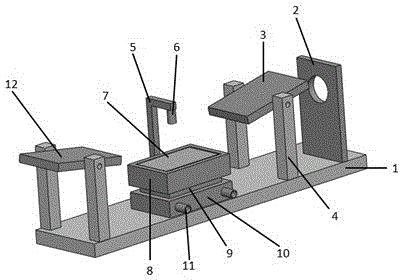
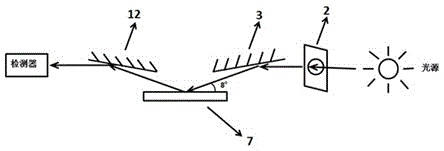
A Grazing Angle Reflection Infrared Spectroscopy Device with Controllable Temperature
A technology of infrared spectroscopy and angular reflection, applied in the field of grazing angle reflection infrared spectroscopy devices, can solve the problems of temperature measurement deviation, complicated steps, low thermal conductivity, etc., to avoid pollution and damage, realize program temperature control, and simple device structure. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
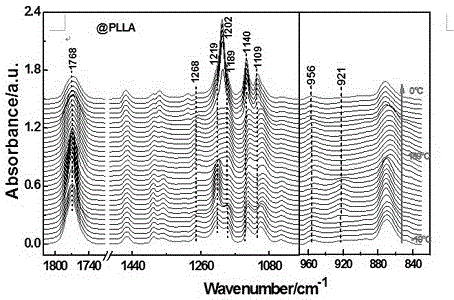
[0060] The crystallization behavior of polylactic acid (PLLA) was measured during heating and cooling.
[0061] Place the substrate coated with polylactic acid (PLLA) samples on the hot stage, set the heating rate and set temperature through the temperature controller, start the cooling water and the cooling plate, and conduct infrared spectrum testing. image 3 It is the infrared spectrum change map measured when polylactic acid rises from minus 10 degrees Celsius at a heating rate of 2 degrees Celsius per minute to 180 degrees and then cools down to room temperature at a cooling rate of 2 degrees Celsius per minute. The scanning frequency is once per minute, but for Obviously observe the spectral changes of the sample during the heating process, and only select part of the spectrum for graphing. From the changes in the characteristic peaks in the figure, we can get the glass transition temperature Tg, crystallization temperature Tc, melting point Tm and other information of t...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Measurement of the crystallization behavior of poly-3-hexylthiophene (P3HT) during heating and cooling (continuous heating).
[0064] Place the substrate coated with poly-3-hexylthiophene (P3HT) sample on the hot stage, set the heating rate and set temperature through the temperature controller, start the cooling water and the cooling plate, and conduct the infrared spectrum test. Figure 4 and Figure 5 (a) is the infrared spectrum change graph measured after poly-3-hexylthiophene rises from minus 10 degrees Celsius to 200 degrees Celsius at a heating rate of 2 degrees Celsius per minute, and the scanning frequency is once per minute. Investigate the changes in the crystal form and orientation structure of the sample during the continuous heating process. In order to clearly observe the spectral changes of the sample during the heating process, only part of the spectrum was selected for mapping.
Embodiment 3
[0066] Measurement of the crystallization behavior of poly-3-hexylthiophene (P3HT) during heating and cooling (step heating).
[0067] Place the substrate coated with poly-3-hexylthiophene (P3HT) sample on the hot stage, set the heating rate and set temperature through the temperature controller, start the cooling water and the cooling plate, and conduct the infrared spectrum test. The heating method adopts a step-by-step heating mode, that is, the sample is heated up quickly, then the sample is kept at a constant temperature for 10 minutes, and then the temperature is quickly cooled to the original temperature, and then the infrared spectrum measurement is performed. For example, the P3HT film is rapidly heated to 50°C, kept at 50°C for 10 minutes, and then quickly lowered back to the original temperature for infrared spectrum measurement. Figure 5 (b) is the infrared spectrum change graph measured after the poly-3-hexylthiophene is raised from minus 10 degrees Celsius to 20...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com