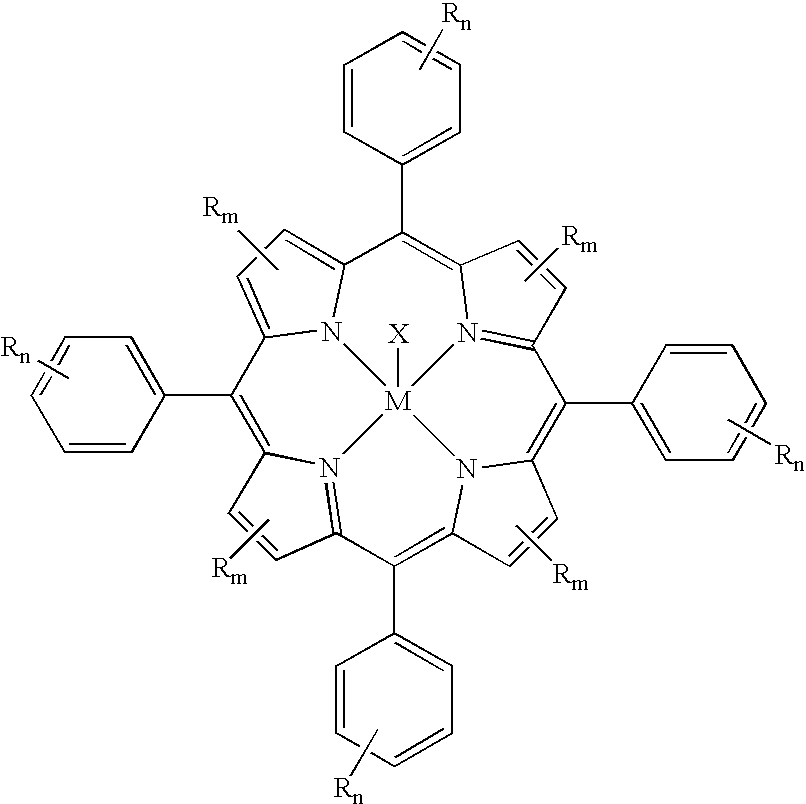
ActiveUS6953868B2Oxygen-containing compound preparationPreparation by oxidation reactionsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
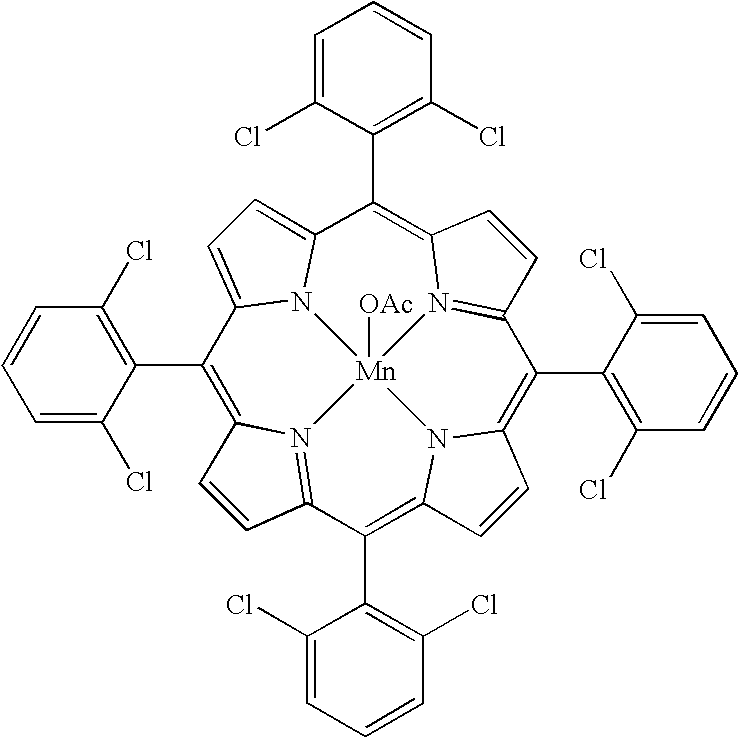
The present invention is a method for oxyfunctionalizing, that is, introducing oxygen functionality to, a polyolefin such as polypropylene and poly(ethylene-alt-propylene). The polyolefin is contacted with an oxygen source such as a persulfate and catalytic amounts of a metal porphyrin complex under mild conditions to yield an oxyfunctionalized polymer that has a polydispersity that is very similar to that of the starting polymer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Shaped, activated metal, fixed-bed catalyst
InactiveUS6262307B1Small volumeOrganic reductionOxygen-containing compound preparationFixed bedVolumetric Mass Density
A shaped, activated metal, fixed-bed catalyst with a pore volume of 0.05 to 1 ml / g and an outer activated layer consisting of a sintered, finely-divided, catalyst alloy and optionally promoters. The catalyst alloy has