ZMIZ1-mediated targeting knockout transcription activator-like effector nuclease, preparation method and applications
A nuclease and nucleotide technology, applied in the fields of biotechnology and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low efficiency and wide application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0113] Design of TALENs module sequence
[0114] 1. Download the genome sequence of human ZMIZ1 (GeneID: 57178) from NCBI as the target.
[0115] 2. Design primers and perform PCR to amplify the target site fragments on the genome and sequence them.
[0116] The sequences of PCR primers and sequencing primers are listed in Table 1.
[0117] Table 1
[0118]
[0119] 3. Design TALENs recognition sequence: Determine the TALENs recognition sequence according to the sequencing sequence and the following principles:
[0120] The base at position 0 is T (referring to the base preceding the first position adjacent to the recognition sequence);
[0121] The last base is T;
[0122] The length of the recognition sequence is between 14-19;
[0123] The length of the spacer sequence between the two recognition sequences is controlled between 12-21, preferably between 14-21,
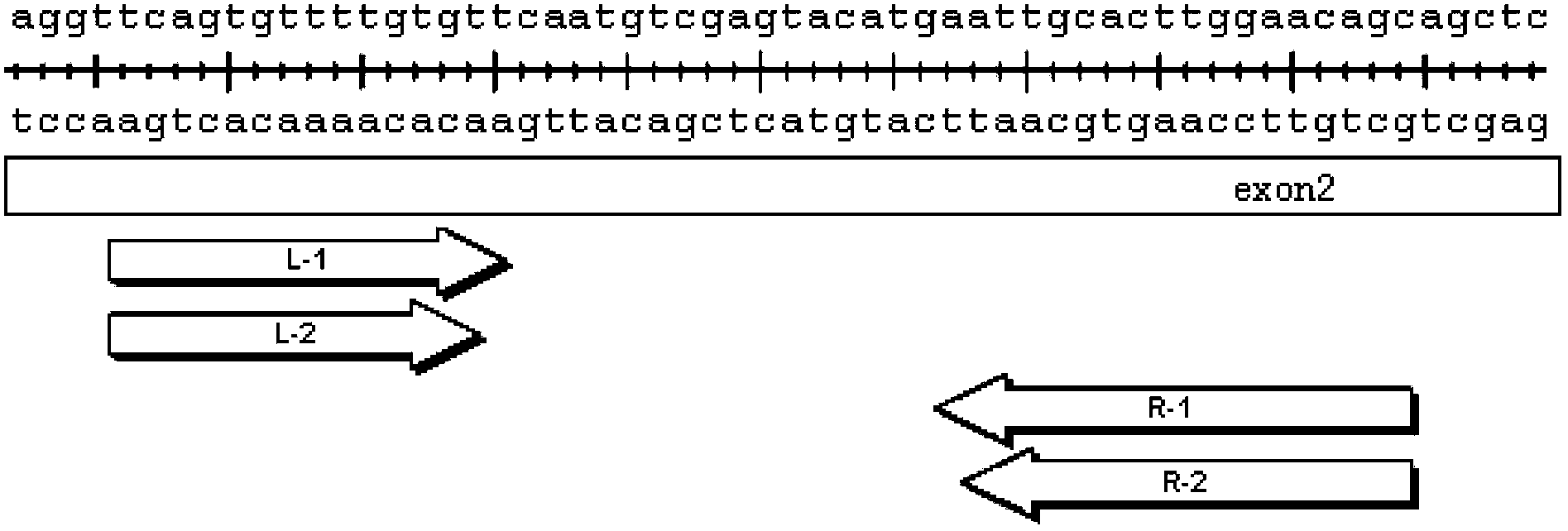
[0124] The position of the designed target sequence is as follows figure 1 , the sequence of the identi...
Embodiment 2
[0128] Connection between TALENs recognition modules and construction of recombinant vector
[0129] 1. Obtaining the identification module
[0130] The sequences of four recognition modules NI, NG, HD, and NK (SEQ ID NO: 14-17) for synthesizing recognition bases A, T, C, and G are shown in Table 3.
[0131] table 3
[0132]
[0133]
[0134] Ligate the four fragments into the pEASY-B vector (purchased from Beijing Quanshijin Company), the ligation method is as follows: take 3 μl of PCR primers; add 1 μl of pEASY-B vector; 25°C, 7min; transfect DH5α competent cells, Coat the kanamycin plate; pick clones, extract plasmids in a small amount, digest and sequence; finally obtain the recognition templates NI, NG, HD and NK connected to the vector pEASY-B.
