Agarase immobilization method
A technology of agarase, chitosan, applied in isotropic immobilization on/in an organic carrier
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
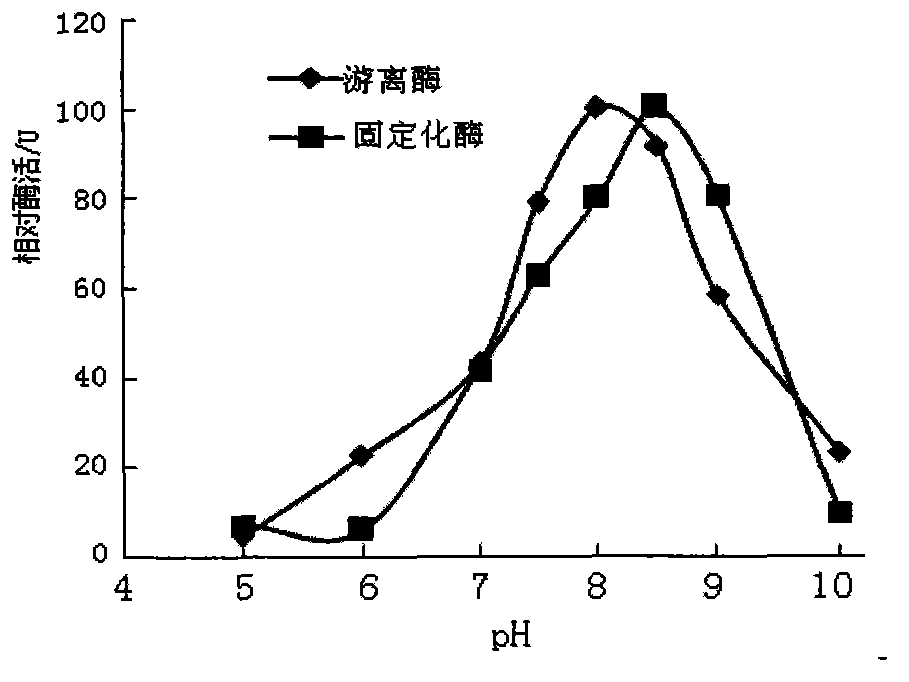
[0021] Example 1: Effect of pH value on enzyme activity
[0022] Get prepared chitosan immobilized enzyme 0.5g and corresponding free enzyme in parallel, add substrate and free enzyme and immobilized enzyme respectively under different pH (4.0-9.0) conditions, measure its enzyme activity respectively, the result is as follows figure 1 shown.
[0023] figure 1 It shows that the optimal pH value of the free enzyme is 8.0, and the enzyme activity decreases with the increase of the pH value; for the immobilized enzyme, under the experimental conditions, the enzyme activity reaches the maximum when the pH value reaches 8.5, and the immobilized enzyme The optimal pH of the enzyme is increased by 0.5 units to the alkaline side, which is in line with the basic law after the combination of the enzyme and the carrier.
Embodiment 2
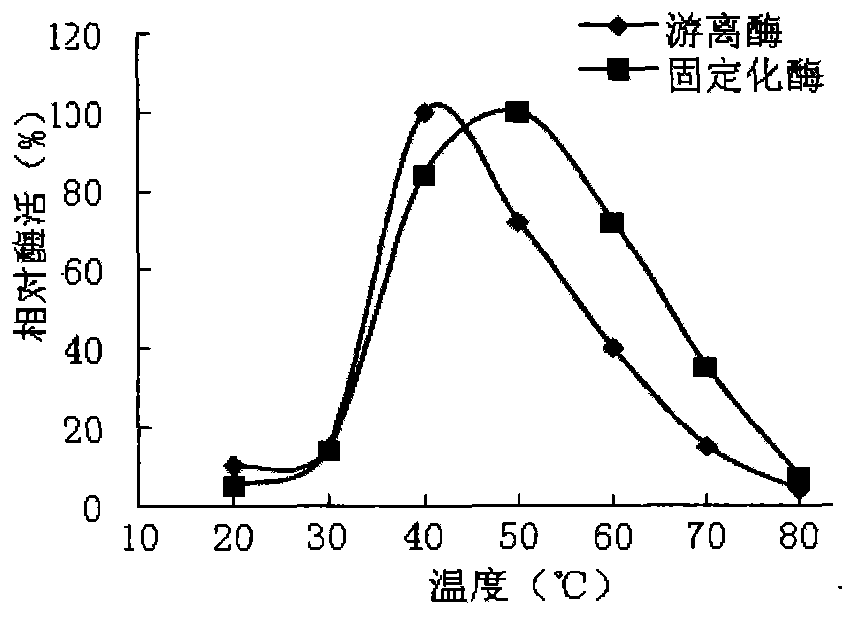
[0024] Example 2: Effect of Temperature on Enzyme Activity
[0025] Take the prepared chitosan-immobilized enzyme 0.5g and the corresponding free enzyme in parallel, add the substrate to react with the free enzyme and the immobilized enzyme respectively under different temperature (30°C-80°C) conditions, and measure the enzyme activity respectively. The result is as figure 2 shown.
