High-speed train alloy cast steel brake disc material and smelting process thereof
A technology of alloy cast steel and high-speed trains, applied in the field of metal materials, can solve the problems of non-wear-resistant brake friction surfaces, short service life, poor toughness, etc., and achieve less debris inclusions, low production costs, and good wear resistance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
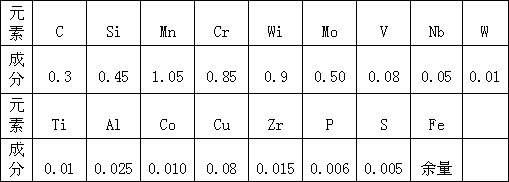
[0021] The molten steel is smelted in a 500Kg medium-frequency induction furnace, and the manufacturing process steps are as follows:
[0022] (1) Load high-quality steel ingots with a size of 70cm2, and add them in two times;
[0023] (2) Electric melting, allowing the use of the maximum power to melt the steel ingot. When the temperature of the molten steel rises to 1500-1520°C, add elements: carbon, ferromolybdenum, ferrochromium, nickel, zirconium, vanadium, and continue to heat up. With the melting of the steel ingot, Pound the charge at any time to avoid bridging, and add steel ingots for the second time;
[0024] (3) When the molten steel temperature rises to 1550-1560°C, add ferrosilicon;
[0025] (4) When the molten steel temperature rises to 1580-1590°C, add ferromanganese;
[0026] (5) Take samples for analysis, and adjust the chemical composition according to the analysis results;
[0027] (6) When the molten steel temperature rises to 1650-1670°C, stop the powe...
Embodiment 2
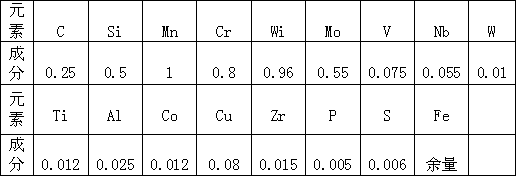
[0033] Melting molten steel with a 1000Kg intermediate frequency induction furnace, the manufacturing process steps are:
[0034] (1) Load high-quality steel ingots with a size larger than 80mm2, and add them in two times;
[0035] (2) Electric melting, allowing the use of the maximum power to melt the steel ingot. When the molten steel temperature rises to 1550-1560 ° C, add elements: carbon, ferromolybdenum, ferrochromium, nickel, zirconium, vanadium, and then continue to heat up, as the ingot melts , beat the charge at any time to avoid bridging, and add steel ingots for the second time;
[0036] (3) When the molten steel temperature rises to 1570-1580°C, add ferrosilicon;
[0037] (4) When the molten steel temperature rises to 1590-1600°C, add ferromanganese;
[0038] (5) Take samples for analysis, and adjust the chemical composition according to the analysis results;
[0039] (6) When the molten steel temperature rises to 1650-1660°C, stop the power supply, insert 0.5K...
Embodiment 3
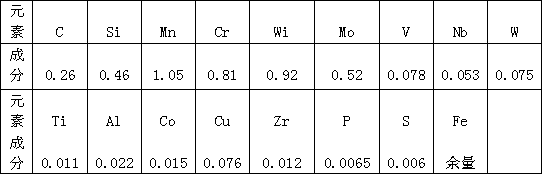
[0045] Using a 5000Kg intermediate frequency induction furnace to make molten steel, the manufacturing process steps are:
[0046] (1) Load high-quality steel ingots, the size of which is not greater than 120mm2, and add in two times;
[0047] (2) Electric melting, allowing the use of the maximum power to melt the steel ingot. When the molten steel temperature rises to 1540-1550 ° C, add elements: carbon, ferromolybdenum, ferrochromium, nickel, zirconium, vanadium, and then continue to heat up, as the ingot melts , beat the charge at any time to avoid bridging, and add steel ingots for the second time;
[0048] (3) When the molten steel temperature rises to 1560-1570°C, add ferrosilicon;
[0049] (4) When the molten steel temperature rises to 1580-1590°C, add ferromanganese;
[0050] (5) Take samples for analysis, and adjust the chemical composition according to the analysis results;
[0051] (6) When the molten steel temperature rises to 1640-1650°C, stop the power supply,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com