Method for knocking out ZFNs (zinc finger nucleases)-mediated bovine MSTN (myostatin) gene and integrating exogenous gene at fixed point
A foreign gene and gene knockout technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems that have not been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
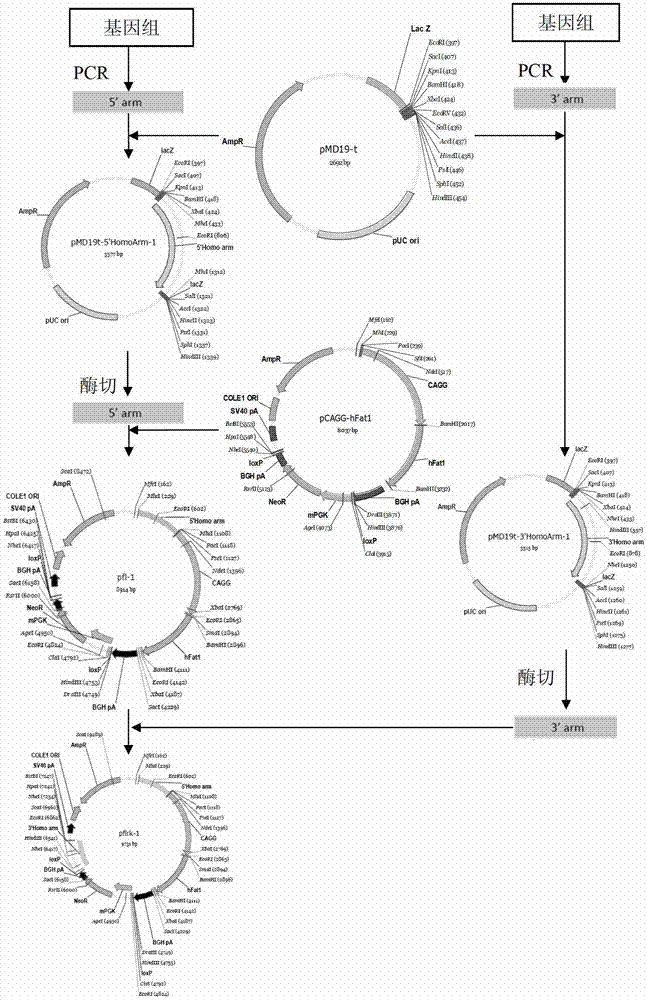
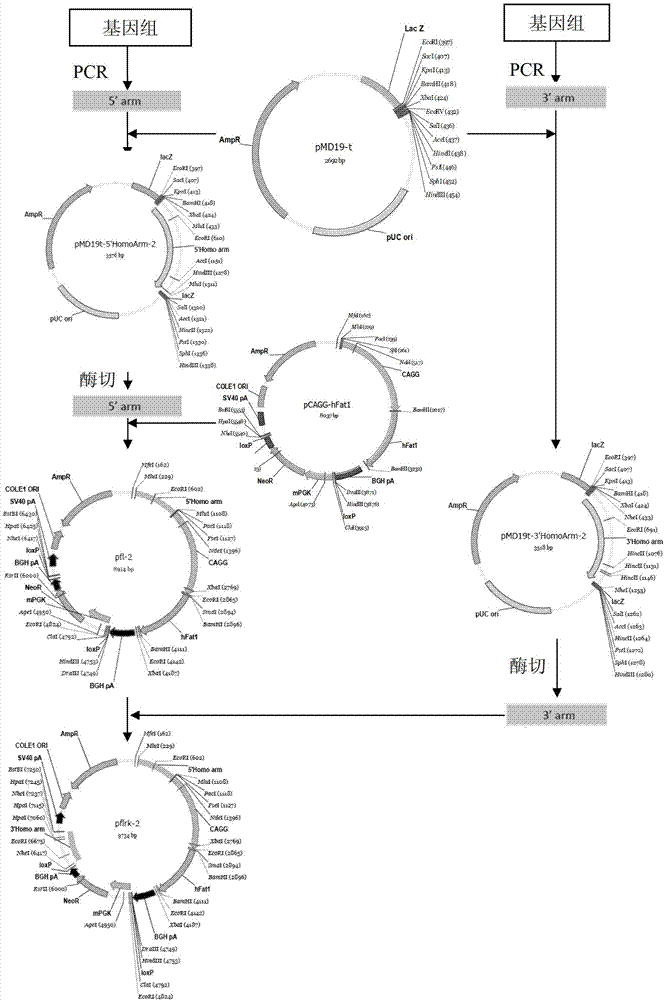
[0075] Example 1 Construction of ZFN expression vector
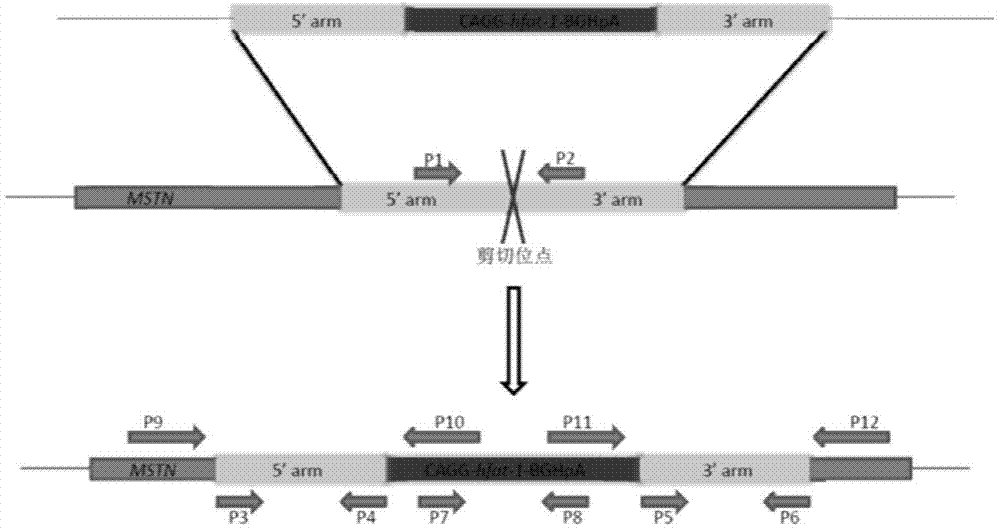
[0076] The full-length DNA sequence of MSTN was obtained from GenBank, and two sets of zinc finger ribozyme vectors were designed for the second exon, named bMK-I and bMK-II, respectively. bMK-I includes bZFN-1 and bZFN-2. Plasmids, bMK-II includes two plasmids, bZFN-3 and bZFN-4 (completed by Sigma-Aldrich), and two sets of zinc finger ribozyme vectors were introduced into different bovine fetal embryos by liposome co-transfection. In the fibroblasts, single cells were then picked to establish multiple single cell lines, the same cell line was divided into two parts, passaged and cryopreserved respectively, the genome was extracted from the passaged cell lines, and PCR detection primers across the action sites were used for amplification. The amplified products were sequenced and identified, and finally the mutant cell line at the action site of the zinc finger ribozyme was obtained.
[0077] Genomic DNA was obtained f...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Example 2 Extraction of bovine fetal fibroblast genome
