Nonvolatile memory element, production method therefor, nonvolatile memory unit, and design assistance method for nonvolatile memory element
一种非易失性存储、制造方法的技术,应用在非易失性存储元件及其制造领域,能够解决妨碍电阻变化元件初始化等问题,达到维持导电性、抑制接触电阻的增加、漏电流减少的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
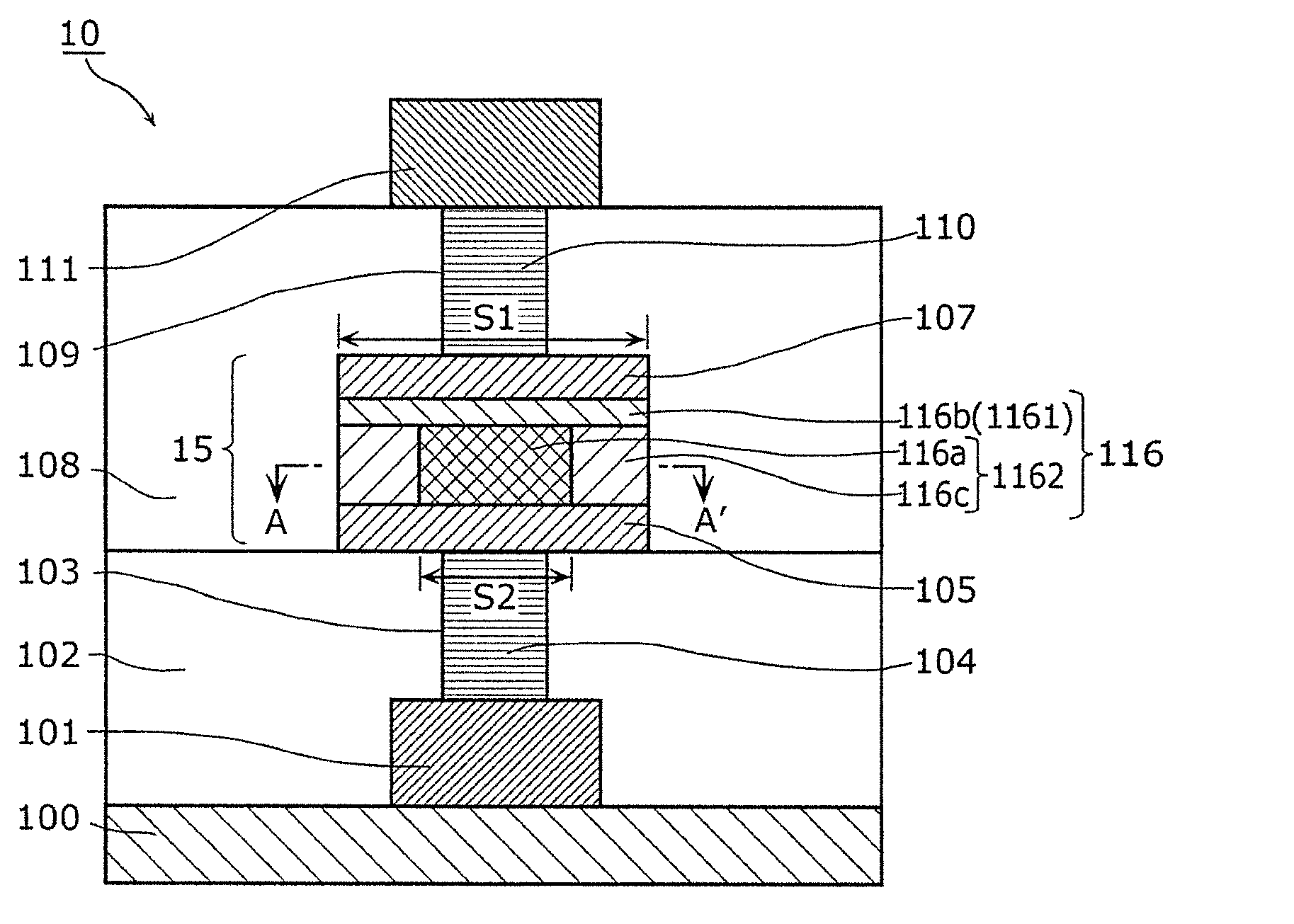
[0101] First, the nonvolatile memory element in Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described.
[0102] [constitute]
[0103] Figure 2A It is a sectional view of the nonvolatile memory element 10 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Figure 2B yes Figure 2A Sectional view of line AA' in . Such as Figure 2A As shown, the nonvolatile memory element 10 of this embodiment is a variable resistance nonvolatile memory element, and includes a substrate 100, a first wiring 101, a first interlayer insulating layer 102, a first contact plug 104, a resistor The variable element 15 , the second interlayer insulating layer 108 , the second contact plug 110 and the second wiring 111 . Furthermore, when an actual memory cell is configured using the nonvolatile memory element 10 of this embodiment, either one of the first wiring 101 and the second wiring 111 is connected to a switching element (diode or transistor), and It is determined that the switching elem...
Embodiment approach 2
[0152] Next, the nonvolatile memory element in Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described.
