Method for preventing fermented bean curd from generating white crystal sediment
A sediment and fermented bean curd technology, applied in the field of food processing, can solve the problems of product quality deterioration, mistaking it as glass slag, and affecting the appearance quality of finished products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
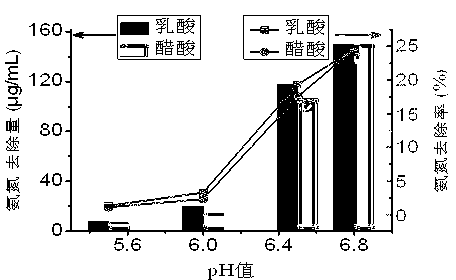
[0022] figure 1 It shows that with the decrease of the adjusted pH value, the removal rate and amount of ammonia nitrogen decrease significantly, and the effect of lactic acid and acetic acid has little difference. Compared with the control group, when pH=6.0, the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen decreased from 25% to 1%, and the removal amount decreased from 150μg / mL to 20μg / mL. At the same time, no crystallization was observed in the simulated solution with pH≤6.0 . It shows that lactic acid or acetic acid can effectively prevent the crystallization of magnesium ammonium phosphate by adjusting the pH of the simulated solution to ≤6.0.
[0023] Embodiment 2, adding 0.2% citric acid can effectively prevent crystallization of magnesium ammonium phosphate
[0024] Take 50mL of the prepared N and P stock solutions and place them in a clean and dry 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 0.0g, 0.1g, 0.2g, 0.3g of citric acid respectively, after fully dissolving, add 50mL of Mg stock soluti...
Embodiment 2
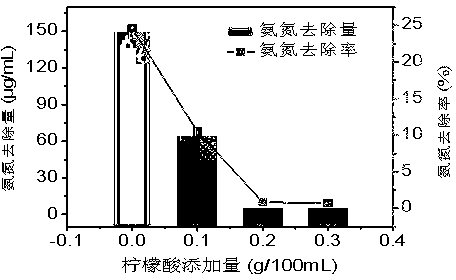
[0025] figure 2It can be seen that when the addition of citric acid increases from 0.1% to 0.2%, the removal rate and removal amount of ammonia nitrogen are significantly reduced. When the addition of citric acid is greater than 0.2%, the removal rate and removal amount of ammonia nitrogen are basically unchanged. When 0.2% citric acid was added, the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen decreased from 25% to 0.85%, and the solution was clear and transparent without crystallization, which indicated that adding 0.2% citric acid could effectively prevent the crystallization of magnesium ammonium phosphate. The addition of citric acid in the solution complexes magnesium ions on the one hand, and on the other hand reduces the pH value in the solution. This may be the reason why sodium citrate prevents crystallization of magnesium ammonium phosphate significantly.
[0026] Embodiment 3, the prevention of polyphosphate to the crystallization reaction of magnesium ammonium phosphate
...
Embodiment 3
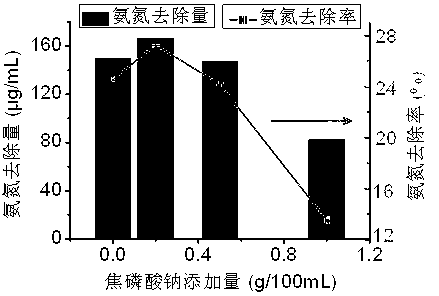
[0028] Take 50mL of the prepared N and P stock solutions and place them in 8 clean and dry 250mL Erlenmeyer flasks, add 0.0g, 0.2g, 0.5g, 1.0g of sodium pyrophosphate to 4 bottles, and add tripolyphosphoric acid to the other 4 bottles Sodium 0.0g, 0.5.g, 1.0g, 1.5g, after fully dissolved, add 50mL Mg stock solution successively to mix, shake well and let it stand for 24h, take the supernatant, measure the ammonia nitrogen removal rate and removal amount, the experimental results are as follows image 3 , Figure 4 .
[0029] image 3 , 4 It shows that with the increase of sodium pyrophosphate and sodium tripolyphosphate addition, the ammonia nitrogen removal rate and removal amount first increase and then decrease, indicating that low addition of sodium pyrophosphate and sodium tripolyphosphate not only does not inhibit the crystallization of magnesium ammonium phosphate The reaction increased the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen and promoted the crystallization of magnesiu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com