metallurgical phase domains, resulting from the method of preparation of the alloy, in which the largest phase by volume has a specific interface density of more than 0.5 mum-1.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Catalyst and process using the catalyst
InactiveUS20090177016A1High activityHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy group formation/introductionParticulatesOxygen
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method for deriving methanol from waste generated methane and structured product formulated therefrom
InactiveUS20060264683A1Less capitolInexpensively separatedPreparation by oxidation reactionsOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystReactive distillation
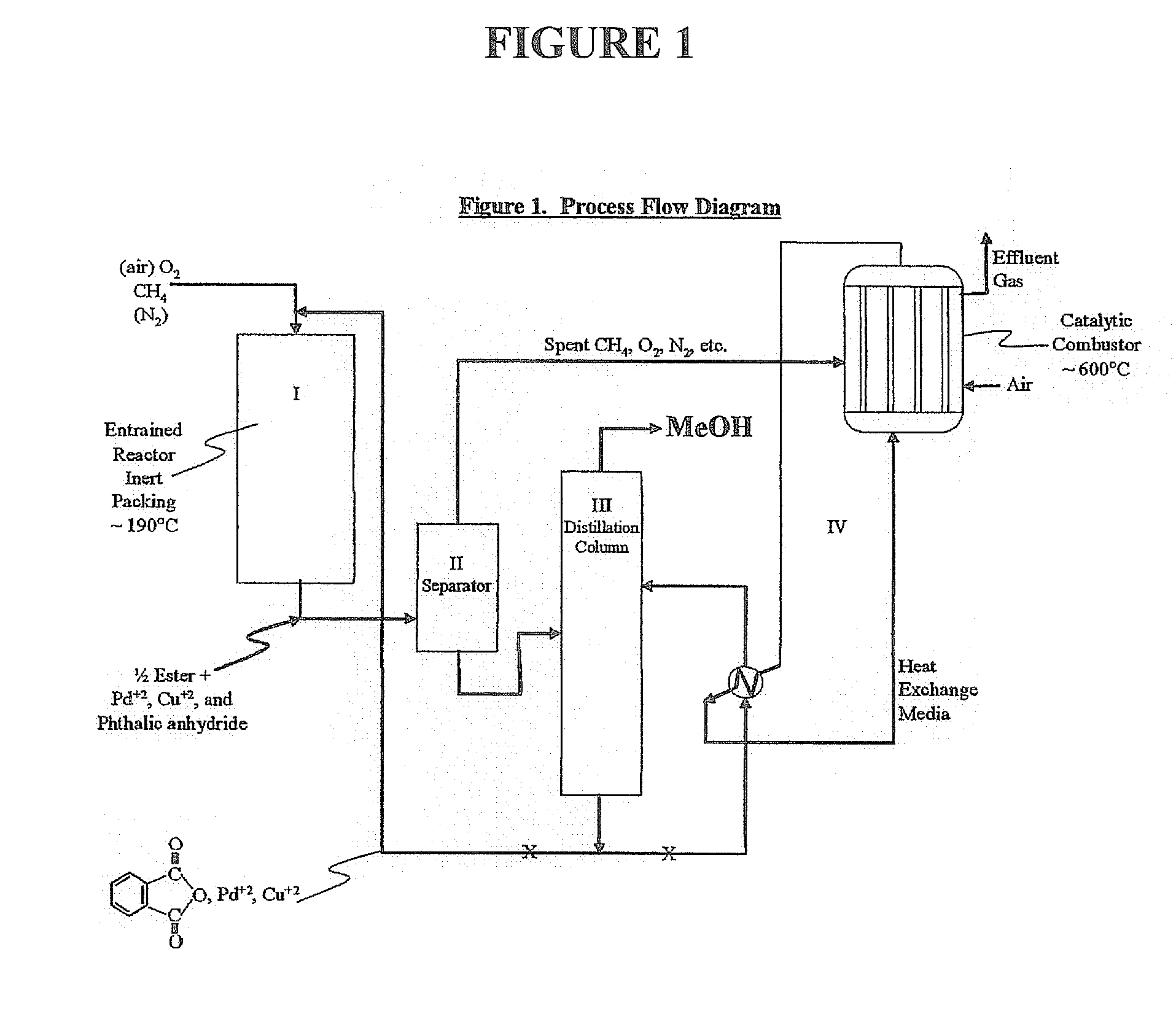
Methanol is produced from bacterially oxidized waste methane by reaction with Pd+2, Cu+2 air, and molten phthalic anhydride in an entrained oxidizer generating half ester of methyl phthalate which is reaction distilled to prodtice methanol and recycle phthalic anliydride containing the Pd+2,Cu+2 phthalate catalyst.