[0026] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the free agarase exhibits the highest activity at 40°C, and as the temperature rises, the activity drops sharply, and the enzyme begins to inactivate, but for the immobilized enzyme, there is a large enzyme activity in the range of 40-60°C, The enzyme activity reaches the maximum at 50°C, and the heat resistance of the immobilized enzyme is significantly improved.
Embodiment 3
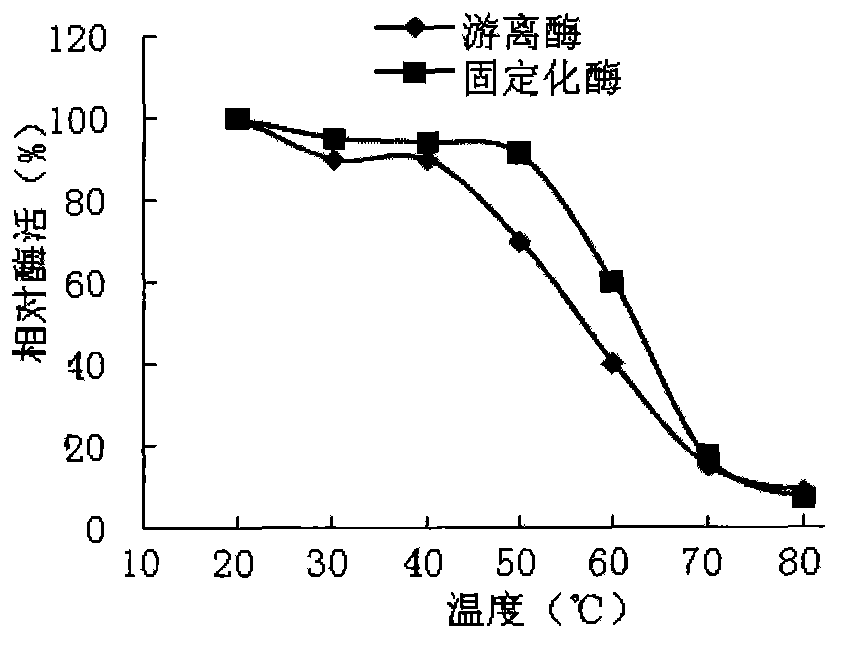
[0027] Example 3: Thermostability of free and immobilized enzymes
[0028] Take the prepared chitosan-immobilized enzyme 0.5g and the corresponding free enzyme in parallel, incubate at different temperatures (20°C-80°C) for 0.5h, then add the substrate to interact with it, and measure the enzyme activity respectively. The results are as follows: image 3 shown.
[0029] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that short-term incubation of the enzyme solution below 40°C has little effect on the enzyme activity, and when the temperature is further raised to 50°C, the effect on the activity of the free enzyme increases, with a loss of about 27.36%, while the effect on the activity of the immobilized enzyme is still small. At 60°C, the activity of the free enzyme is very low, while the activity of the immobilized enzyme is about 50%. At 70°C, the enzyme has basically no activity at all, indicating that the thermal stability of the immobilized enzyme is higher than that of the free enzy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com