Beauveria bassiana strain capable of killing chrysomelidae insects and application thereof
A technology of Beauveria bassiana and strains, applied in application, pesticides, biocides, etc., can solve problems such as polluted environment, inability to achieve effective control of pest populations, and rampant pests.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Example 1: Workflow of XWY-1 strain acquisition
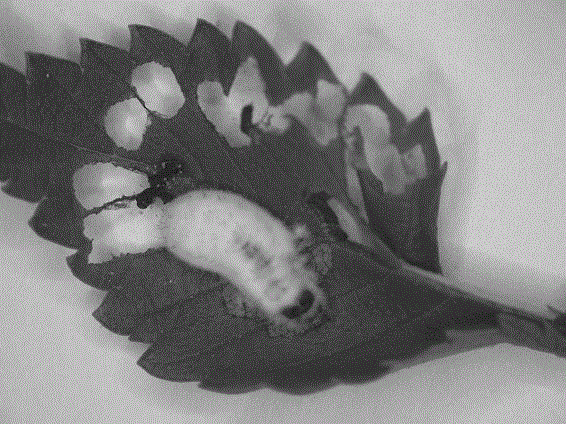
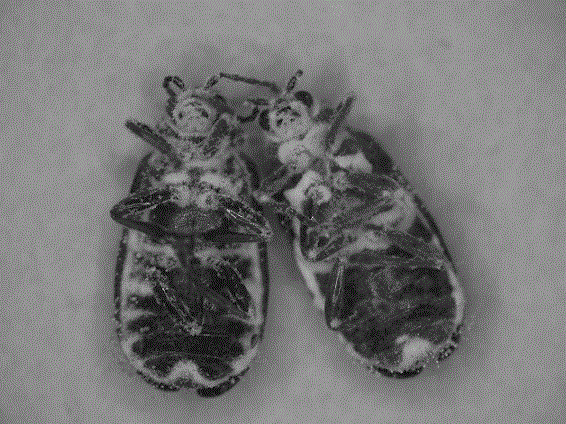
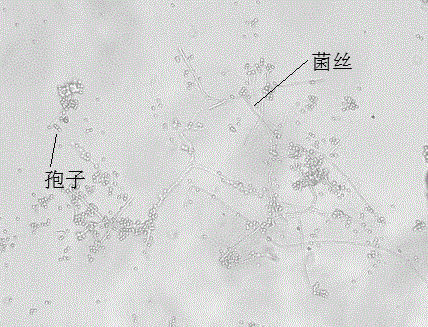
[0015] Collect naturally susceptible dead worms in the field→isolate and purify the strains→inoculate Ulmus indigo beetle larvae to determine the insecticidal virulence→obtain the highly virulent strain XWY-1→strain morphology, spore morphology, identification→extract DNA of the strain and use the ITS sequence of the fungus Universal primers were used to amplify the strain DNA, and the obtained amplified sequence was sequenced and compared in GenBank → the strain XWY-1 was determined to be Beauveria bassiana.
Embodiment 2
[0016] Embodiment 2: the screening and isolation process of XWY-1 bacterial strain
[0017] The XWY-1 strain was isolated from white susceptible insects collected by the Institute of Plant Protection, Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences in 2010 during the survey of sweet potato fields in Xiong County, Hebei Province. The white susceptible insects were brought back to the laboratory and treated with moisture. When spores were produced on the body surface, the spores were inoculated in SDAY (10 g peptone, 10 g yeast, 40 g glucose, 15 g agar, 1000 mL distilled water, natural pH ) on plate medium until conidia were produced, collected and freeze-dried at 4°C for later use.
Embodiment 3
[0018] Embodiment 3: Bacterial strain culture and spore suspension preparation
[0019] The XWY-1 strain was inoculated on the SDAY plate medium and cultivated under constant temperature and light (14L:10D) at 25±1°C. After the formation of conidia, the spores were collected with 0.05% (v / v) sterile Tween 80 aqueous solution, stirred with a magnetic stirrer for 30 min, the spores were completely and evenly dispersed, and then filtered through 4 layers of sterile gauze to obtain a pure spore suspension , counted with a hemocytometer and prepared into a gradient concentration of spore suspension for the determination of pathogenicity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com