Preparation method of iron-based low-rare earth NdFeB rapid quenching permanent magnetic powder
A technology of permanent magnetic powder and rare earth, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, magnetic objects, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of high production cost, achieve the effect of improving economic benefits and saving mineral resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
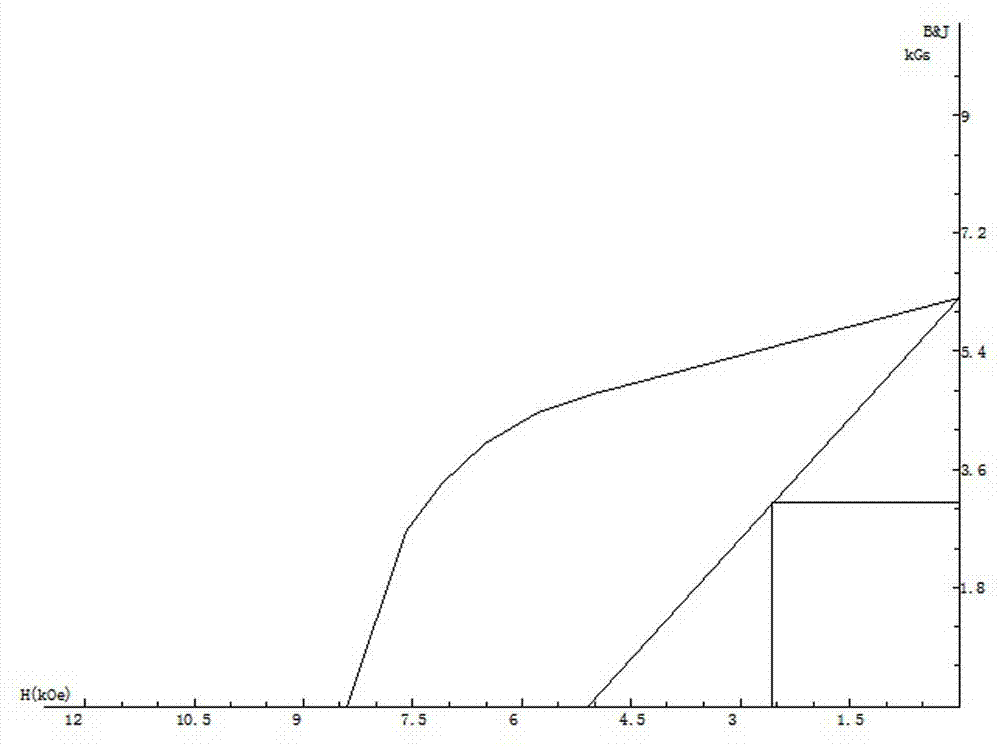
Embodiment 1
[0022] A method for preparing iron-based low-rare earth NdFeB quick-quenching permanent magnet powder, which sequentially includes a batching process, a vacuum smelting process, a vacuum quick-quenching process, an initial pressing process, a crystallization heat treatment process, a powder making process, and a magnetic property and fluidity testing process.
[0023] (1) In the batching process, the mass percentage of raw materials is: 15.5% praseodymium neodymium alloy, 7% lanthanum cerium alloy, 4.5% zirconium, 1.15% boron, and the rest is iron to form a batching.
[0024] (2) In the vacuum smelting process, put the ingredients into a vacuum induction furnace, under the protection of argon, the argon pressure is 0.04Pa; during the smelting process, the temperature rises to 1650°C, until all the materials are melted , and fully boil for 3 to 5 minutes to appear reddish, forming alloy liquid, and start casting. After casting, cool for 20 minutes to form a master alloy.
[002...
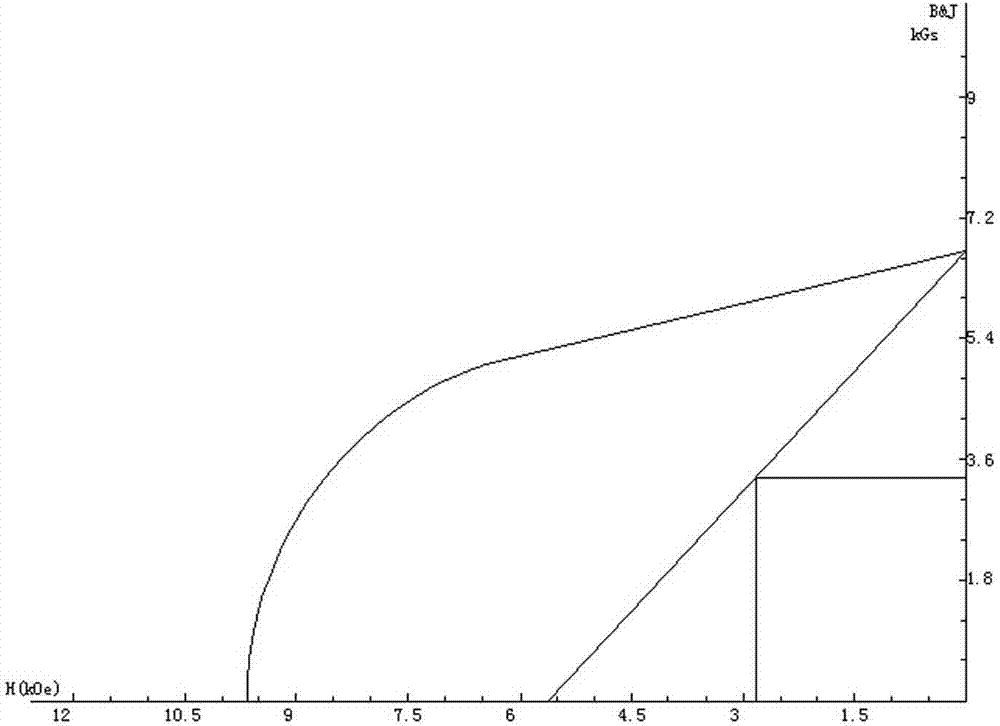
Embodiment 2
[0035] A method for preparing iron-based low-rare earth NdFeB quick-quenching permanent magnet powder, which sequentially includes a batching process, a vacuum smelting process, a vacuum quick-quenching process, an initial pressing process, a crystallization heat treatment process, a powder making process, and a magnetic property and fluidity testing process.
