A 3D Spectral Data Correction Method
A spectral data and correction method technology, applied in the direction of fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems that the component decomposition effect is greatly affected by the number of components, the quantitative analysis of the analysis results is affected, the output spectrum deviates from the actual spectrum, etc., to achieve calculation Fast speed, easy operation, and accurate calibration results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
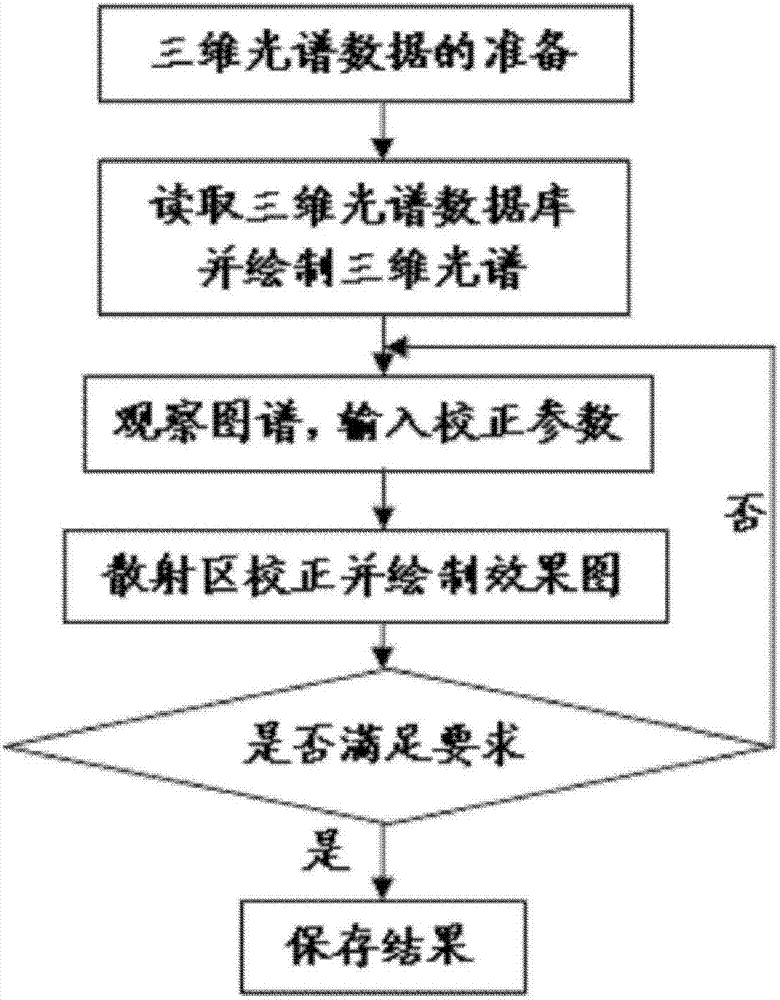
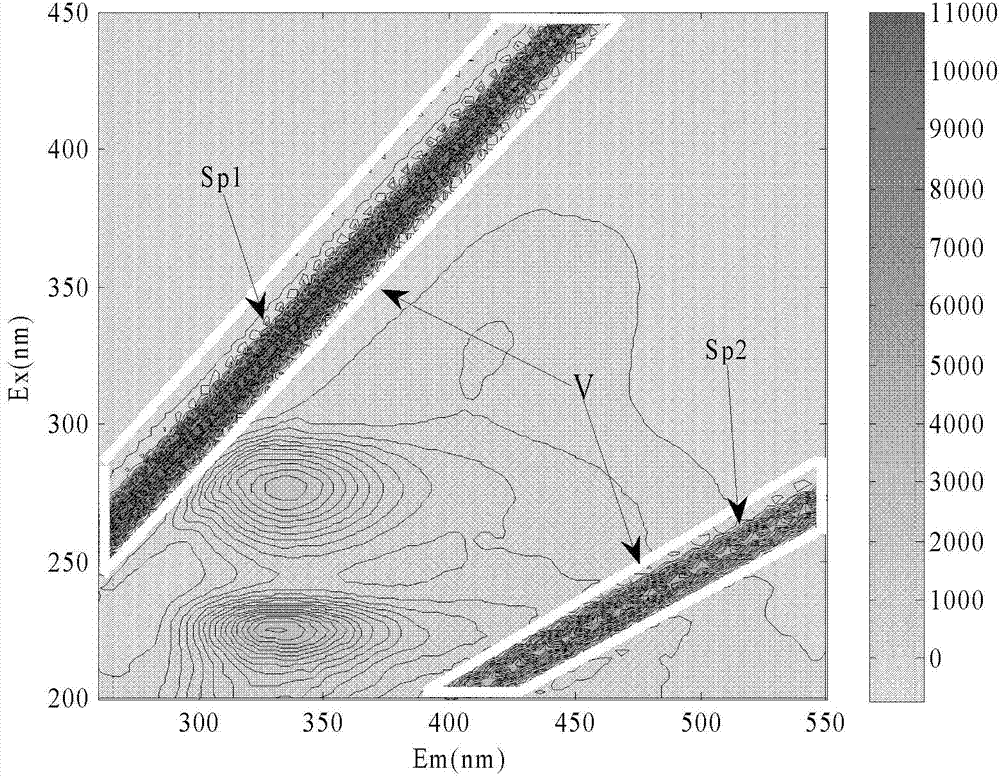
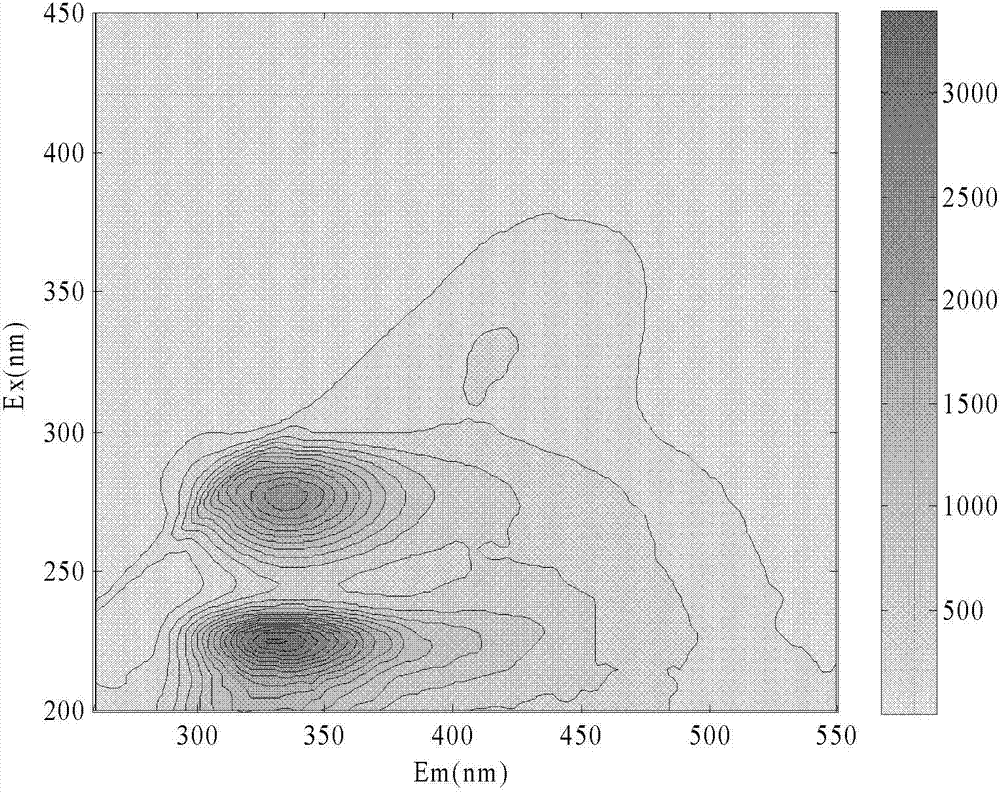
[0020] The new fast correction method for three-dimensional spectral data of the present invention adopts a three-dimensional spectral correction method based on an 8-parameter method. Its main steps are as follows:
[0021] Step 1: Read the data with a computer. The computer reads the three-dimensional spectral data in the MATLAB R2009a environment. The data comes from the fluorescence spectrophotometer or the collected three-dimensional excitation / emission (EX / EM) spectrum or converts the two-dimensional excitation (EX) spectrum into EX / EM spectrum ( Conversion method: Arrange the EX spectra from small to large in rows, the first column is the excitation wavelength, and the first row is the emission wavelength), to obtain the (EX / EM) spectrum matrix F of the original data, set the excitation light band of the original EX / EM spectrum There are n, F=(f 1 , f 2 ,..., f n ), f jis the spectral column vector of the jth excitation band, assuming that there are m emission band...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com