Method for extracting pea molasses and pea protein isolate from pea starch production wastewater
A technology for pea protein separation and waste water production, which is applied in the fields of application, food preparation, food science, etc., can solve the problems of underutilization of waste water, impact on functional purity, and low protein yield, so as to increase animal feed intake, Effect of improving feed palatability and reducing production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
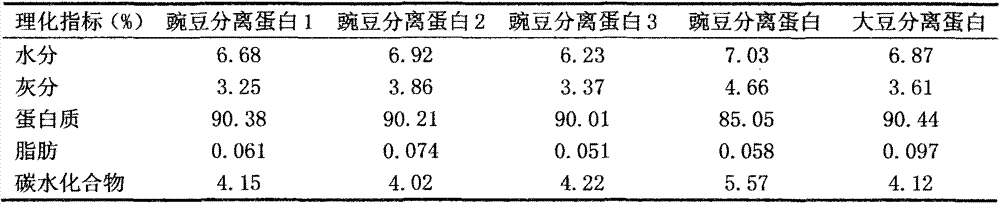
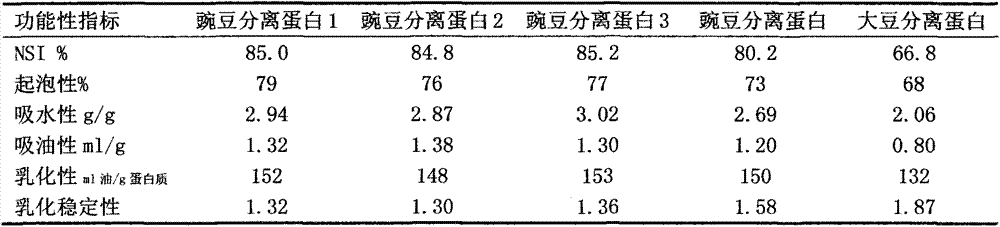
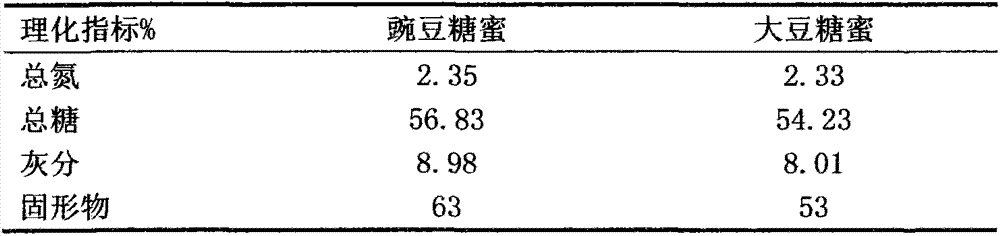
[0025] Put the starch slurry in the premix tank, pour the prepared dilute lye into the premix tank evenly while stirring, adjust the pH value of the slurry to 11.0, control the extraction temperature at 35°C, and extract for 30 minutes to make the protein fully dissolve. Then pump the mixed solution to a decanter centrifuge for centrifugation, pour the separated protein-rich solution into a precipitation tank, slowly add dilute hydrochloric acid while stirring, adjust the pH to 4.0, and precipitate the protein. The precipitation time is 30 minutes. The precipitated liquid is separated by a stacked plate centrifuge to obtain whey and primary curd containing protein. Pump the whey into the whey neutralization tank, slowly add dilute lye while stirring, adjust the pH to 6.8, inject the neutralized whey into the vacuum concentration equipment for concentration, reduce the water content to 45%, and concentrate The liquid is homogenized with a homogenizer, and a brown syrupy substa...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Put the starch slurry in the premix tank, pour the prepared dilute lye into the premix tank evenly while stirring, adjust the pH value of the slurry to 11.5, control the extraction temperature at 30°C, and extract for 60 minutes to make the protein fully dissolve. Then pump the mixed solution to a decanter centrifuge for centrifugation, pour the separated protein-rich solution into a precipitation tank, slowly add dilute hydrochloric acid while stirring, adjust the pH to 4.0, and precipitate the protein. The precipitation time is 20 minutes. The precipitated liquid is separated by a stacked plate centrifuge to obtain whey and primary curd containing protein. Pump the whey into the whey neutralization tank, slowly add dilute lye while stirring, adjust the pH to 7.2, inject the neutralized whey into the vacuum concentration equipment for concentration, reduce the water content to 47%, concentrate The liquid is homogenized with a homogenizer, and a brown syrupy substance-...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Put the starch slurry in the premix tank, pour the prepared dilute lye into the premix tank evenly while stirring, adjust the pH value of the slurry to 12.4, control the extraction temperature at 40°C, and extract for 40 minutes to make the protein fully dissolve. Then pump the mixed solution to a decanter centrifuge for centrifugation, pour the separated protein-rich solution into the precipitation tank, slowly add dilute hydrochloric acid while stirring, adjust the pH to 4.5, and precipitate the protein. The precipitation time is 30 minutes. The precipitated liquid is separated by a stacked plate centrifuge to obtain whey and primary curd containing protein. Pump the whey into the whey neutralization tank, slowly add dilute lye while stirring, adjust the pH to 7.5, inject the neutralized whey into the vacuum concentration equipment for concentration, reduce the water content to 55%, and concentrate The liquid is homogenized with a homogenizer, and a brown syrupy subs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com