Owner:RINNOVI
Catalyst based on cobalt and/or rhodium employed in a two-phase medium
InactiveUS6677268B2Oxygen-containing compound preparationPreparation by oxidation reactionsPhosphoniumNitrogen
An improved catalyst based on cobalt and / or rhodium dissolved in a non-aqueous ionic solvent which is liquid at a temperature of less than 90° C. More particularly, the catalyst comprises at least one complex of cobalt and / or rhodium co-ordinated with at least one nitrogen-containing ligand and the non-aqueous ionic solvent comprises at least one quaternary ammonium and / or phosphonium cation and at least one inorganic anion.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method of hydrocarbon preservation and environmental protection
InactiveUS20050043572A1Preparation by oxidation reactionsOxygen-containing compound preparationLiquid productGas phase
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
Method for direct-oxygenation of alkane gases
InactiveUS7456327B2Organic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationPreparation by oxidation reactionsAlkaneReactor system
A method for alkyl oxygenate (e.g., methanol) manufacture via partial oxidation of alkane (methane) uses an injectively-mixed backmixing reaction chamber in fluid communication with a tubular-flow reactor. Alkyl free radicals are induced in the backmixing reaction chamber prior to being fed through a flow-restriction baffle to the tubular-flow reactor. Injective intermixing of feed streams agitates the backmixing reaction chamber. In one embodiment, a variable position flow restriction baffle is axially moved to commensurately modify the backmixing reaction chamber and tubular-flow reactor volumes. In another embodiment, the tubular-flow reactor is quenched with a variable position quenching input. The method further provides for condensing the output stream from the reaction system in a condensing scrubber and also for recycling a portion of the scrubbed output stream to the reactor system.
Owner:GAS TECH
Combined production method for substituted benzaldehyde, substituted benzyl alcohol and substituted benzoic acid
ActiveCN105237317AAvoid the major pitfalls of rectification separationsIncrease profitPreparation by oxidation reactionsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationBenzoic acidDistillation
The invention discloses a combined production method for substituted benzaldehyde, substituted benzyl alcohol and substituted benzoic acid. The method comprises the following steps: (1) oxidation: a step of continuously introducing substituted toluene, a catalyst and oxygen-contained gas into an oxidation reactor and carrying out reaction so as to obtain oxidation reaction liquid; (2) hydrolyzation: a step of allowing the oxidation reaction liquid to continuously enter a hydrolysis reactor, and continuously adding water into the hydrolysis reactor and carrying out reaction so as to obtain a hydrolysis reaction mixture; (3) liquid-liquid layering: a step of layering the hydrolysis reaction mixture so as to obtain