Bacillus subtilis strain for producing high-purity chiral D-(-)-2,3-butanediol, and construction and applications
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and butanediol, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, bacteria, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as no modification of Bacillus subtilis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1 The construction of the starting strain of the Bacillus subtilis system without antibiotic markers and the construction of the basic operation plasmid pCU
[0031] (1) Construction of starting strains for screening Bacillus subtilis system without antibiotic markers
[0032] The strain obtained by knocking out the upp gene in Bacillus subtilis B. subtilis168 was selected as the starting strain of the Bacillus subtilis system without antibiotic markers, and was named BSF1.
[0033] The steps for constructing the starting strains of the Bacillus subtilis system without antibiotic markers are as follows:
[0034] Use the plasmid containing the upper and lower homology arms of the upp gene and the neo resistance marker to transform into Bacillus subtilis B. subtilis 168 by Spizizen, select the transformant on the LB plate containing 5ug / mL kanamycin, and pass through the colony After PCR verification, the starting strain BSF1 with upp gene knockout was obtained. ...
Embodiment 2
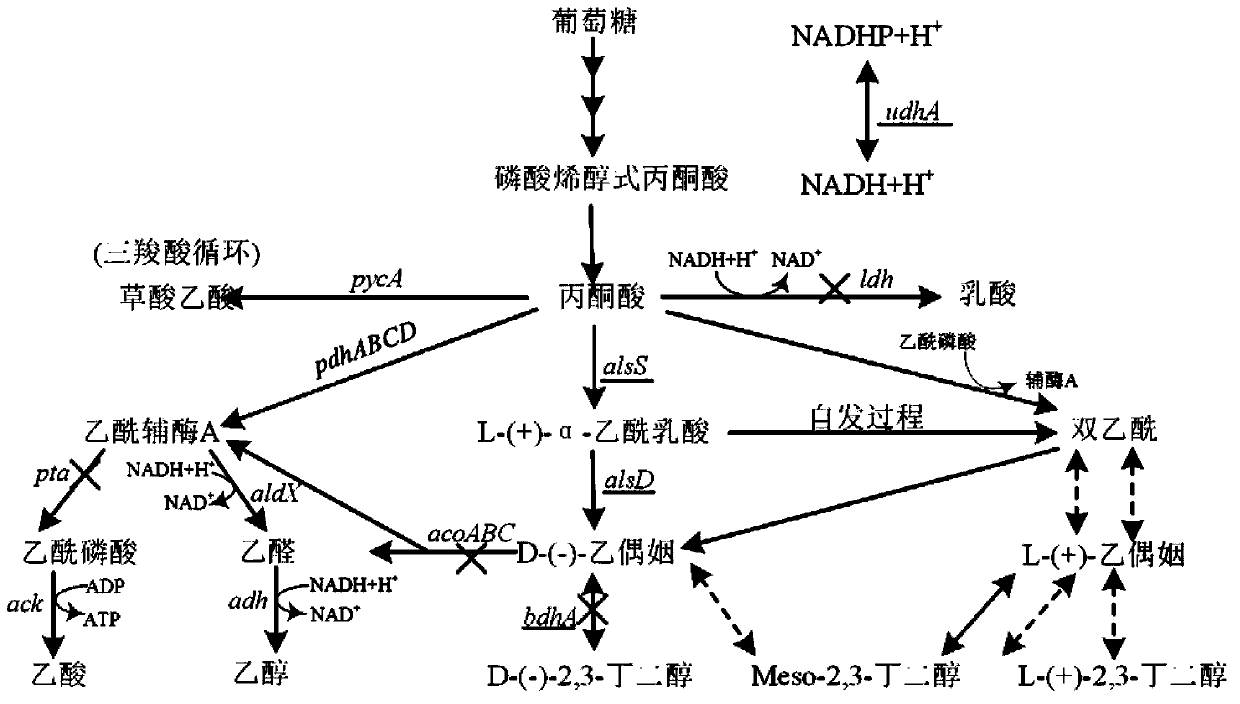
[0037] Example 2: Knockout of the acoA gene in the degradation pathway of the direct substrate acetoin of 2,3-butanediol
[0038] The specific operations for knocking out the acoA gene in the degradation pathway of acetoin (the direct substrate of 2,3-butanediol) are as follows:
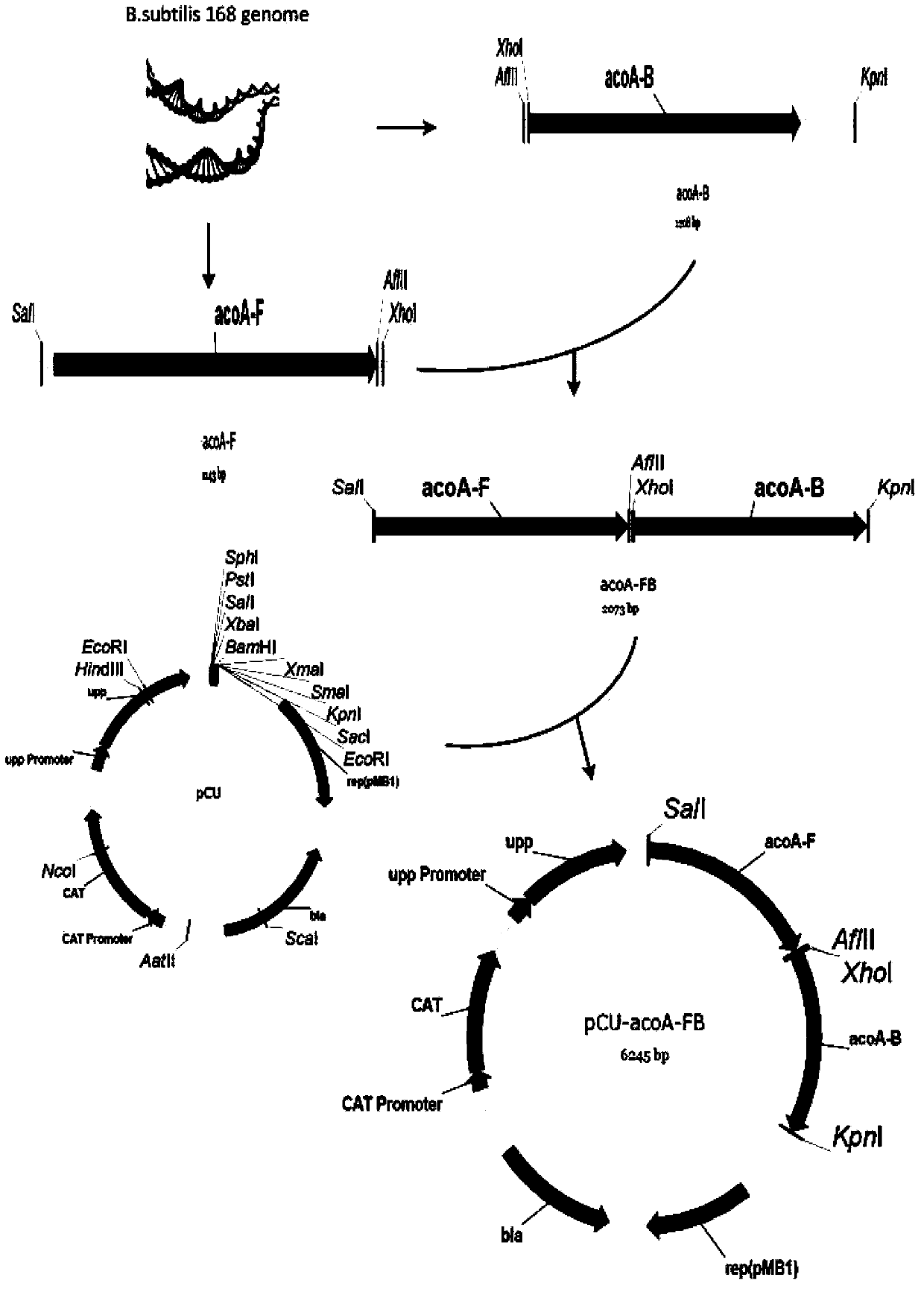