[0036] (1) In the batching process, the formula mass percentage of raw materials is: 19% praseodymium neodymium alloy, 3% lanthanum cerium alloy, 5.5% zirconium, 1.25% boron, and the rest is iron to form a batching.
[0037] (2) In the vacuum smelting process, put the ingredients into a vacuum induction furnace, under the protection of argon, the argon pressure is 0.05Pa; during the smelting process, the temperature rises to 1650°C, until all the materials are melted , and fully boiled for 3 to 5 minutes to appear reddish, forming alloy liquid, and started casting. After casting, cooled for 40 minutes to form a master al...
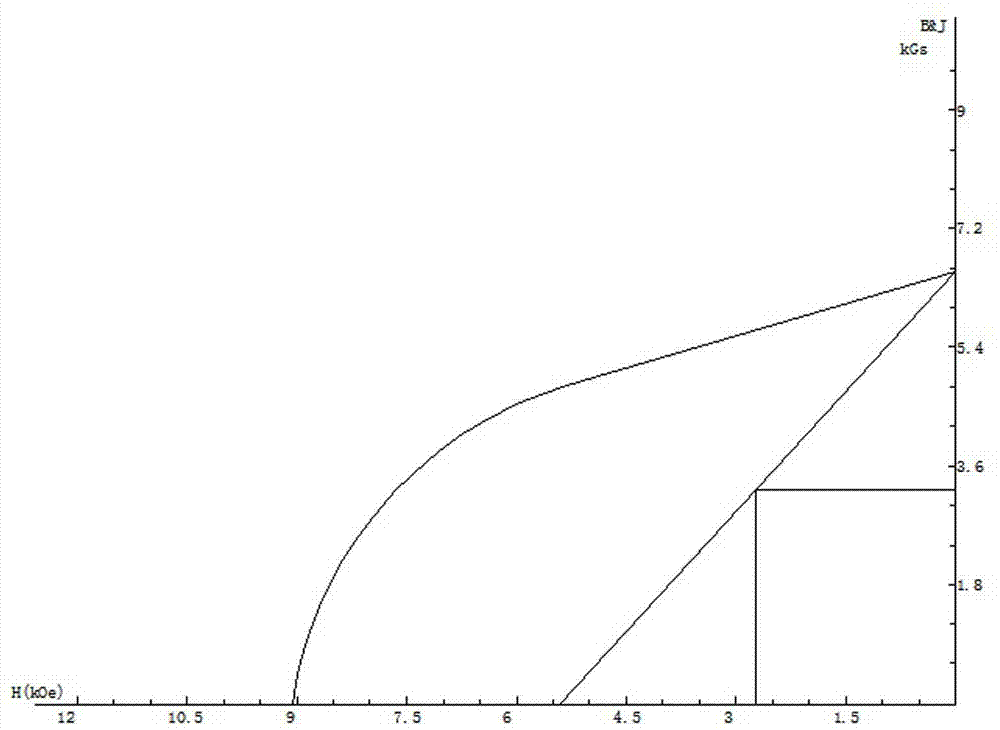
Embodiment 3
[0048] A method for preparing iron-based low-rare earth NdFeB quick-quenching permanent magnet powder, which sequentially includes a batching process, a vacuum smelting process, a vacuum quick-quenching process, an initial pressing process, a crystallization heat treatment process, a powder making process, and a magnetic property and physical property testing process.
[0049] (1) In the batching process, the formula mass percentage of raw materials is: 17% praseodymium neodymium alloy, 5% lanthanum cerium alloy, 5% zirconium, 1.2% boron, and the rest is iron to form a batching.
[0050] (2) In the vacuum smelting process, put the ingredients into a vacuum induction furnace, under the protection of argon, the pressure of argon is 0.045Pa; during the smelting process, the temperature rises to 1650°C, until all the materials are melted , and fully boil for 3-5 minutes to appear reddish, forming alloy liquid, and start casting. After casting, cool for 30 minutes to form a master a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com