an oil phase and an aqueous phase; and (4) separation of products: a step of subjecting the oil phase to distillation so as to respectively obtain incompletely-reacted substituted toluene, substituted benzyl alcohol and substituted benzaldehyde, and subjecting the aqueous phase to cooling, crystallizing and filtering so as to obtain filtrate and substituted benzoic acid. The combined production method provided by the invention has the advantages of high raw material conversion rate, few by-products, good selectivity of target products, greenness and environmental protection.
Owner:山东友道化学有限公司
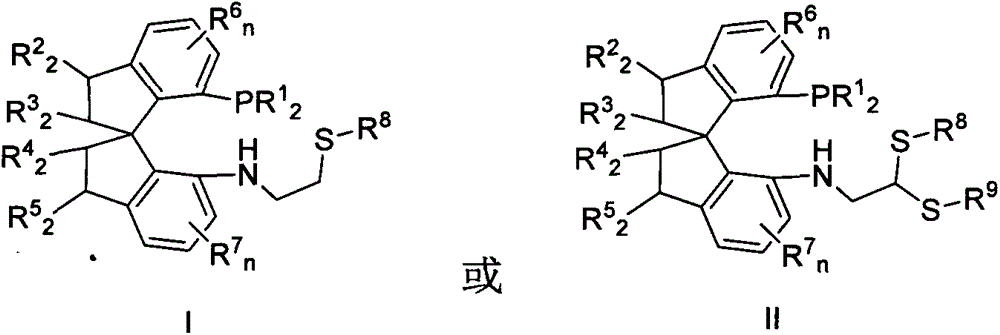
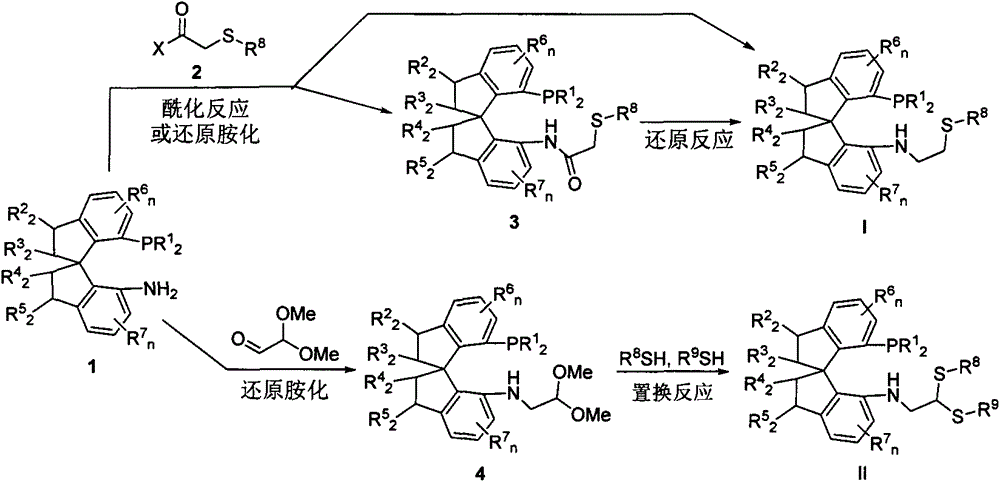
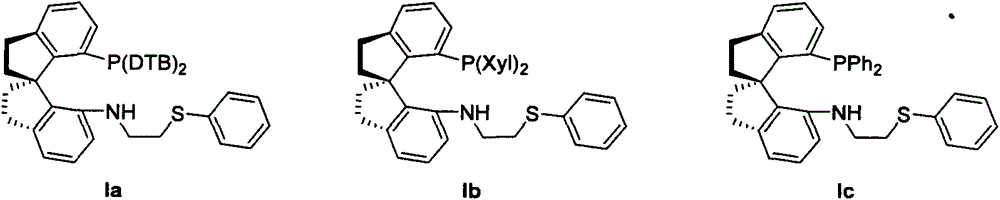
Chiral spiro phosphine-nitrogen-sulfur tridentate ligand and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104892672AHigh catalytic activityHigh enantioselectivityCarbamic acid derivatives preparationIndium organic compoundsIridiumSulfur
The invention relates to a chiral spiro phosphine-nitrogen-sulfur tridentate ligand and a preparation method and application thereof. The chiral spiro phosphine-nitrogen-sulfur tridentate ligand is a compound with a formula I or formula II, or a racemate or optical isomer thereof, or a catalytically-acceptable salt thereof, and has the main structure characteristic of having a chiral spiro indan skeleton and a sulfoether group. The chiral spiro phosphine-nitrogen-sulfur tridentate ligand can be synthesized from chiral starting materials of 7-diaryl / alkyl phosphino-7'-amino-1,1'-spiro indan compound with a spiro skeleton. The chiral spiro phosphine-nitrogen-sulfur tridentate ligand and transition metal salt form a complex, which can be used in catalysis of an asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation reaction of a carbonyl compound. Especially, the iridium complex shows high catalytic activity (catalyst amount of 0.0002% mol) and enantioselectivity (up to 99.9%ee) in asymmetric hydrogenation reaction of beta-alkyl-beta-keto ester, and has practical value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG RAYBOW PHARM CO LTD
Process for the partial oxidation of hydrocarbon and process for preparation of oxygen-containing organic compound
InactiveUS6124505AEfficient partial oxidationHigh catalytic activityPreparation by oxidation reactionsOrganic compound preparationPartial oxidationGold particles
The invention provides a catalyst for partial oxidation of hydrocarbon in the presence of a reducing compound, the catalyst comprising ultra-fine gold particles immobilized on a titanium-containing oxide, and a process for preparing an oxygen-containing organic compound, the process comprising the step of oxidizing hydrocarbon with oxygen in the presence of the above catalyst and a reducing compound.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
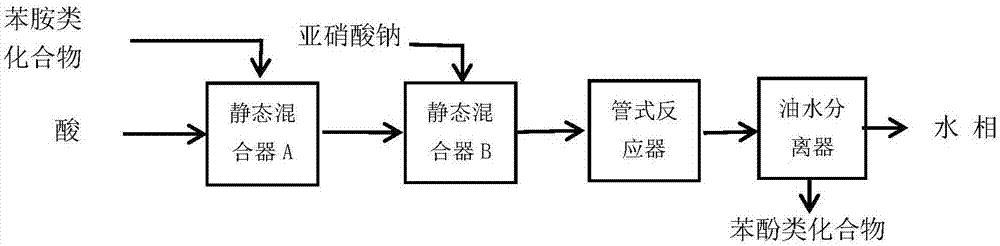
Method for continuous flow synthesis of phenol-based compound
InactiveCN106905096AOrganic compound preparationHydroxy group formation/introductionContinuous flowAniline
