Disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis (DSAP) related gene
A kind of optical and genetic technology, applied in the field of molecular genetics, disease diagnosis and treatment, can solve the problems of unclear pathological relationship, huge psychological burden, affecting the appearance of patients, etc., and achieve the effect of effective diagnosis or treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1D
[0060] The identification of embodiment 1DSAP pathogenic gene
[0061] We found a four-generation DSAP family in Anhui Province, China (family 1, figure 1 a), two diseased individuals (I2, II4) and one non-diseased individual (II1) ( figure 1 a) The exome sequence was sequenced.
[0062] 1. DNA sample extraction
[0063] The peripheral blood of the subjects was collected, and the genomic DNA in the peripheral blood leukocytes was extracted using a FlexiGene DNA (commercially available, purchased from Qiagen, CA) kit.
[0064] 2. Exome sequence sequencing
[0065] Two diseased individuals (I2, II4) and one non-diseased individual (II1) ( figure 1 a) The exome sequence was sequenced. Exome sequencing methods are as follows:
[0066] 1) Randomly break the genomic DNA into fragments of about 150-200bp, and then connect adapters to both ends of the fragments to prepare a hybrid library (see the Illumina / Solexa standard library construction instructions provided by http: / / www....
Embodiment 2D
[0099] The verification of embodiment 2DSAP pathogenic gene
[0100] In order to further confirm that the MVK gene is the causative gene of DSAP, the Sanger sequencing method was used to detect the genes of another 57 family samples (from 7 families), 27 sporadic samples and 676 normal people outside the family, and verified the relationship between the MVK gene and DSAP. correlation between.
[0101] 1. DNA sample extraction
[0102] Peripheral venous blood from 57 pedigree samples, 27 sporadic samples and 676 normal persons outside the pedigree were collected, and genomic DNA was extracted according to the method in Example 1.
[0103] 2. Sanger sequencing verification
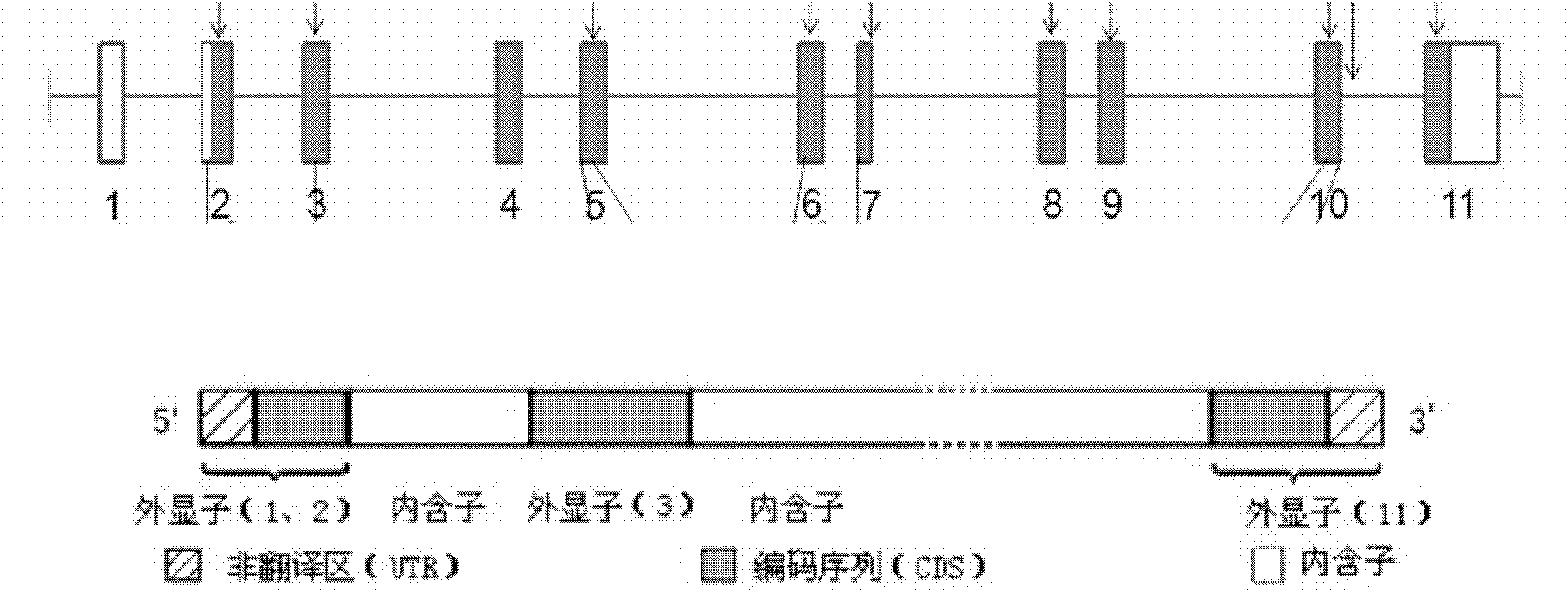
[0104] For the MVK gene (for the structure of the MVK gene, see figure 2 ) Design primers for all exons and exon-intron border regions, amplify by PCR, purify the product, use Sanger sequencing to obtain the MVK gene related sequences of all subjects in step 1, and determine according to the sequence det...
