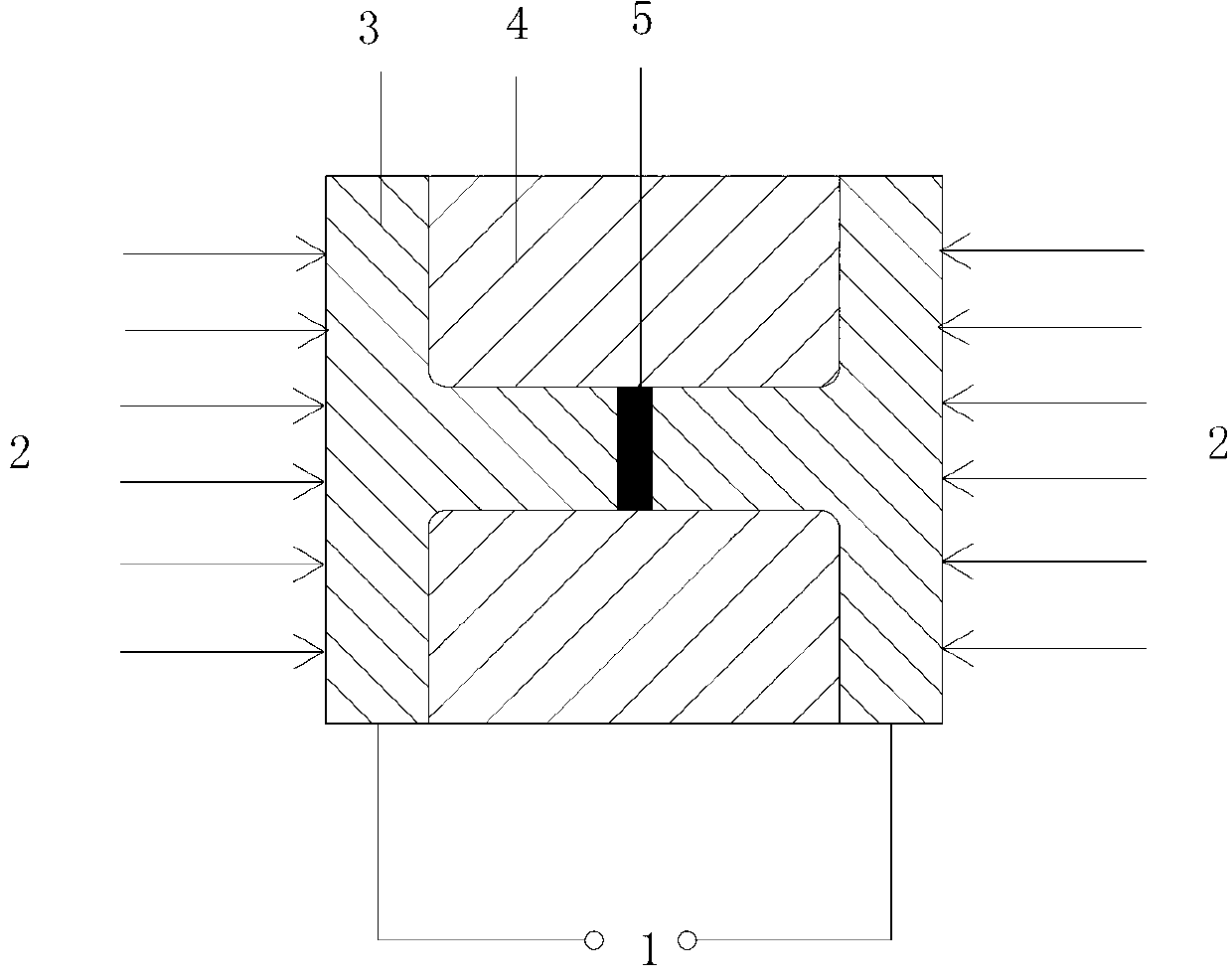
Method for preparing WC-Co hard alloy by rapid sintering under multi-physics coupling action
A rapid sintering, multi-physics technology, applied in the field of rapid sintering to prepare tungsten carbide-cobalt (WC-Co) cemented carbide, can solve the problems of complex process, environmental pollution, long preparation cycle, etc., to simplify the process flow, improve the Product quality, effect of shortening sintering time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The mass of the powder is calculated according to the size of the cemented carbide tool (the side length of the triangle is 3.26mm and the thickness is 2.4mm) and the theoretical density of the corresponding powder. Mix the powder with a weight ratio of WC:Co=94:6, weigh it evenly, put it into the mold and fix it with a chuck, and control the heating rate at 30°C / s under the vacuum condition of ≤0.01Pa. The end loading force is 100Mpa. When the temperature reaches 950°C, it is lowered to 400°C at a cooling rate of 50°C / s, and then heated to 950°C at a heating rate of 50°C / s, and the cycle is repeated for 5 times. Just take out the parts. The relative density of the parts obtained is 89.52%, the Rockwell hardness is 90.1HRA, and the coercive force is 35.43KA / m.
Embodiment 2
[0029] The mass of the powder is calculated according to the size of the cemented carbide tool (the side length of the triangle is 3.26mm and the thickness is 2.4mm) and the theoretical density of the corresponding powder. Mix the powder with a weight ratio of WC:Co=92:8, weigh it evenly, put it into the mold and fix it with a chuck, and control the heating rate at 30°C / s under the vacuum condition of ≤0.01Pa. The end loading force is 100MPa. When the temperature reaches 950°C, it drops to 400°C at a cooling rate of 50°C / s, and then reheats to 950°C at a heating rate of 50°C / s. The cycle is 5 times, and the powder is formed in the mold and completed. Dense, and finally turn off the power and air-cool and take out the parts. The relative density of the parts obtained is 95.28%, the Rockwell hardness is 92.2HRA, and the coercive force is 32.24KA / m.
Embodiment 3
[0031]The mass of the powder is calculated according to the size of the cemented carbide tool (the side length of the triangle is 3.26mm and the thickness is 2.4mm) and the theoretical density of the corresponding powder. Mix the powder with a weight ratio of WC:Co=90:10, weigh it evenly, put it into the mold and fix it with a chuck, and control the heating rate at 30°C / s under the vacuum condition of ≤0.01Pa. The end loading force is 100MPa. When the temperature reaches 950°C, it is lowered to 400°C at a cooling rate of 50°C / s, and then heated to 950°C at a heating rate of 50°C / s. The cycle is 5 times, and the powder is formed in the mold and completed. Dense, and finally turn off the power and air-cool and take out the parts. The relative density of the parts obtained is 99.89%, the Rockwell hardness is 93.1HRA, and the coercive force is 30.52KA / m.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com