Energy-saving transmission adaptive LMS (Least-Mean Squares) distributed detection method for wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and detection method technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of reducing the service life of nodes, huge communication burden, high energy consumption of nodes, etc., and achieve the effect of saving energy consumption, avoiding network information interaction and node computing load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1: The wireless sensor network is applied in the field of cognitive radio, and the current radio environment is detected to determine whether there is a certain known signal w in the current radio signal s , at this time the wireless sensor network node collects the radio signal in the current environment, and the collected signal d k (i) Contains ambient noise and may contain a known signal w s , and then use the collected signal to estimate the signal parameters, and then use this estimated value for hypothesis testing to determine whether there is this certain signal w in the current environment s , to complete the distributed detection function, and realize that under the given false alarm probability condition index, the signal w s Whether it appears to make the correct cognitive judgment. For the current wireless sensor network, as long as the embedded algorithm design is supported, the wireless sensor network that can obtain the bridge node network i...
Embodiment 2
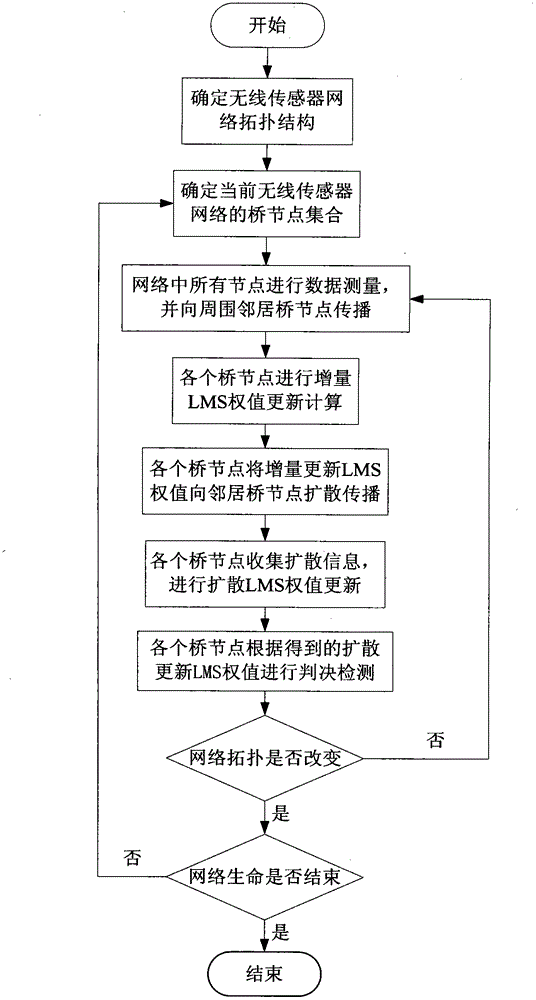
[0061] Embodiment 2: The energy-saving propagation adaptive LMS distributed detection method of the wireless sensor network is the same as the embodiment 1, and will be described in detail below in conjunction with the engineering implementation.
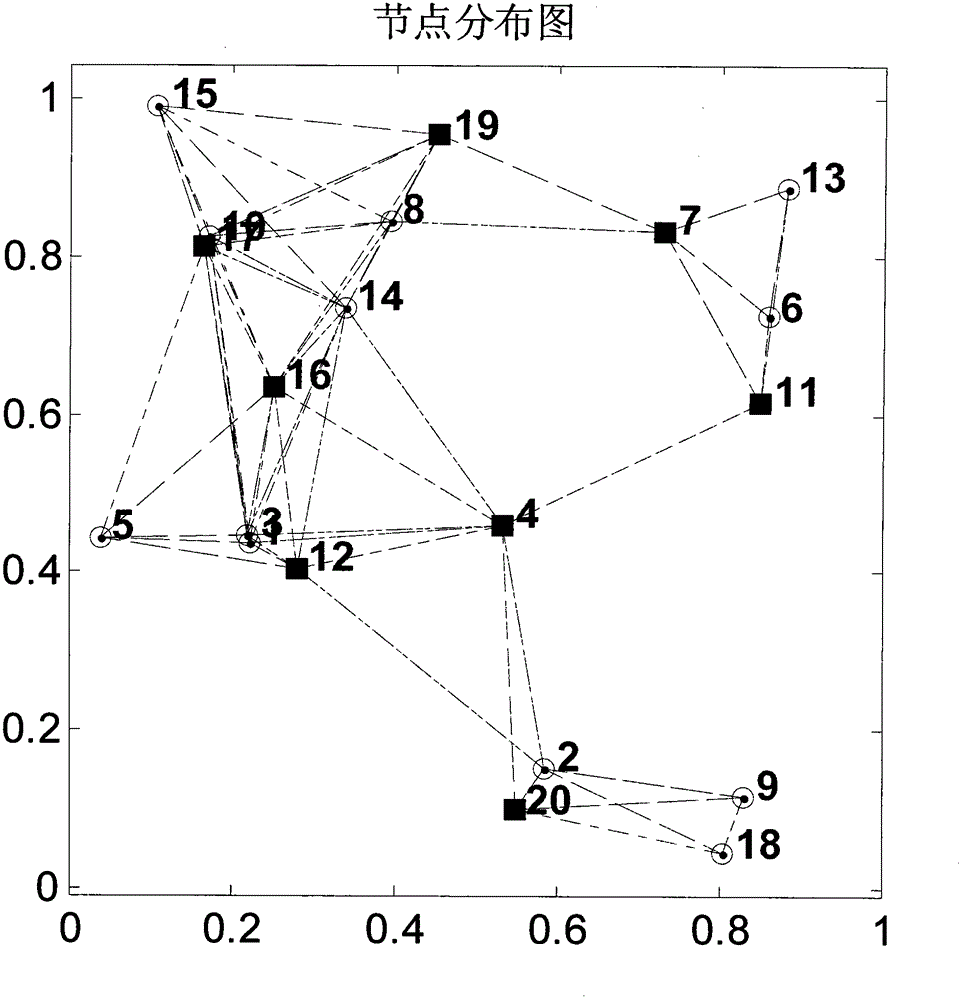
[0062] Step 1: Randomly spread N isomorphic wireless sensor network nodes in a rectangular plane area with a normalized width of 1, assuming that the normalized communication distance between the two nodes is at most r, and determine the topology of the wireless sensor network.