The present invention provides a method for continuous flow synthesis of a phenol-based compound represented by a formula (III), wherein the method is performed in two static mixers, a tubular reactor and an oil-water separator, wherein the two static mixers, the tubular reactor and the oil-water separator are sequentially connected in series. The method comprises that an acid solution and an aniline compound represented by a formula (I) are pumped into the static mixer A; the mixture of the acid solution and the compound represented by the formula (I) flows out from the static mixer A and flows into the static mixer B connected to the static mixer A; a sodium nitrite solution is pumped into the static mixer B, and a reaction is performed to produce a diazonium salt solution represented by a formula (II); and the solution represented by the formula (II) flows out from the static mixer B, is pumped into the tubular reactor connected to the static mixer B, and then into the oil-water separator connected to the tubular reactor, and the water phase is separated to obtain the compound represented by the formula (III). According to the present invention, the method has characteristics of short reaction time, solvent saving and high yield, and can well solve the problems in the synthesis of the phenol-based compound through diazotization hydrolysis in the intermittent kettle type reactor. The formulas (I), (II) and (III) are defined in the specification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
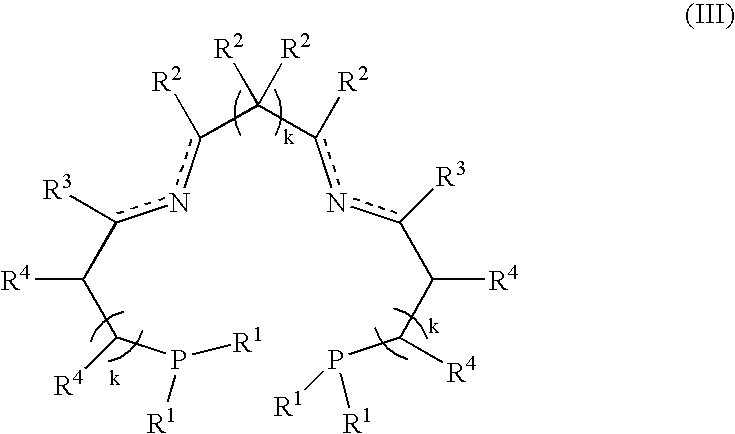
Process for hydrogenation of carbonyl and iminocarbonyl compounds using ruthenium catalysts comprising tetradentate diimino-diphosphine ligands
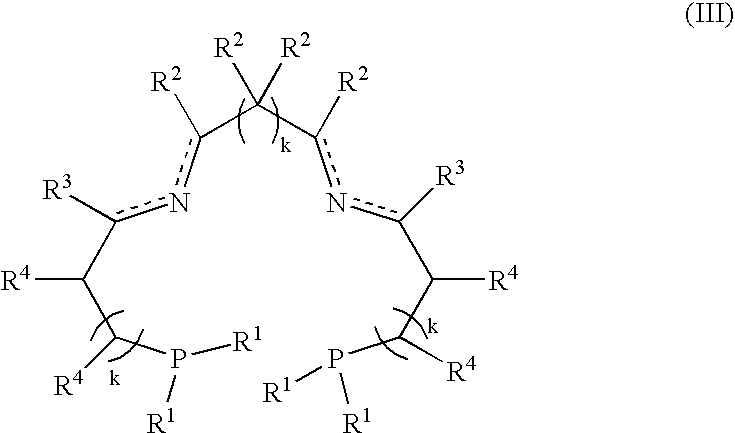
A process for the hydrogenation, using molecular hydrogen (H2), of a catalytic system, wherein the catalytic system comprises a base and a complex of formula; (II) wherein Y represents simultaneously or independently a hydrogen or halogen atom, a hydroxy group, or an alkoxy, carboxyl or other anionic radical, and N2P2 is a tetradentate diimine-diphosphino ligand.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Electrochemical deblocking solution for electrochemical oligomer synthesis on an electrode array
InactiveUS20070034513A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsElectrolysis componentsOligomerElectrochemistry
There is disclosed an electrochemical deblocking solution for use on an electrode microarray. There is further disclosed a method for electrochemical synthesis on an electrode array using the electrochemical deblocking solution. The solution and method are for removing acid-labile protecting groups for synthesis of oligonucleotides, peptides, small molecules, or polymers on a microarray of electrodes while substantially improving isolation of deblocking to active electrodes. The method comprises applying a voltage or a current to at least one electrode of an array of electrodes. The array of electrodes is covered by the electrochemical deblocking solution.
