Preparation method of medical cellulose sponge
A cellulose and sponge technology, applied in the field of preparation of cellulose medical sponges, can solve the problems of harming the environment, secondary pollution, trauma and wounds, etc., and achieve excellent antibacterial properties and tensile strength, simple manufacturing process, and low production cost. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
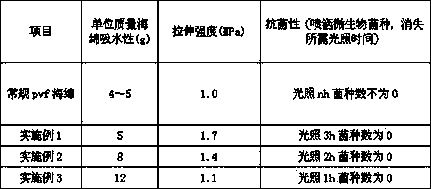
Embodiment 1
[0036] 1000 g of sisal was treated with compound enzymes at 45°C for 30 minutes, washed with water until neutral, crushed, and dried for later use. Mix the NMMO solution with a mass fraction of 50% and the urea solution with a mass fraction of 20% at a volume ratio of 1:1, adjust the temperature of the solution system to 10°C, add the treated fiber raw materials, and stir slowly at a stirring speed of 150rpm. After the fibers are completely dissolved, add 10 g of composite photocatalyst preparation, continue to cool down to 5°C, the offset is ±1°C, then add 30g of sponge pore-forming agent, the sponge pore-forming agent is sodium chloride, and increase the speed to 350rpm . Finally, all the solution is poured into the mold, shaped, boiled in immersion water to remove the pore forming agent and generate a sponge product.
[0037] In this example:
[0038] The composite photocatalyst preparation is obtained by the following preparation method: add 10 ml of a mixed solution of ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] 1000 g of Manila hemp was subjected to enzyme treatment at 45°C for 30 min, then washed with water until neutral, crushed, and dried for later use. Mix the NMMO solution with a mass fraction of 80% and the urea solution with a mass fraction of 5% at a volume ratio of 1:1, adjust the system temperature to 10°C, add the treated fiber raw materials, and stir slowly at a stirring speed of 120rpm. After the fibers are completely dissolved, add 30g of composite photocatalyst preparation, continue to cool down to 5°C, with an offset of ±1°C, then add 40g of sponge pore-forming agent, which is sodium sulfate, and increase the speed to 400rpm. Finally, all the solution is poured into the mold, shaped, boiled in immersion water to remove the pore forming agent and generate a sponge product.
[0042] In this example:
[0043]The composite photocatalyst preparation is obtained by the following preparation method: 10 ml of a mixed solution of butyl titanate and ethanol is added in ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] 1000 g of screened sisal and Manila hemp fiber wastes were treated with enzymes at 45°C for 30 minutes, washed with water until neutral, crushed, and dried for later use. Mix the NMMO solution with a mass fraction of 60% and the urea solution with a mass fraction of 10% at a volume ratio of 1:1, adjust the system temperature to 10°C, add treated fiber waste, and stir slowly at a stirring speed of 100rpm. After the fibers are completely dissolved, add 50g of composite photocatalyst preparation, continue to cool down to 5°C, and the offset is ±1°C. At this time, add 50g of sponge pore-forming agent, which is sodium nitrate, and increase the speed to 400rpm. Finally, all the solution is poured into the mold, shaped, boiled in immersion water to remove the pore forming agent and generate a sponge product.
[0047] In this example:
[0048] The composite photocatalyst preparation is obtained by the following preparation method: add 10 ml of a mixed solution of butyl titanat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com