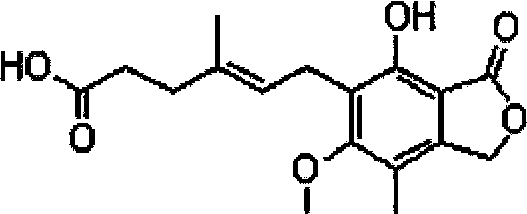
Method for extracting mycophenolic acid
A technology of mycophenolic acid and sulfide, applied in the field of medicinal chemistry, can solve problems such as difficult to remove color, achieve the effects of improving quality, reducing harm and environmental pollution, and improving yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
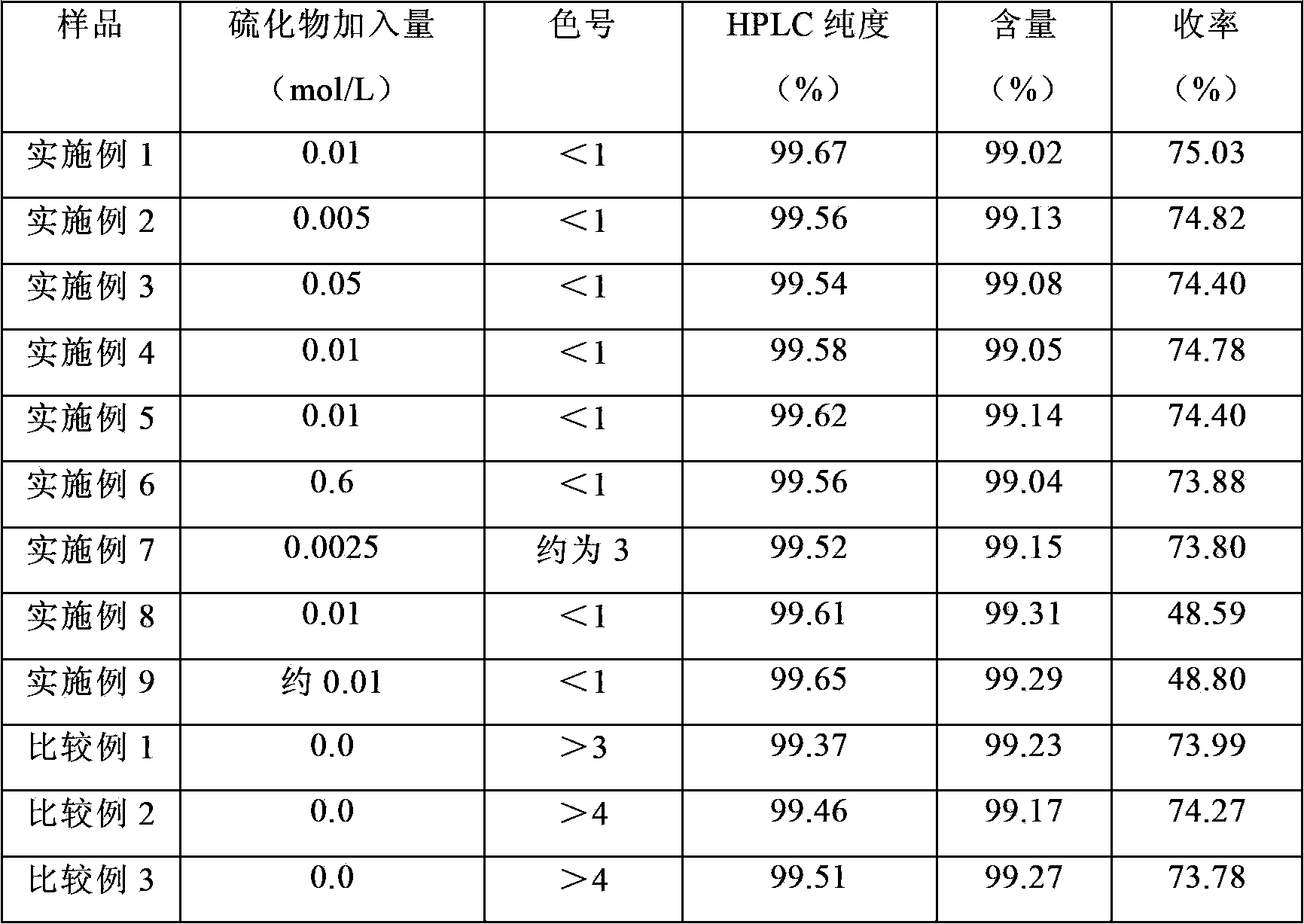
[0066] Under stirring, add 3.12g (0.01mol / L) of sodium sulfide to 4L of mycophenolic acid fermentation broth (unit: 4563.2ug / ml), adjust the pH to 9.0 with 3N sodium hydroxide, filter, discard the filter residue, and add 800ml of butyl acetate, adjusted to pH 4.5 with 3N hydrochloric acid, and extracted; the water phase was extracted with 300ml of butyl acetate for the second time, the organic phase was combined, concentrated, set to 200ml, left standing, cooled to 7°C for crystallization, and kept warm After 4 hours, the crystals were separated to obtain the crude product. The crude product was dissolved in 150ml of ethanol, decolorized by adding 1.0g of activated carbon, heated to filter, fixed to 150ml, cooled to 3°C for recrystallization, kept for 4 hours, separated and crystallized, and dried in vacuum to obtain 13.83g of white mycophenolic acid product. The HPLC purity is 99.67%, the calculated content is 99.02%, and the calculated yield is 75.03%.
Embodiment 2
[0068] Under stirring, add 1.56g (0.005mol / L) of sodium sulfide to 4L of mycophenolic acid fermentation broth (unit: 4623.7ug / ml), adjust the pH to 9.0 with 3N sodium hydroxide, filter, discard the filter residue, and add 800ml of butyl acetate, adjusted to pH 4.5 with 3N hydrochloric acid, and extracted; the water phase was extracted with 300ml of butyl acetate for the second time, the organic phase was combined, concentrated, set to 200ml, left standing, cooled to 7°C for crystallization, and kept warm After 4 hours, the crystals were separated to obtain the crude product. The crude product was dissolved in 150ml of ethanol, decolorized by adding 1.0g of activated carbon, heated to filter, set the volume to 150ml, cooled to 3°C for recrystallization, kept for 4 hours, separated and crystallized, and dried in vacuum to obtain 13.96g of white mycophenolic acid product. The HPLC purity was 99.56%, the calculated content was 99.13%, and the calculated yield was 74.82%.
Embodiment 3
[0070] Under stirring, add 15.6g (0.05mol / L) of sodium sulfide to 4L of mycophenolic acid fermentation broth (unit: 4587.9ug / ml), adjust the pH to 9.0 with 3N sodium hydroxide, filter, discard the filter residue, and add acetic acid to the filtrate 800ml of butyl ester was adjusted to pH 4.5 with 3N hydrochloric acid for extraction; the water phase was extracted for the second time with 300ml of butyl acetate, the organic phase was combined, concentrated, and the volume was adjusted to 200ml, left to stand, cooled to 7°C for crystallization, and kept warm After 4 hours, the crystals were separated to obtain the crude product. The crude product was dissolved in 150ml of ethanol, decolorized by adding 1.0g of activated carbon, heated to filter, set the volume to 150ml, cooled to 3°C for recrystallization, kept for 4 hours, separated and crystallized, and dried in vacuum to obtain 13.78g of white mycophenolic acid product. The HPLC purity is 99.54%, the calculated content is 99.0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com