[0063] Step 2: Obtain the bridge node set of the current network according to the network topology, so that all nodes in the network system are either in the current bridge node set, or are neighbor nodes of the bridge node set. There are many ways to determine the bridge node set, such as distance vector based strategy, connection state based strategy, cluster based strategy, etc. There is no special requirement here, as long as the bridge node set is obtai...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Embodiment 3: Energy-saving propagation adaptive LMS distributed detection method of wireless sensor network is the same as Embodiment 1-2, and the present invention can be further illustrated by the following simulation experiment results.
[0099] 1. Simulation conditions:
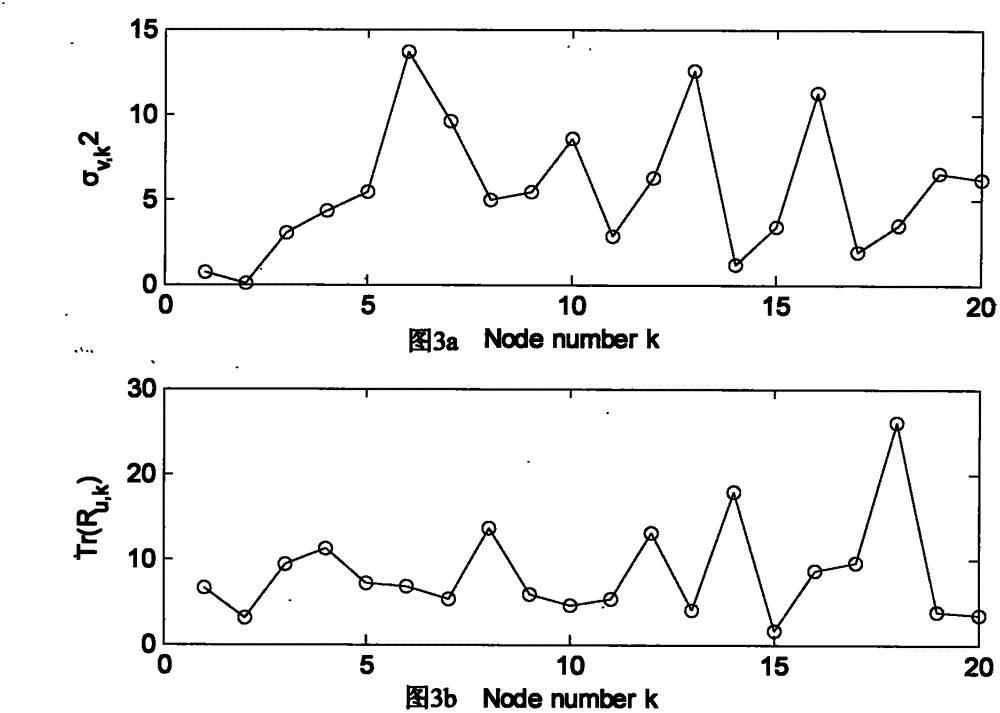
[0100] The conditions of the simulation experiment are as follows: N isomorphic wireless sensor network nodes are randomly scattered in a rectangular plane area with a normalized width of 1. Here, N=20 is selected, and the maximum normalized communication distance between two nodes is assumed to be r=0.4 . Unknown complex vector w o Dimension M = 3 dimensions. In order to generate the consistent regression vector u k,i , node k draws u from a complex Gaussian random process with zero mean k,i , whose covariance matrix is R u,k , independent and identically distributed in time and space, this regression vector u k,i remains constant throughout the simulation. False alarm probability P for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com