Molecular marker for raphanus sativus L. downy mildew resistant gene close linkage
A technology of molecular markers and resistance genes, applied in the field of crop genetics and breeding, can solve the problems affecting the accuracy of plant resistance identification results, resistance selection efficiency, and time-consuming, so as to improve the selection efficiency of radish downy mildew resistance, improve the Efficiency, the effect of overcoming environmental impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
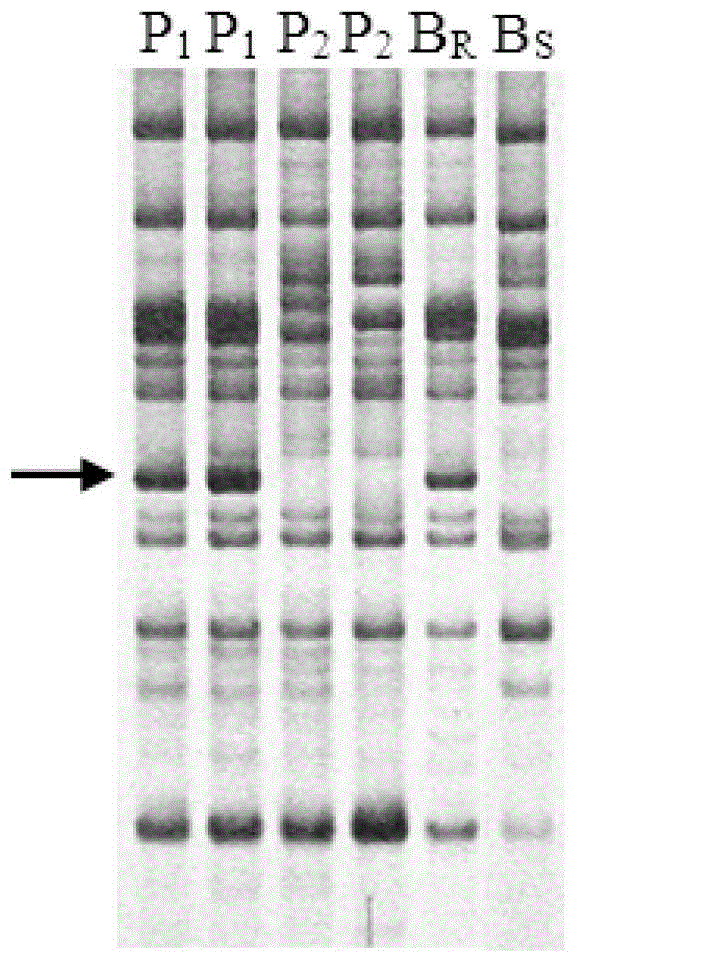
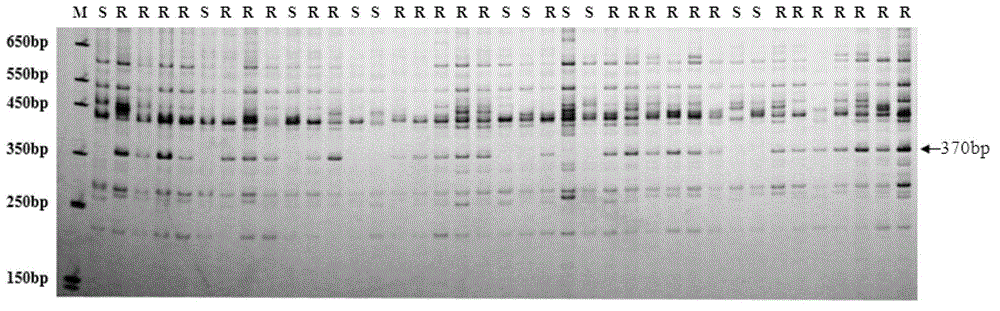
[0038] 1. Screen radish resistant materials and build a genetic research group for radish downy mildew resistance
[0039] F 1 , F 1 F 2 , while F 1 Backcrossing produces BC.
[0040] 2 Identification of individual downy mildew resistance
[0041] Rinse the mold layer and its attachments on the surface of the harvested radish downy mildew leaves with tap water, then rinse with distilled water, and place them in a dark condition at 20°C to keep moisture (RH=95%), put the diseased leaves in a petri dish During the process, the leaves were covered with moist absorbent paper or filter paper) for 24 hours, and the newly produced sporangia were gently peeled off with wet cotton balls in distilled water to make a suspension. Spore concentration, final dilution to 1×10 5 spores / mL, and finally add 0.1% Tween 20 of the calibration volume to prepare the inoculum. At the 4-leaf stage of the seedlings, use the spray method to inoculate the single leaf, the inoculation amount is 150...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com