[0039] Using two pairs of primers D-acoA-FU, D-acoA-FL and D-acoA-BU, D-acoA-BL, using B. subtilis 168 as a template, using KOD-plus high-fidelity DNA polymerase to amplify the size The upstream and downstream homology arms acoA-F and acoA-B are 1143bp and 1208bp. After gel cutting and recovery, primers D-acoA-FsnU and D-acoA-FsnL were used, and KOD-plus high-fidelity DNA polymerase was also used for fusion PCR amplification to obtain the 2073bp splicing product acoA-FB of the upstream and downstream homology arms. Then the fusion product acoA-FB and pCU plasmid were digested with Thermo Fast digest SalI and KpnI, and after ligation and transformation, the acoA gene knockout vector pCU-acoA-FB was obt...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Knockout of the bdhA gene encoding acetoin reductase
[0043] Using two pairs of primers D-bdhA-FU, D-bdhA-FL and D-bdhA-BU, D-bdhA-BL, using B.subtilis 168 as a template, using KOD-plus high-fidelity DNA polymerase to amplify the size The upstream and downstream homology arms bdhA-F and bdhA-B are 1096 and 973bp. After gel cutting and recovery, use primers D-bdhA-FsnU and D-bdhA-FsnL, and KOD-plus high-fidelity DNA polymerase to perform fusion PCR amplification to obtain the 1796bp splicing product bdhA-FB of the upstream and downstream homology arms. Then the fusion product bdhAFB and pCU plasmid were digested with Thermo Fast digest SphI and KpnI, and after ligation and transformation, the bdhA gene knockout vector pCU-bdhA-FB was obtained (see Figure 4 ). The plasmid with the correct sequencing result was transformed into Bacillus subtilis BSF2 by Spizizen, the positive clones with successful recombination were screened with chloramphenicol, and verifi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com