Owner:CUSTOMARRAY
Hydrogenation of esters with ru/bidentate ligands complexes
ActiveUS20100280273A1Ruthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationAlcoholHydrogenation process
The present invention relates to the field of catalytic hydrogenation and, more particularly, to the use of Ru complexes with bidentate ligands, having one amino or imino coordinating group and one phosphino coordinating group, in hydrogenation processes for the reduction of esters or lactones into the corresponding alcohol or diol respectively.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Method for processing asymmetric hydroxylamination and dihydroxylation reaction by use of supported bi-cinchoni alkaloid ligand
InactiveCN1524835AOrganic compound preparationHydroxy group formation/introductionHydroxylamineSide chain
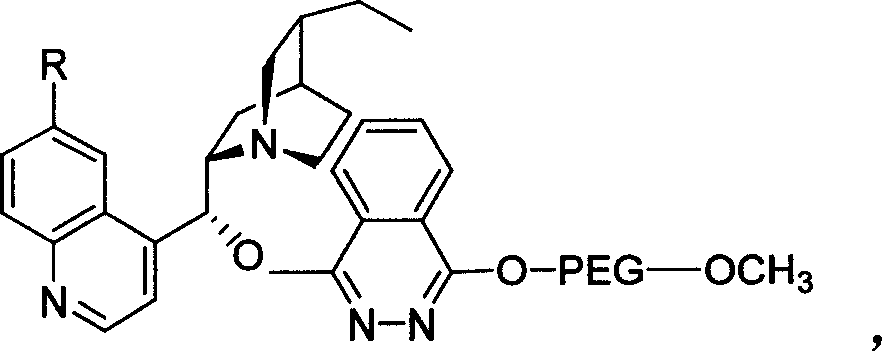
The invention relates to a process for carrying out asymmetrical hydroxylamine amination reaction and dual hydroxide reaction, wherein synthesized high polymer tethered Cinchonideine alkaloid ligand is utilized for raising yield and selectivity for the reaction product, the catalyst can be used repeatedly. The process is especially suitable for the mass production of Taxol synthesis and its C13 side chains, the used synthesized high polymer tethered Cinchonideine alkaloid ligand has the structural formula as disclosed in the specification, wherein PEG is polyoxyethylene glycols, R=H or OCH3.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for hydrogenation of carbonyl and iminocarbonyl compounds using ruthenium catalysts comprising tetradentate diimino-diphosphine ligands
A process for the hydrogenation, using molecular hydrogen (H2) of a catalytic system, wherein the catalytic system includes a base and a complex of formula (II):Ru(P2N2)Y2 (II)wherein Y represent simultaneously or independently a hydrogen or halogen atom, a hydroxy group, or an alkoxy, carboxyl or other anionic radical, and P2N2 is a tetradentate diimino-diphosphine ligand.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Novel ruthenium complex and method for preparing methanol and diol
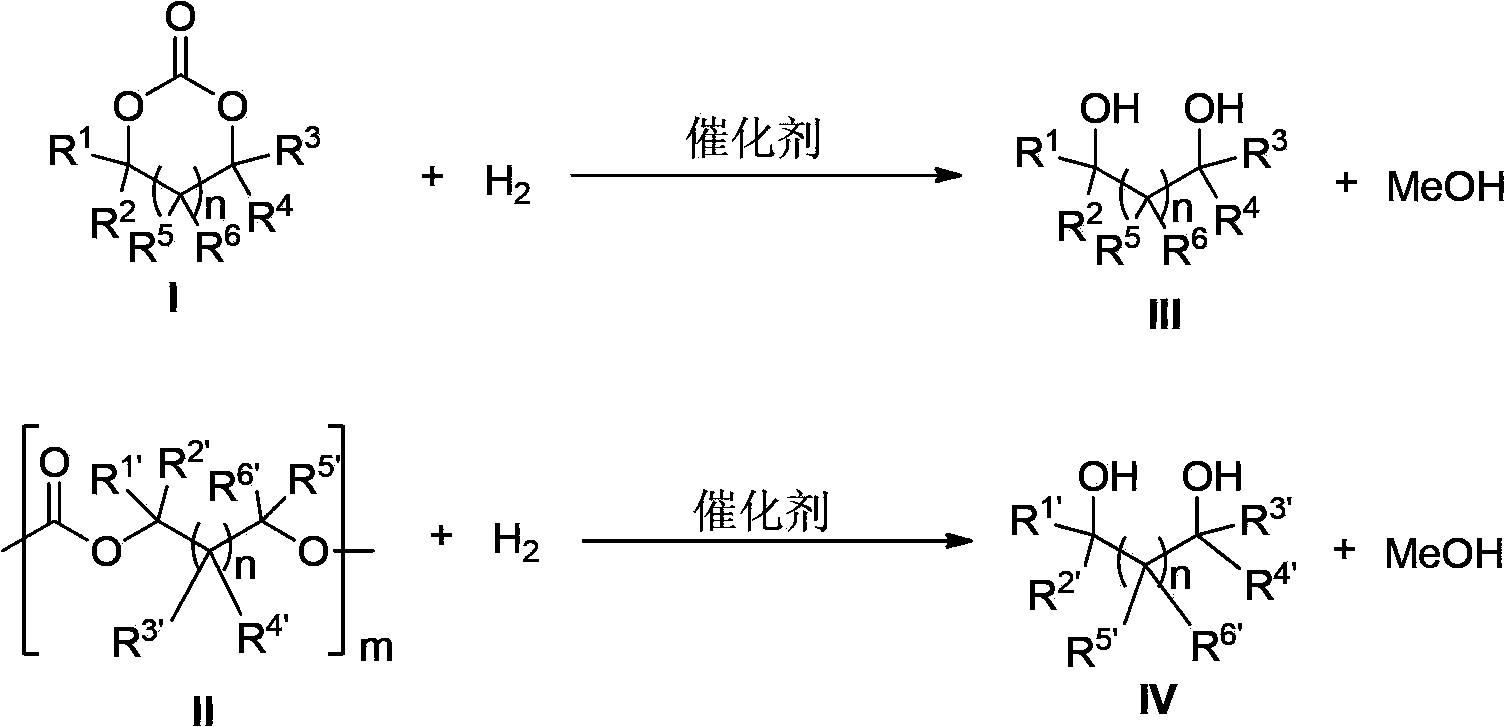
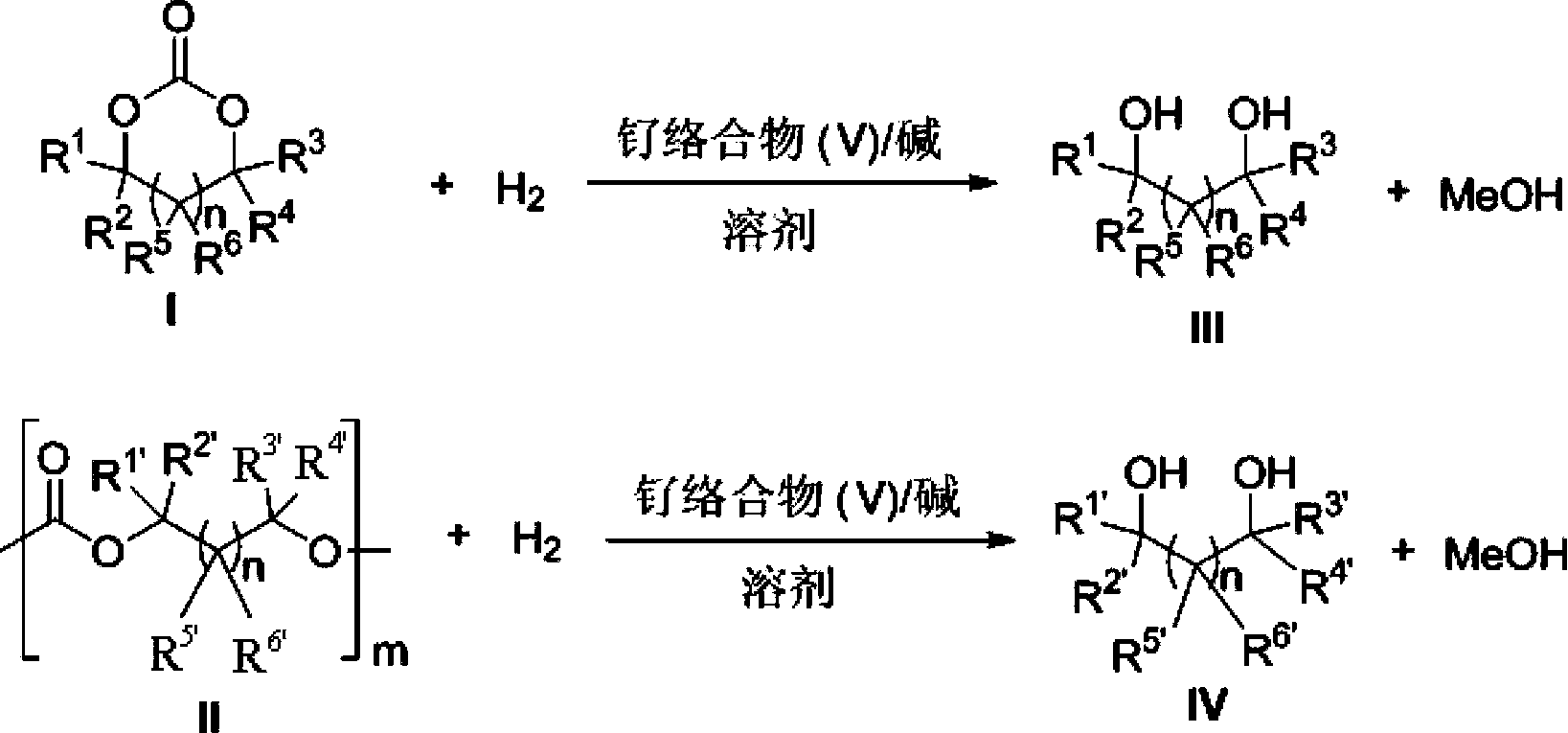
ActiveCN103772142AFacilitate large-scale industrial productionImprove efficiencyRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationOrganic solventHydrogen atmosphere
