Manganese oxide nanoparticle contrast agent for specifically targeting brain glioma
A brain glioma, manganese oxide technology, applied in the preparations, emulsion delivery, pharmaceutical formulations and other directions for in vivo experiments, can solve the problems of low relaxation rate, inability to clearly define the tumor boundary, etc., and achieve a good biological phase. Capacitive, obvious contrast-enhancing effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] 1) Preparation of manganese oxide nanoparticles coated with oleic acid:
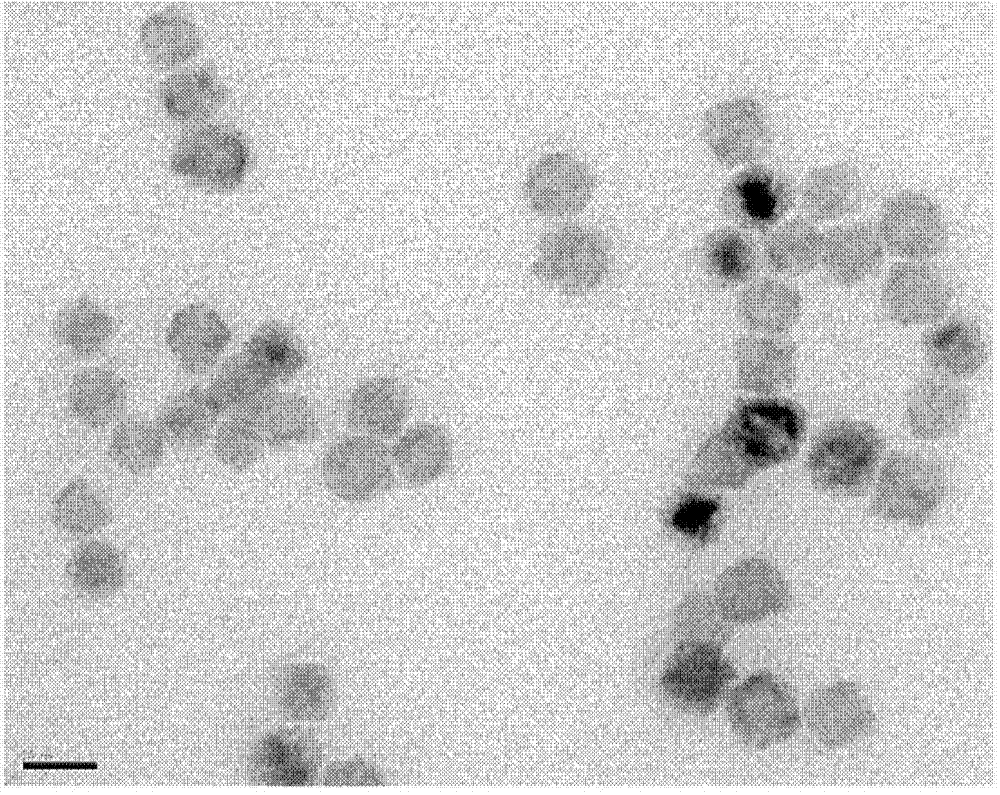
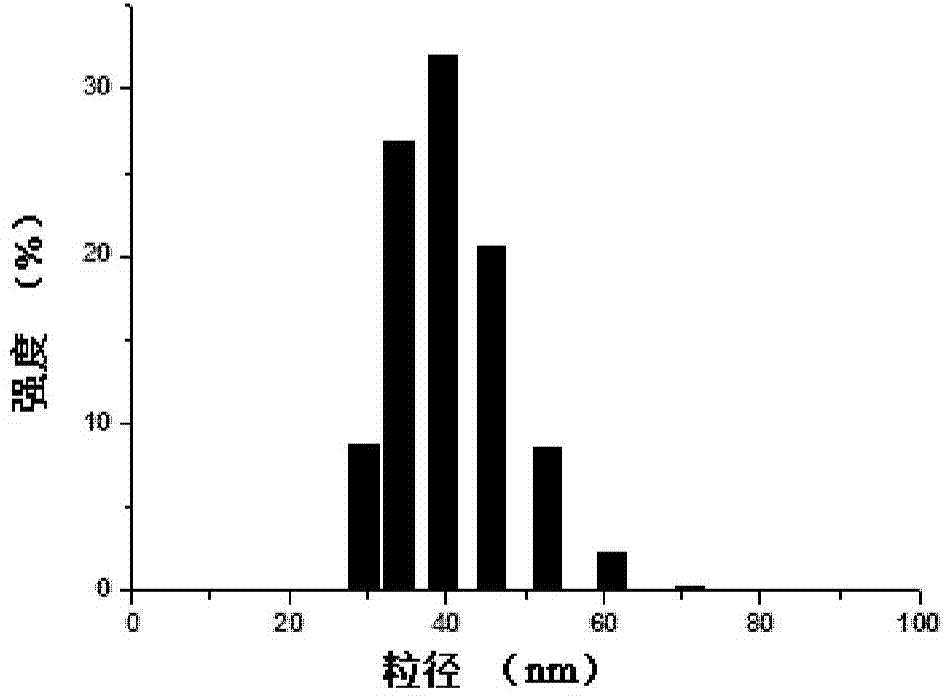
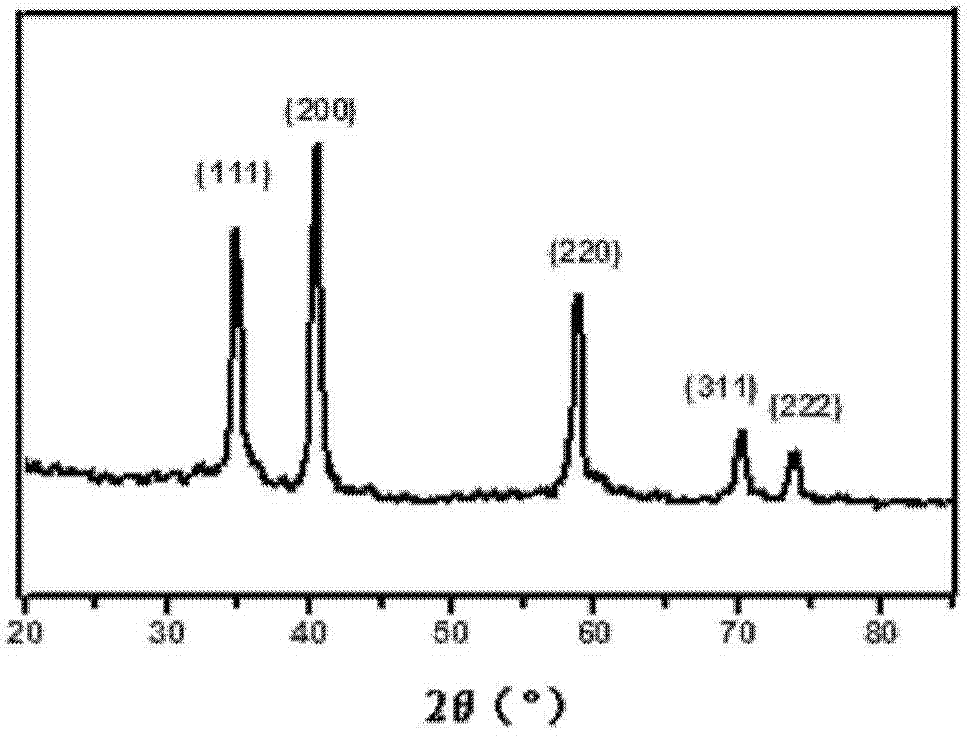
[0038] Manganese oxide nanoparticles coated with oleic acid were synthesized by pyrolysis: manganese chloride tetrahydrate (3.96g, 20mmol), sodium oleate (12.17g, 40mmol) were dispersed in ethanol (40ml), water (30ml), n-hexane (70ml) of the mixed solution was stirred at 70°C for 4 hours, the organic phase was taken and washed with a small amount of water, and the solvent was removed to obtain a manganese oleate precursor. The prepared manganese oleate precursor (2.468g, 4mmol) was dissolved in 1-octadecene (50ml), and stirred under vacuum at 100°C for 30-60min. Under the protection of nitrogen, the temperature was raised to 300°C and refluxed for 15 minutes, then cooled to room temperature. After adding absolute ethanol and centrifuging, the resulting black precipitate was dispersed in n-hexane and washed with a small amount of absolute ethanol to obtain manganese oxide nanoparticles coated with...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Determination of relaxation rate:
[0050] Manganese oxide nanoparticles in Example 1 are prepared into a series of concentration suspensions, and the RARE-T is used on the 7T nuclear magnetic resonance instrument 1 +T 2 -map sequences to determine relaxation rates. The parameters are set as follows: TR=800ms, TE=11ms, 33ms, 55ms, 77ms, 99ms, matrix size=256×256, FOV=4.0×4.0cm 2 , flip angle(FA)=180° and slice thickness=1mm, T 1 weighted imaging scan, the resulting transverse relaxation time (T 1 ) is linearly fitted to the concentration, and the slope of the obtained line is the relaxation rate. Its fitting curve see Figure 5 . From Figure 5 It can be seen that the relaxation time decreases significantly with the increase of manganese concentration. Obtain manganese oxide nanoparticles r in embodiment 1 by linear fitting 1 Relaxation rate 4.8mM -1 the s -1
Embodiment 3
[0052] Cytotoxicity:
[0053] 1) Cell culture: C6 glioma cells were cultured in DMEM medium (containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100U / ml penicillin, 100U / ml streptomycin) at 37°C with 5% CO 2 for 24 hours in a humidified incubator.
[0054] 2) Cytotoxicity: C6 glioma cells were treated with 1×10 5 The cell density was seeded in a 96-well plate and incubated for 24 hours. The manganese oxide nanoparticles in Example 1 were formulated into solutions with a manganese concentration of 0, 6.125, 12.5 and 25 μg / mL, respectively, and added to 96-well plates, and after co-incubating for 24 hours and 48 hours, discard the solutions containing Wash the medium of nanoparticles twice with PBS, add MTT (100μl, 0.5mg / ml), incubate for another 4 hours, discard MTT, add 150μl DMSO, shake for 5 minutes in the dark, and use a microplate reader to measure at 570nm wavelength OD value of each well. The calculated cell viability at different manganese oxide nanoparticles concentrations is shown...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com