Embodiment 3
[0127] Example 3 Splice site mutation analysis
[0128] Studies of MVK gene splice site mutations using affected and non-affected individuals in pedigrees (see Figure 4 ), respectively, RNAiso Plus reagent (TaKaRa code: D9108A) and PrimeScript II 1st strand cDNA synthesis kit (TaKaRa code: D6210A) were used to extract fresh peripheral blood RNA from a diseased individual and a non-diseased individual in family 4 and reverse it to cDNA, exon 10 was amplified by PCR, followed by Sanger sequencing.
[0129] Primers were designed with reference to the human genome sequence database hg18 / build36.3. The specific sequences of the designed primers are shown in Table 5. The primer system, reaction conditions and purification steps are all known technologies.
[0130] Table 5. Primer sequences
[0131]
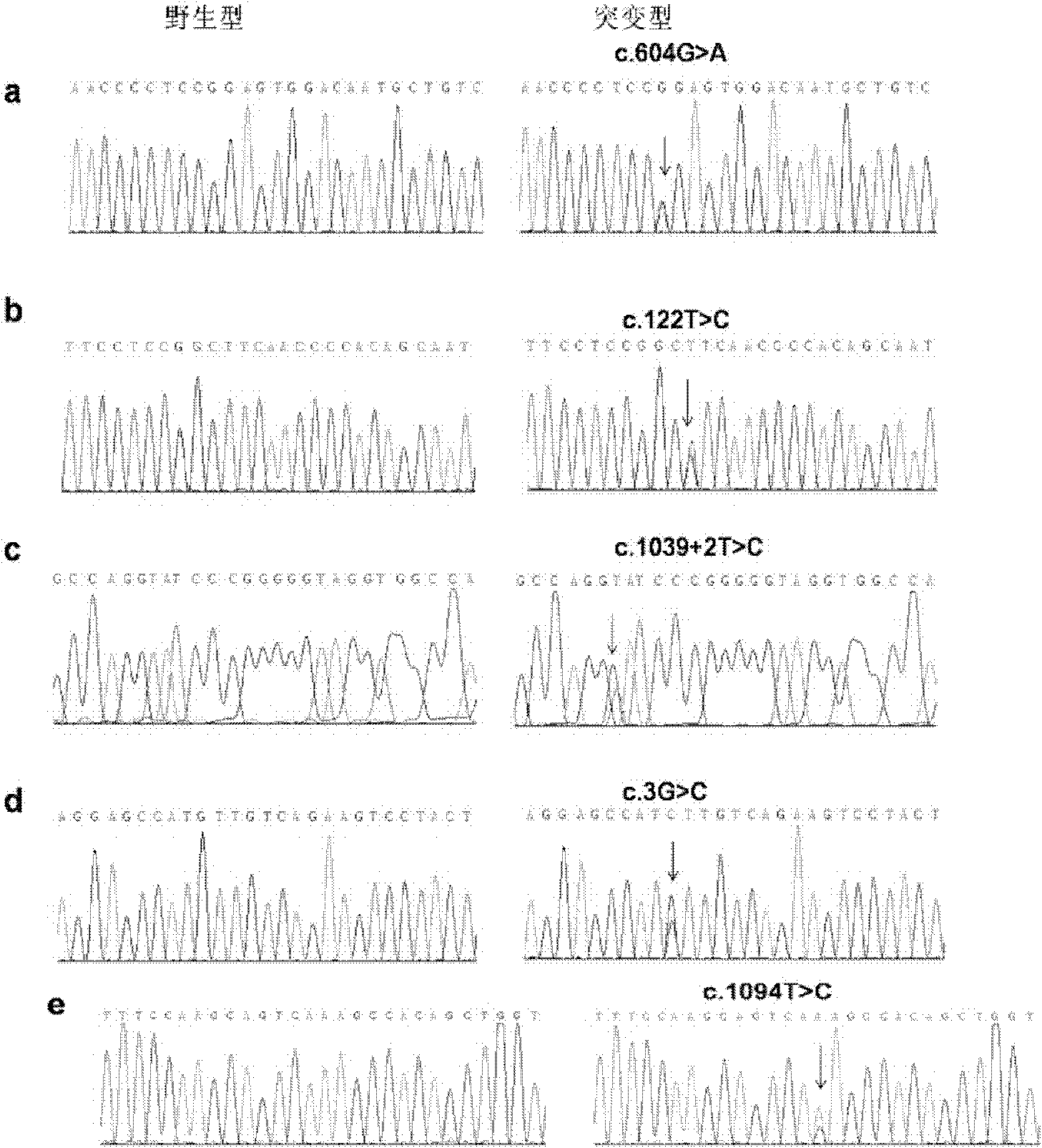
[0132] Figure 4 The gcatcccgggg marked in red in b becomes the coding sequence after the c.1039+2T>C mutation, causing a frameshift.
[0133] Conclusion: The site mutation (c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com