Preparation method for nano-iron particles and application thereof
A nano-iron and iron particle technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, reduced water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of complex process, high cost, unseen and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
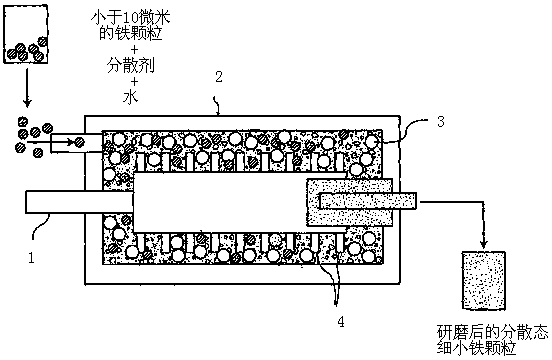
[0087] An imported high-precision grinding machine is used. The operating parameters are as follows:
[0088] ① 0.6 liter grinding volume,
[0089] ②Fill 80-85% of the balls,
[0090] ③20-50% iron particles (1-10 microns),
[0091] ④1.5-1.8kwh / L input power,
[0092] ⑤ Speed 2200-2400 RPM,
[0093] ⑥ Grinding temperature o C (the water in it plays a cooling role),
[0094] We tried grinders with a volume of 10, 25 and 60 liters with similar results. The grinding machines mentioned above can use different grinding balls, such as iron, steel, aluminum, zirconium (Zivconia), talc (Steatite), silicon nitride (Silicon Nitride), silicon carbide (Silicon Carbon) and tungsten carbide (Tungsten Carbon). We ended up using steel balls, which eliminates cross-contamination from other materials. The steel balls used as grinding balls belong to the same metal as the nano-iron produced in the end.
[0095] At the production base, according to the inventor's laboratory experience a...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2: Fill the grinding machine with 85% grinding balls, the grinding balls are steel balls, the diameter of the grinding balls is 100 microns, and the raw material of iron particles of 1-10 microns, water and dispersant are in a weight ratio of 20:3:77 Mixing and adding in the grinder, the dispersant is polymethacrylic acid, which is mechanically extruded and mixed through a rotating shaft, and the grinding time is 5 hours. The obtained particles are sieved through a 200-nanometer filter membrane. Compliant with the nanometer level, it is returned to the production line with new raw materials for the second production grinding. That is to say, fine dispersed nano-iron particles that meet the requirements are obtained, and the unqualified particles continue to enter the grinding machine together with water and dispersant to repeat the above process. Among them: the input power of the grinding machine is 1.8kw.h / L, the grinding temperature is 20-55oC, and the rota...
Embodiment 3
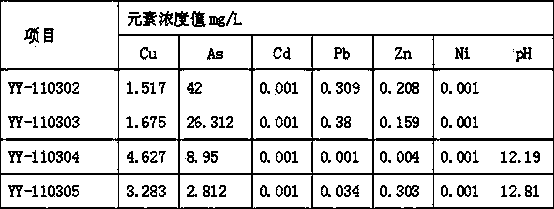
[0098] Example 3: Using the nano-iron particles obtained in Example 1 for a copper company in a certain place to treat complex polymetallic wastewater projects
[0099] Project Overview
[0100] The waste water treated by this project-copper-precipitated liquid comes from the production waste water of the first workshop (precious metal workshop) of a certain factory. Treatment supernatant, power wave liquid, gold and silver waste water, excess silver reducing liquid and other streams of waste water. Wastewater characteristics:
[0101] (1) The sources of wastewater are complex, and the volume and quality of wastewater fluctuate greatly;
[0102] (2) The composition of wastewater is complex, containing a variety of complex heavy metals (arsenic, copper, cadmium, gold, silver, etc.);
[0103] (3) The content of chloride ion in wastewater is high (up to 60-150g / L), high in salinity (concentration is about 15%-25%), sulfite ion, COD, etc. are also relatively high.
[0104]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com