[0153] [constitute]
[0154] Figure 14A It is a sectional view of the nonvolatile memory element 20 according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. Figure 14B is looking in the direction of the arrow Figure 14A A cross-sectional view of the section of the line BB' in the figure. Such as Figure 14A As shown, the nonvolatile memory element 20 of the second embodiment is a variable resistance nonvolatile memory element, and includes a substrate 100 made of silicon (Si), a first wiring 101, a first interlayer insulating layer 102, The first contact plug 104 , the variable resistance element 25 , the second interlayer insulating layer 108 , the second contact plug 110 , and the second wiring 111 .
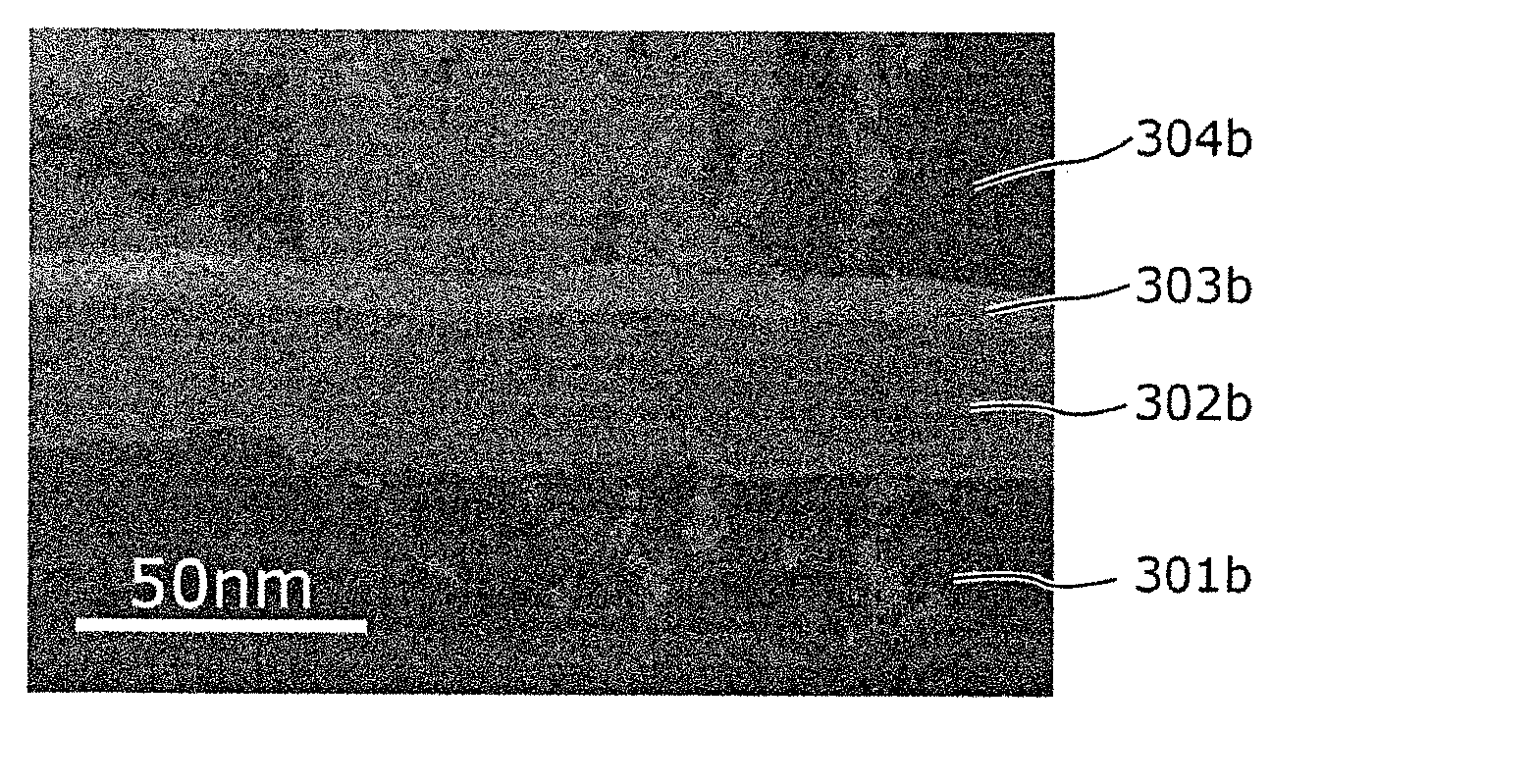
[0155] The variable resistance element 25 is composed of a lower electrode 105 , a variable resistance layer 126 , and an upper electrode 107 . The variable resistance...
Embodiment approach 3
[0169] Next, the nonvolatile memory element in Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described.
[0170] [constitute]
[0171] Figure 16 It is a sectional view of the nonvolatile memory element 30 in Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Such as Figure 16 As shown, the nonvolatile memory element 30 of this embodiment is a variable resistance nonvolatile memory element, and includes a substrate 100 such as silicon (Si), a first wiring 101, a first interlayer insulating layer 102, a first 1. Contact plug 104, variable resistance element 35, second interlayer insulating layer 108, second contact plug 110, and second wiring 111. The variable resistance element 35 is composed of a lower electrode 105 , a variable resistance layer 136 , and an upper electrode 107 . The variable resistance layer 136 is interposed between the lower electrode 105 and the upper electrode 107, and reversibly changes the resistance value based on an electric signal applied between the two e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com