Method for microencapsulating pitaya peel pigment
A technology of pitaya peel and microencapsulation, which is applied in food forming, food preparation, food science, etc., can solve the problems that dragon fruit peel pigment is easily affected by external conditions and limits its wide application, so as to improve stability, The effect of amplifying technical effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
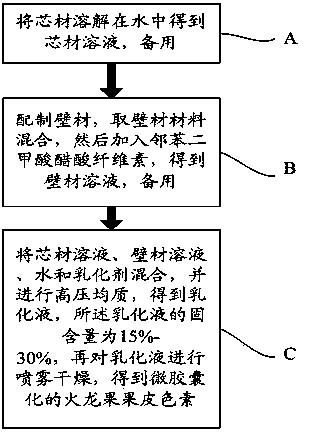
[0038] Get 1:1 gum arabic and maltodextrin, mix evenly, add cellulose acetate phthalate to obtain a wall material solution; take dragon fruit peel pigment to dissolve to obtain a core material solution; mix the wall material solution, core material solution, The water and the emulsifier are mixed and stirred evenly, and homogenized under high pressure to obtain an emulsion, wherein the ratio of the core material to the wall material is 1:1.2, and the solid content of the emulsion is 20%; then the emulsion is spray-dried, Obtain the pitaya peel pigment of microencapsulation.
[0039] In this example, the homogenization pressure is 30Mpa, the number of homogenization is 4 times, the feed temperature during the spray drying process is 50°C, the feed concentration is 15%, the inlet air temperature is 140°C, and the outlet air temperature is 70°C , The feed rate is 40ml / min.
[0040] In this embodiment, the dosage of cellulose acetate phthalate is 0.2% of the emulsion.
[0041] I...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Get 4:1 modified starch and gum arabic, mix evenly, add cellulose acetate phthalate, obtain wall material solution; get pitaya peel pigment to dissolve, obtain core material solution, mix wall material solution, core material solution, water Mix and stir with an emulsifier evenly, and carry out high-pressure homogenization to obtain an emulsion, wherein the ratio of the core material to the wall material is 1:1, and the solid content of the emulsion is 15%; then the emulsion is spray-dried to obtain Microencapsulated dragon fruit peel pigment.
[0045] In this example, the homogenization pressure is 40Mpa, the number of homogenization times is 2, the feed temperature during the spray drying process is 60°C, the feed concentration is 25%, the inlet air temperature is 180°C, and the outlet air temperature is 100°C , The feed rate is 50ml / min.
[0046] In this example, the dosage of cellulose acetate phthalate is 1% of the emulsion.
[0047] In this embodiment, the emuls...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Get 0.8:1 polyethylene glycol and ethyl cellulose, mix evenly, add phthalate cellulose acetate, obtain wall material solution; Get pitaya peel pigment to dissolve, obtain core material solution; Wall material solution, core material The solution, water and emulsifier are mixed and stirred evenly, and homogenized under high pressure to obtain an emulsion, wherein the ratio of the core material to the wall material is 0.6:1, and the solid content of the emulsion is 30%; then the emulsion is sprayed Dried to obtain the microencapsulated dragon fruit peel pigment.
[0051] In this example, the homogenization pressure is 35Mpa, the number of homogenization is 3 times, the feed temperature during the spray drying process is 60°C, the feed concentration is 20%, the inlet air temperature is 160°C, and the outlet air temperature is 85°C , The feed rate is 45ml / min.
[0052] In this example, the dosage of cellulose acetate phthalate is 0.5% of the emulsion.
[0053] In this emb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com