The invention provides a method for preparing methanol and diol from cyclic carbonates and polycarbonates. The method comprises: in hydrogen atmosphere, in an organic solvent, and in the presence of a ruthenium complex (Ru(L)XYY') and an alkali, performing hydrogenation reduction reaction on a cyclic carbonate or a polycarbonate, so as to obtain methanol and diol, wherein all groups in the formula are defined in the specification. The invention also provides the ruthenium complex formed by ruthenium and a tridentate amino diphosphine ligand. The invention also provides a method for preparing deuterated methanol and deuterated diol by employing the above preparation method. The method provided by the invention is high in efficiency, high in selectivity, economic, environment-friendly, and simple for operation, can be performed under mild conditions, and has complete atom economy.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nitrogen heterocycle ligand transition metal complex, and preparation and catalytic application thereof
ActiveCN102417523AThe synthesis method is simpleRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationDiphosphinesKetone
The invention relates to a novel nitrogen heterocycle ligand / phosphine ligand transition metal complex, and preparation and application thereof in asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation and hydrogen transfer. The complex has the following structural formula: [MLnL' XY], wherein the transition metal M is Ru, Rh, Ir, Pd, Pt, Co, Ni or Os. The complex also contains a nitrogen heterocycle ligand, two monophosphine ligands or one diphosphine ligand, and the like. The transition metal compound, dinitrogen or mononitrogen ligand and diphosphine or monophosphine ligand react at 0-120 DEG C in an organic solvent for 0.5-20 hours to obtain the complex. The complex is used for asymmetric catalytic transfer hydrogenation or asymmetric hydrogenation reaction, and especially for asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation reaction of ketones, esters, hypnones and derivatives thereof, diphenyl ketones and derivatives thereof, beta-N,N-dimethylamino-alpha hypnones and derivatives thereof and other ketone compounds of which the alpha site is a large steric hindrance alkyl group.
