Transcriptional activation subsample effect factor nuclease and coding gene and application thereof
A transcriptional activation and encoding technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low transfection efficiency, low efficiency, and undetectable genetic modification of targets, and achieve high targeting efficiency, high targeting specificity and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
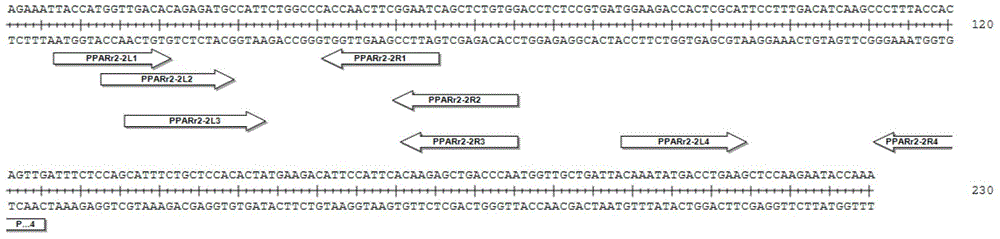
[0043] The design of embodiment 1 TALENs target sequence
[0044] 1. Select the exon of the mouse chromosome 6 PPARγ2 gene (gene sequence source http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) to design TALENs target sequences.
[0045] 2. TALENs target sequences are designed according to the following main design principles:
[0046] (1) The 0th base is T, that is, the base before the first in the recognition sequence is the 0th, which is T;
[0047] (2) The length of the spacer sequence (Spacer) between the two recognition sequences is between 15-30bp;
[0048] (3) The length of the recognition sequence is between 15-24bp.
[0049] 3. Design the four sets of target sequences (i.e. RVD binding recognition sequences) shown in Table 1 according to the above principles:
[0050] Table 1
[0051]
[0052] Among them, the site sequences of the above four groups of target sequences are as follows: figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
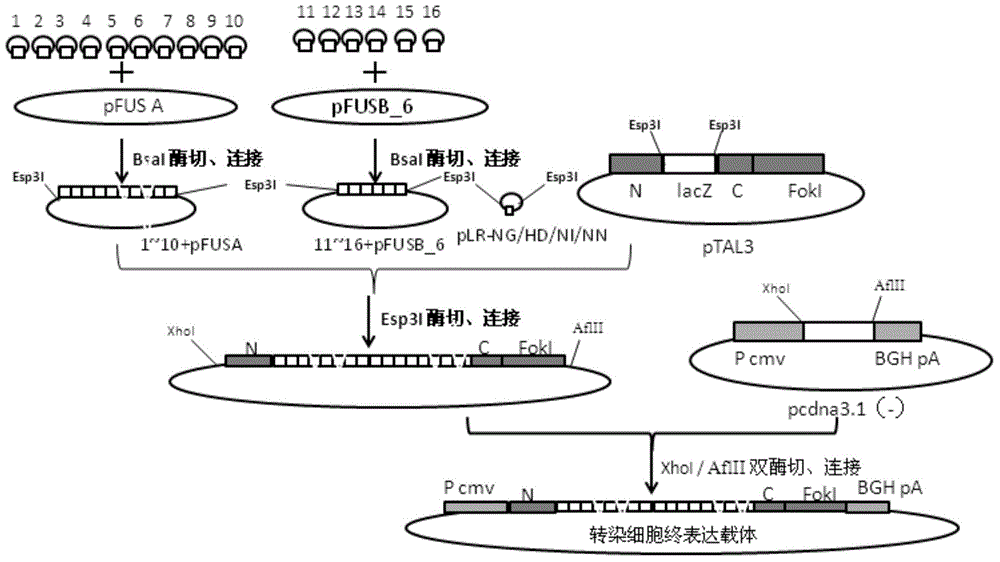
[0053] The design of embodiment 2 TALENs recognition module, the construction of connection and recombinant vector
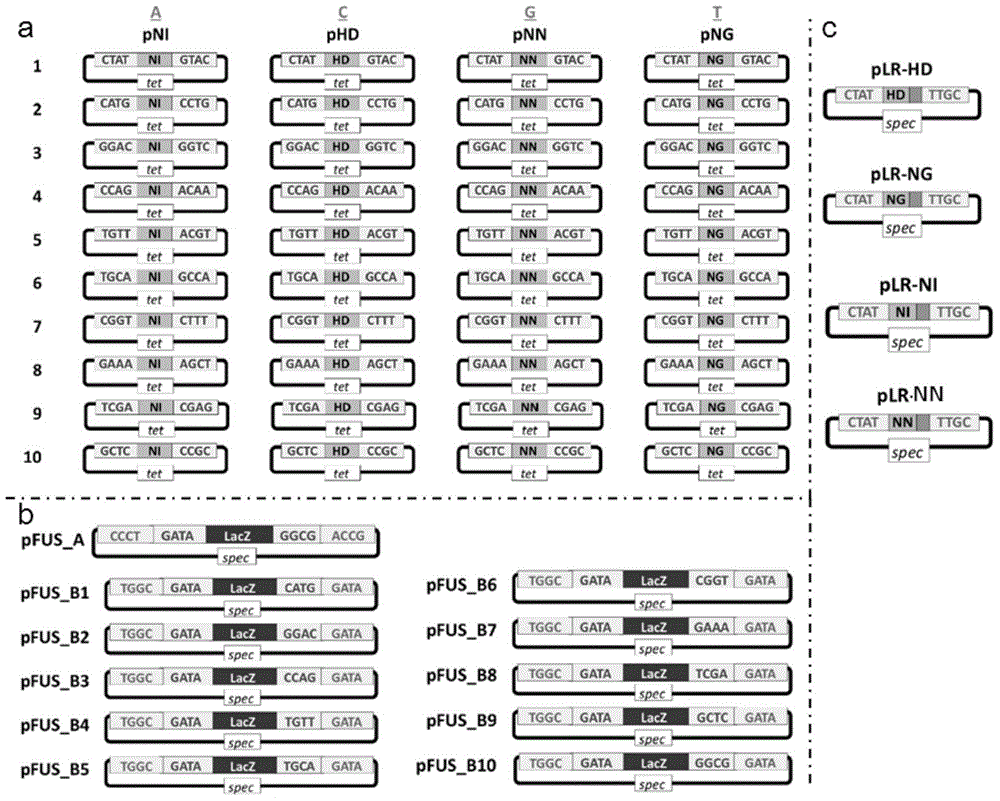
[0054] 1. According to the principle that NG recognizes T, HD recognizes C, NI recognizes A, and NN recognizes G, determine the TALENs recognition modules that respectively recognize the above target sequences, as shown in Table 2.