[0083] The cells cultured in a 100mm petri dish were digested and collected by centrifugation. The Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega) was used to extract bovine genomic DNA according to the method for extracting cell genomes. Finally, the DNA was re-dissolved in 100 μL of ultrapure water. . Use a UV spectrophotometer to detect the concentration and purity of the extracted DNA for subsequent work.
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3 Construction of MSTN gene homology arms pMD19-T-LA-1 and pMD19T-LA-2, pMD19-T-RA-1 and pMD19T-RA-2
[0085] According to Accession No.NC_007300.5 in the template sequence GenBank, the upstream primer LH-1U ( ACGCGT ATCCTGGAATAGATTTGCCTTACT) and downstream primer LH-1D ( ACGCGT GGATTTGCACAAACACTGTCGC); the upstream primer RH-1U ( GCTAGC ATCCGATCTCTGAAACTTGAC) and downstream primer RH-1D ( GCTAGC TTTTAATTTTACCAGGGGTAATT ); upstream primer LH-2U ( ACGCGT TGTCCCAGCGTCCTAACATAACA) and downstream primer LH-2D ( ACGCGT CAGCAAGATCATGGCCATTCTC); the upstream primer RH-2U ( GCTAGC GTGATTACTGAAAAATAACATGC) and downstream primer RH-2D ( GCTAGC GAAGAGTGAGTAGCTCTAAAC); the underlined part is the restriction site. Using the above-mentioned bovine genomic DNA as a template, the homology arms were synthesized by PCR respectively.
[0086] PCR reaction system (20 μL): 1 μL of upstream and downstream primers, 1 μL of template, 2 μL of 10× reaction, 1.6 μL of 2.5mM...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com