[0135] 2. Identify connections between modules
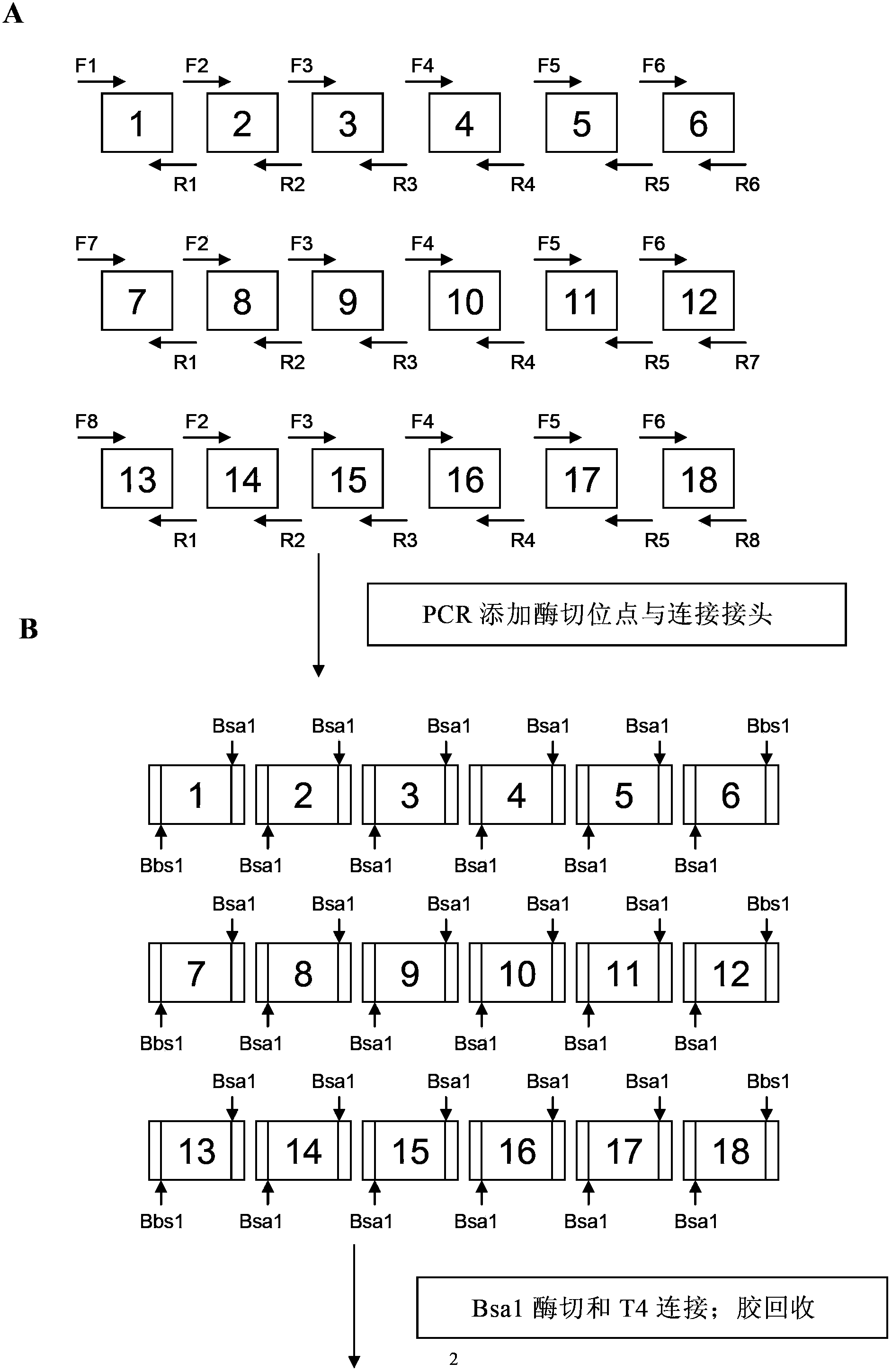
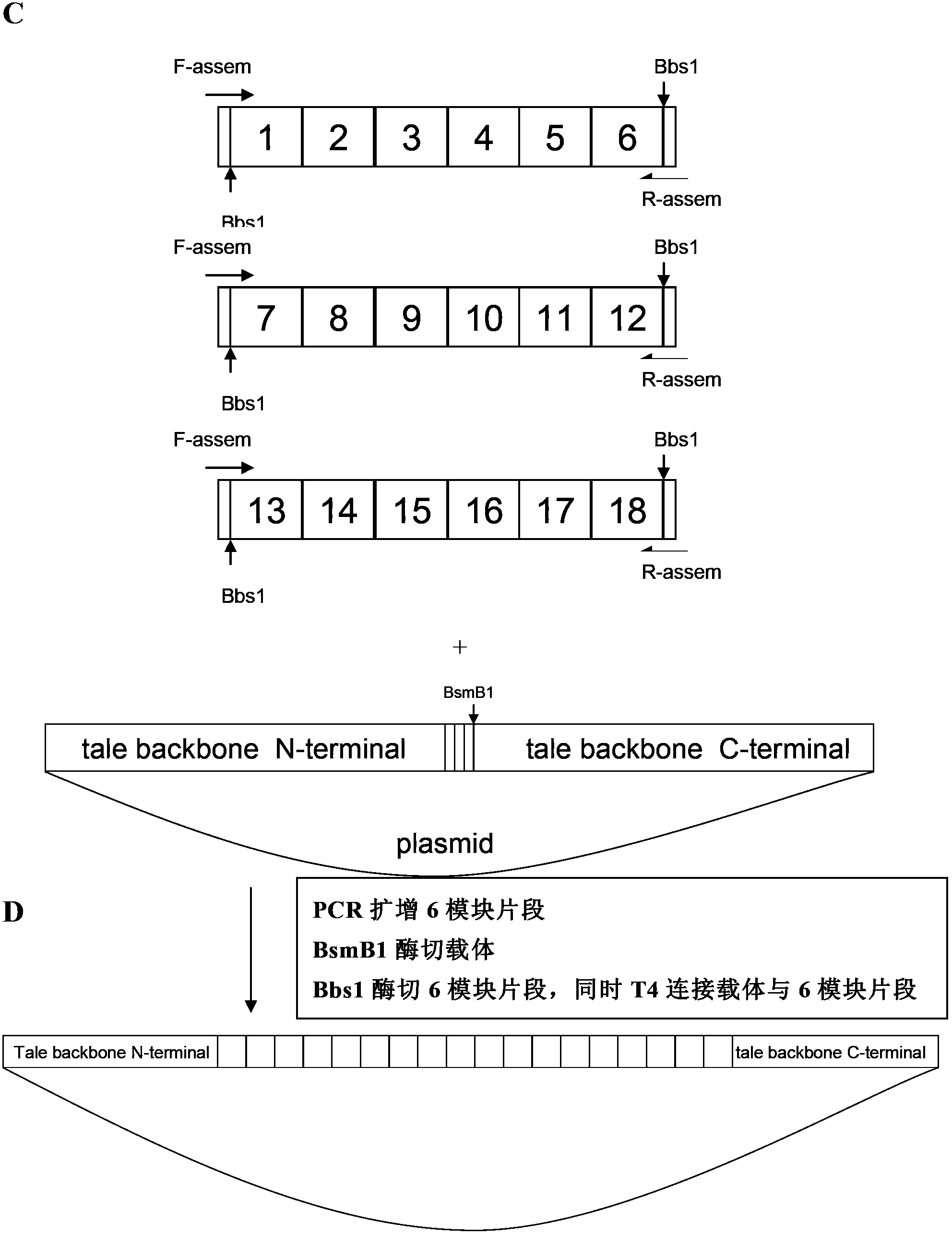
[0136] Connection strategy: Take the connection of 19 recognition modules as an example to illustrate the connection strategy, because the last half module that can recog...
Embodiment 3
[0203] The transfection of embodiment 3 plasmids
[0204] 1. Add 300 μl of gelatin to each space of the 6-well plate, shake it back and forth, so that the gelatin covers the bottom of the entire well, and place it in a 5% CO2 incubator for 10 minutes after spreading.
[0205] 2. Aspirate the culture medium in the T25 bottle of cultured 293T cells, wash it once with PBS, add 1ml of 0.25% trypsin, shake back and forth to make it evenly cover the bottom of the bottle, and place it in a 5% CO2 incubator for 5 minutes.
[0206] 3. After digestion, add 1ml 10% DMEM to neutralize trypsin, transfer the digested cells to a 15ml centrifuge tube, count the cells, and centrifuge at 1200rpm for 5 minutes.
[0207] 4. Resuspend the cells with an appropriate amount of 10% DMEM, take 2 million 293T cells and place them in a 6-well plate covered with gelatin, and add 2ml of fresh 10% DMEM.
[0208] 5. Transfect when the density of 293T cells reaches 80%-90%, no need to change the medium.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com