Owner:ENANTIOTECH CORP
Method for direct-oxygenation of alkane gases
Owner:GAS TECH
Crystalline mww-type titanosilicate catalyst for producing oxidized compound, production process for the catalyst, and process for producing oxidized compound by using the catalyst
InactiveUS20030040649A1Accurate weighingMaterial nanotechnologyPreparation by oxidation reactionsDouble bondOxidizing agent
A crystalline titanosilicate catalyst which is usable as a catalyst in the oxidation reaction of a compound having a carbon-carbon double bond and at least one other functional group, a process for producing the catalyst, and a process for producing an oxidized compound by an oxidation reaction using the catalyst. It has been found that a crystalline titanosilicate having a structural code of MWW effectively functions as a catalyst in an oxidation reaction of a compound having a carbon-carbon double bond and at least one other functional group wherein the carbon-carbon double bond of the compound is oxidized by using a peroxide as an oxidizing agent, thereby to highly selectively provide an intended oxidized compound.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Catalytic hydrogenation processes
ActiveUS20040063966A1High hydrogenation yieldHigh yieldRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationHalogenHydrogen
The catalysts of formula (II): [Ru(L)m(L')wXY], wherein X and Y represent simultaneously or independently a hydrogen or halogen atom, a hydroxy group, or an alkoxy, carboxyl or other anionic radical, m is 1 or 2, w is 1 when m is 1 and w is 0 when m is 2, L is a phosphino-amine or phosphino-imine bidentate ligand and L' a diphosphine, are useful for the hydrogenation of substrates having a carbon-hetero atom double bond.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Hydrogenation method for hydroformylation mixture
InactiveCN1358701AReduce consumptionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy group formation/introductionAlcoholHydrogen
The present invention provides a process, which includes: in a homogeneous liquid phase including water, and over a fixed-bed catalyst, continuously hydrogenating at least one hydroformylation product obtained from a hydroformylation of one or more C4-16 olefins to produce at least one output mixture; wherein the output mixture includes at least one corresponding alcohol and from 0.05 to 10% by weight of water; and wherein in a steady-state operation of the process, from 3 to 50% more hydrogen is fed to the hydrogenation than is consumed by the hydrogenation.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Catalytic conversion of alcohols and aldehydes
ActiveUS20130211146A1Reduce decreaseSuitable for preparationOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationActivated carbonCatalytic transformation
The invention provides a process for preparing higher alcohols and / or aldehydes and also mixtures thereof by catalytic reaction of ethanol, the reaction taking place in the presence of at least one catalyst, the catalyst comprising an activated-carbon substrate which is provided with at least one metal, and more particularly has at least one metal dope.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Hydrocarbon catalyzed selective oxidation method
InactiveCN102755907AImprove adsorption capacityFacilitate desorptionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydroxy group formation/introductionSolventAldehyde
Disclosed is a hydrocarbon catalyzed selective oxidation method. Super hydrophobic nano-sized complex oxide material is used as catalyst to apply to a solvent-free hydrocarbon selective oxidation reaction. Due to the super hydrophobic property of the material, absorption of substrate and desorption of product are facilitated, and high conversion rate and selectivity of organic oxygen-contained compounds (alcohol, ketone, aldehyde, and (or) acid) are obtained simultaneously.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Popular searches
Hydroxy compound preparation Amino group formation/introduction Cyano group formation/introduction Ketenes preparation Oxygen compounds preparation by hydrocarbon oxidation Graphene Ether/acetal/ketal group formation/introduction Amino compound preparation Carboxylic preparation by oxidation Liquid hydrocarbon mixture production
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com