[0055] Table 2
[0056]
[0057]
[0058] 2. The coding sequences of the four modules NI, NG, HD and NN except the last module (the module marked with bold and underlined in Table 2) are shown in Table 3.
[0059] table 3
[0060]
[0061]
[0062] 3. The last module (the module marked with bold and underlined in Table 2) is actually half a module sequence, and its coding sequence is shown in Table 4. The rules for each module in Table 4 to recognize the corresponding bases are: LR-NI recognizes A, LR-HD recognizes C, LR-NG recognizes T, and LR-NN recognizes G.
[0063] Table 4
[0064]
[0065] 4. Perform TALEN a...
Embodiment 3
[0128] Embodiment 3 transfection and drug screening
[0129] 1. In vitro culture of 3T3-L1 cell line
[0130] (1) Select DF-12 medium with 10% FBS for culture, and add cytokine FGF if necessary;
[0131] (2) Subculture when the cell density reaches about 80%, and contact inhibition occurs when the cell density exceeds 90%;
[0132] (3) Before transfection, the cell density should be about 80%, and observed under an inverted microscope, the cells should have clear edges, clear shapes, plump and bright.
[0133] 2. The four groups of expression vector plasmids and liposomes (lipofectamine2000) listed in Table 4 were used to co-transfect 3T3-L1 cells (6-well plate).
[0134] (1) The cells were replaced with 2 ml of fresh medium (DF-12 containing 10% FBS), and the medium was preheated.
[0135] (2) In a 1.5ml EP tube, dilute about 4.0μg of each paired TALENs expression vector plasmid DNA into serum-free OPTI-MEM medium to a total volume of 50μl, and mix gently.
[0136] (3) Gent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com