On-line composite manufacturing method of melt-blown fiber and kapok fiber and thermal insulation material thereof
A technology of melt-blown fiber and kapok fiber, applied in non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve problems such as low strength, achieve good resilience, improve strength and overall formability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
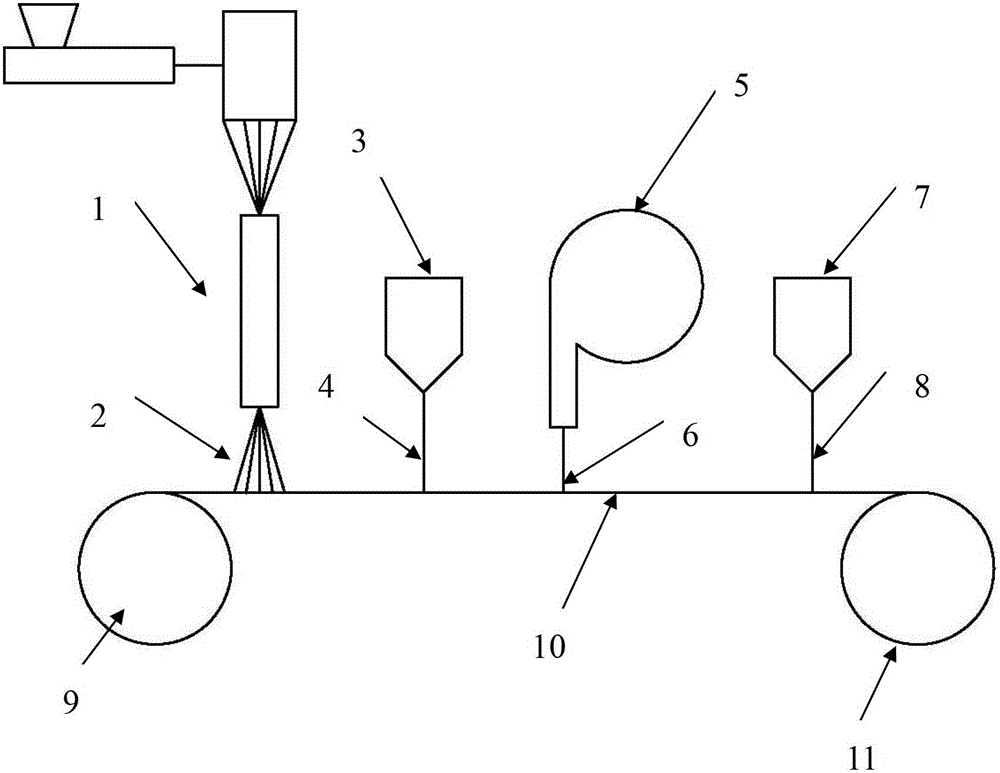
[0030] Please refer to figure 1 Shown, be the production line of this example, comprise: mesh belt equipment, comprise mesh belt 10, be driven by the first drive roller 9 and the second drive roller 11; 3. The first air-laid device 5 and the second jet-spinning device 7 . In the advancing direction of the mesh belt, the spinning outlet of the first spunbonded spinning equipment 1, the spinning outlet of the first melt blown spinning equipment 3, the spinning outlet of the first air-laid device 5 and the first The spinning outlets of the two-jet spinning equipment 7 are arranged sequentially; the mesh belt 10 keeps the directional transmission, and in the direction of the continuous directional transmission of the mesh belt 10, first the spunbond fibers 2 output by the first spunbond spinning equipment 1 are spread on the mesh. On the belt 10, a layer of spunbond fiber layer is laid; when the mesh belt device 10 advances to the spinning outlet of the first melt-blown spinning ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] On the basis of the above-mentioned embodiment 1, according to the needs, a second spunbond spinning equipment is added, and its spinning outlet is arranged at the end of the moving direction of the mesh belt, and the second spunbond fiber is laid on the second melt-blown fiber layer layer, forming a superposition structure of the first spunbond fiber layer, the first meltblown fiber layer, the first kapok fiber layer, the second meltblown fiber layer and the second spunbond fiber layer from bottom to top to form a composite thermal insulation material. The weight ratio of the five layers is adjusted to 15:10:50:10:15. Because the kapok fiber and melt-blown fiber are clamped and fixed by the spunbonded fiber layer with better strength, the structure is stable and not easy to shift; it is suitable for application.
Embodiment 3
[0041] On the basis of the above-mentioned embodiment one, according to the needs, a second spunbond spinning equipment is added, and its spinning outlet is arranged at the end of the moving direction of the mesh belt; the spinning outlet of the first air-laid device is arranged at the second After the spinning outlet of the first spunbond spinning equipment, it is the spinning outlet of the first melt-blown spinning equipment, and then the second air-laid device is added to cancel the second melt-blown spinning equipment. In this way, each device lays the net on the mesh belt in turn, forming a superposition of the first spunbond fiber layer, the first kapok fiber layer, the first meltblown fiber layer, the second kapok fiber layer and the second spunbond fiber layer from bottom to top . The weight ratio of each layer from bottom to top is set to 12:30:16:30:12.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com